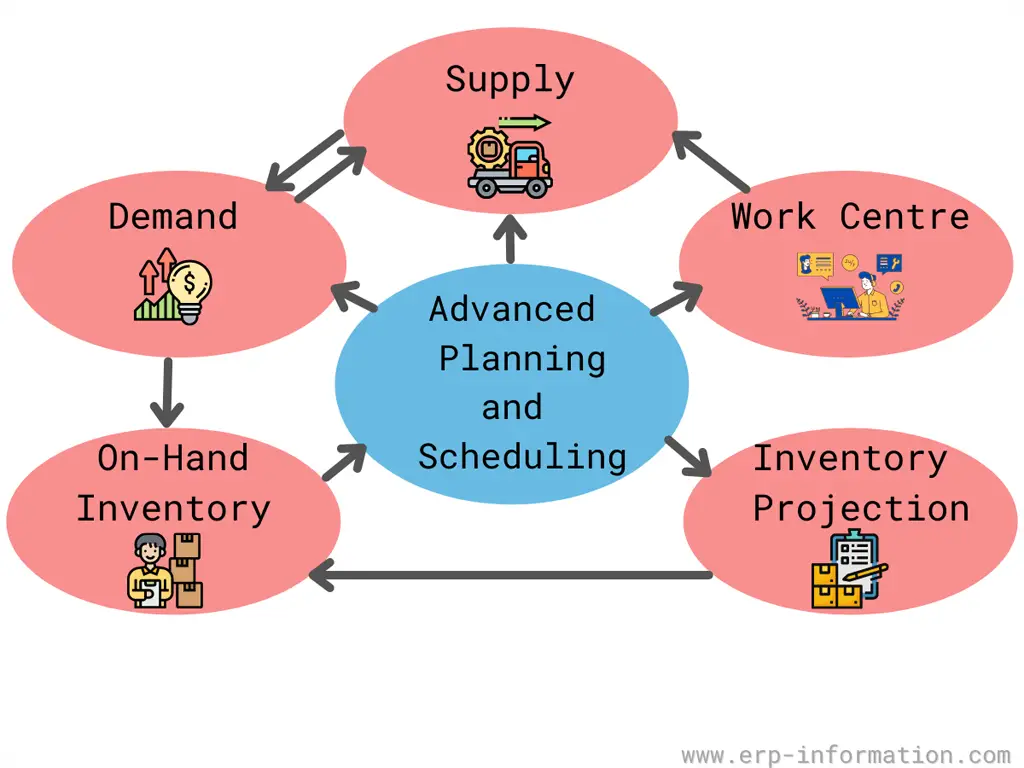
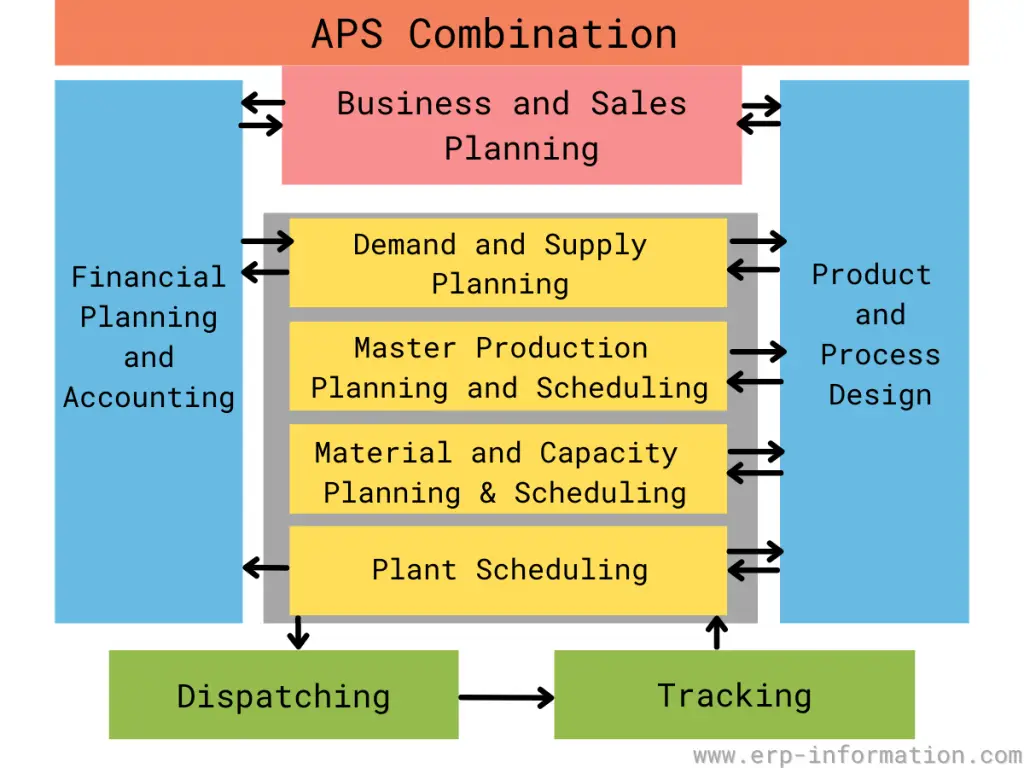
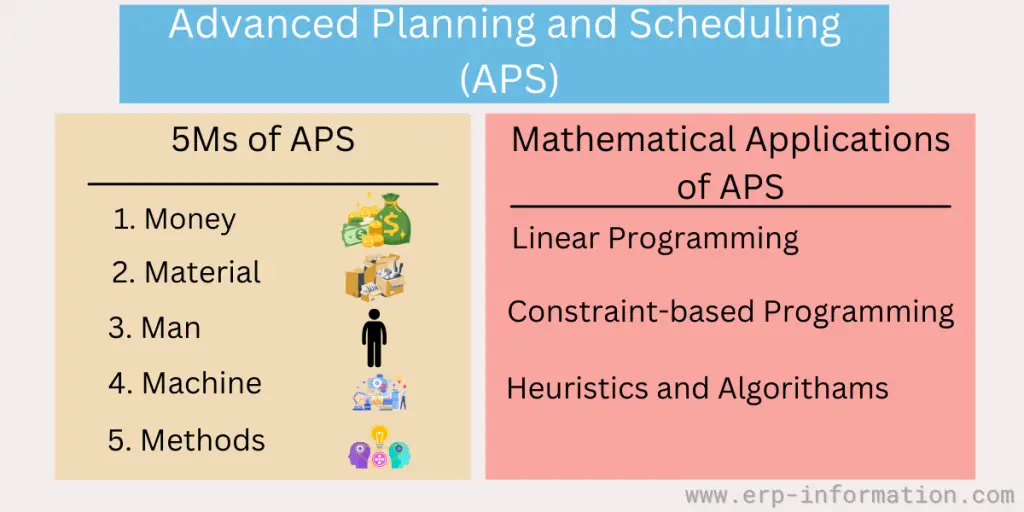
Advanced Planning and Scheduling is a technology solution that helps organizations optimize resources and minimize costs.
It enables planners to create detailed production schedules, allocate resources, and track progress against targets. It can also help identify potential bottlenecks and manage risks. In short, it allows organizations to plan and control their operations more effectively.
This post will look at APS, its components, the five M’s of it, its mathematical applications, advantages, disadvantages, and software.
What is Advanced Planning and Scheduling?
Advanced Planning and Scheduling is a smart system that helps businesses plan and organize their production processes. It ensures that all necessary materials including raw materials and resources are available when needed, helping companies save time and reduce waste. Using advanced software and real-time data, APS optimizes schedules and boosts overall efficiency.
It considers all the major production factors, including people, machines, inventory, and costs, and ensures an appropriate balance between raw materials and the business’s production processes. Therefore, it is an essential division of supply chain management.
How does Advanced Planning and Scheduling Enhance Business?
- It generates realistic reports to help analyze the unit’s production capacity and plan the next course of action accordingly.
- It helps understand the production and list out the required raw materials to ensure smooth working production of the system.
- It helps streamline the inventory system of the business and makes it more efficient.
- It assists in improving the time management system by analyzing and interpreting the time consumed for each process.
- It designs a real-time data system that captures the time and resources required. Thus, it improves the delivery time and delights the customers with prompt services.
- It helps to identify the exact resources that are required for production.
- It helps the manufacturer determine what to make, how much to make, and when and where to make it.
Advanced planning and scheduling help supervise some aspects of the production process. Those are
- Enhancement of advanced schedule
- Controlling advanced materials
- Make-to-order planning
- Make-to-stock planning
- Visualization of the assembling process
- Advanced constrain modeling
- Planning of Bill of Materials (BOM) level
- Master production schedule creation
- Visualization of interactive schedule
Advanced Planning vs Advanced Scheduling
Let us see the differences between advanced planning and advanced scheduling.
| Advanced Planning | Advanced Scheduling |
| Focuses on strategic decision support by combining forecasts and long-term orders to ensure future demand is met. It aims at maintaining target stock levels and managing resource capacities over a longer period. | Concentrates on creating a detailed, executable schedule based on actual resource availability and constraints. It ensures that production activities are achievable and efficient in the short term. |
| Works with long-term periods which can be days, weeks, months, or a combination of these. | Deals with short-term, detailed schedules, often on a day-to-day or hour-to-hour basis. |
| Can operate in both finite and infinite capacity modes. Finite capacity considers the actual limitations of resources, while infinite capacity assumes unlimited resources. | Operates in finite capacity mode, considering the actual availability of resources and multiple constraints. |
| Uses forecasts, long-term orders, and resource capacities to generate plans. It integrates with the scheduling system to update plans based on actual production schedules. | Uses manufacturing orders with associated process routes. It schedules these orders onto individual resources considering detailed constraints. |
| Produces a master production schedule (MPS) which can be adjusted based on actual production schedules. | Generates a detailed dispatch list for each resource, indicating specific tasks and timings. |
Components of Advanced Planning and Scheduling
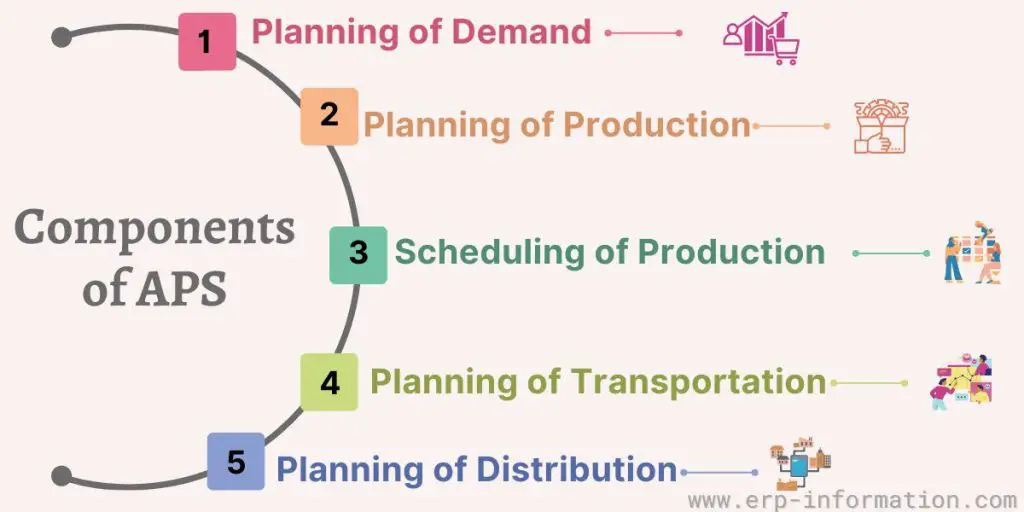
Planning of demand
Demand planning helps to generate an accurate forecast by considering the previous sales data and importing consumer forecasts.
Demand planning allows you to manufacture the exact quantity of products with reduced inventory cost and waste.
Planning of production
Production planning is a process. This process gives a clear picture of available raw materials, general labor, and tools to make products of the specified quantity.
The production plan allows an organization to carry out various activities without interruption.
Scheduling of production
The production schedule is also a process that helps to handle, arrange and optimize the work in the production process. It helps to reduce inventory and load on laborers.
Planning of distribution
This process allows workers to set inventory parameters like on-hand inventory at the beginning and the safety stock requirements for a while to reach order fulfillment.
Planning of transportation
This process helps identify the goals, future policies, and investments required to transport people and goods to destinations.
Five M’s of APS
- Money
- Material
- Man
- Machine
- Methods
Money
The most important of the five Ms is money. Money allows a business to purchase the resources it needs to operate. Without money, a company cannot buy materials, hire workers, or purchase equipment.
Material
Material is anything that a business uses to produce a product or service. This includes raw materials like wood, metals, other natural resources, and finished goods like clothing, food, and electronics.
For a business to be successful, it must have suitable materials in the right quantities at the right time.
Man
The man component of an APS refers to the people who work in a business. Whether it is the CEO, accountants, sales representatives, or customer service employees, companies rely on their employees’ skills and expertise to succeed.
Without people who can manage resources effectively and deliver high-quality products and services to customers, a business would not be able to thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.
Machine
Machines are another vital component of APS. Machines automate many business processes, making it easier and more efficient for employees to do their jobs.
For example, machines can assemble products, optimize supply chains, and process customer orders.
Without machines in modern businesses, production would be much slower and less accurate than today.
Methods
Finally, businesses must have effective methods in place for managing their resources. This includes having systems and processes to track inventory levels, maintain quality control, and ensure that products and services are delivered on time.
Without these methods, businesses would quickly become chaotic and unable to function correctly. In APS, processes are critical for ensuring that a company can achieve its goals and objectives.
Mathematical Applications Used in Advanced Planning and Scheduling
Linear programming
LP is a method to achieve the best outcome (maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships.
Linear programming is a particular case of mathematical programming (also known as mathematical optimization).
Constraint-based programming
CBP is a paradigm for solving problems in which some constraints (relationships) must be satisfied.
In CBP, the programmer specifies a set of constraints and the relationships between them, and the system automatically derives a solution that satisfies all the constraints.
Heuristics and algorithms
These are methods for finding solutions to problems. Heuristics are general guidelines that can help solve a problem, while algorithms are specific sets of steps that consistently produce a correct solution.
APS can offer solutions to various issues that a company might face with time and boost the customer service system.
With the help of APS, a company can formulate accurate strategies by clearly defining the market demand and how the production can gear up to capture a more significant share of the market with adequate supplies.
It will help the business make crucial decisions about business expansion by analyzing its production capacity and sales forecasting.
It can help the company study all aspects of the business, from manufacturing to distribution, and then schedule production accordingly.
Advantages
Improved Synchronization: APS helps align manufacturing processes more effectively. This means that different parts of the production process work together smoothly, reducing bottlenecks and delays.
Enhanced Visibility: APS provides a clearer view of the entire production process. This visibility allows businesses to track progress, manage resources efficiently, and make informed decisions.
Increased Utilization: With better scheduling, resources like machinery and labor are used more efficiently. This not only maximizes their use but also reduces downtime.
On-Time Delivery: APS helps businesses meet delivery deadlines, ensuring products are delivered when promised. This enhances customer satisfaction and trust.
Inventory Reduction: By optimizing production schedules, APS can minimize the need for excess inventory. This leads to cost savings and reduced waste.
Advanced Math: APS relies on complex mathematical algorithms to calculate achievable production schedules. This analytical capability allows manufacturers to make precise plans, considering multiple constraints and business rules.
What-If Scenarios: Planners can create and evaluate “what-if” scenarios. This flexibility enables businesses to explore various options to achieve the best results, adapt to changes, and mitigate risks.
Full Visibility and Control: APS offers a comprehensive view of the manufacturing process, empowering businesses to maintain control over operations.
Inventory Reduction: By optimizing production schedules, APS can minimize the need for excess inventory. This leads to cost savings and reduced waste.
Better Customer Service: Timely delivery and reliability in meeting customer orders improve overall customer service and satisfaction.
Higher Margins: By optimizing operations and reducing waste, APS can contribute to increased profitability and higher profit margins for businesses.
5 Disadvantages
APS can offer significant benefits in streamlining and optimizing production processes in manufacturing. However, they are not without their drawbacks. Here are five disadvantages.
Difficult and painful transition process
Transitioning from a traditional, human-driven process to an APS system can be challenging. The process often involves significant changes to established workflows, which can be disruptive. Moreover, the transition period can see a temporary drop in productivity as workers and managers adapt to the new system.
Expensive transition and risk of failure
Implementing an APS system is a substantial investment. The costs include purchasing software, hardware upgrades, training staff, and potential downtime during the transition.
There is also a risk that the APS system may not deliver the anticipated benefits, leading to financial losses. Additionally, if the system fails to integrate well with existing processes, it can result in wasted resources and time.
Complexity of the system
APS systems are complex and designed to handle intricate production scheduling and planning tasks. This complexity can make the system hard to manage and update.
Dependence on accurate data
APS systems rely heavily on accurate and timely data to function effectively. Inaccurate data inputs can lead to poor planning and scheduling decisions, which can disrupt production and reduce efficiency.
Loss of flexibility
While APS systems are designed to optimize production schedules, they can sometimes reduce the flexibility that human-driven processes offer. In rapidly changing environments, the ability to make quick, on-the-fly adjustments is crucial.
APS systems, due to their reliance on predefined rules and algorithms, may not always be able to adapt swiftly to unexpected changes or urgent orders, potentially causing delays or missed opportunities.
Cloud ERP systems or APS software systems will mitigate these disadvantages.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling Software Systems
Various APS software systems are available both in commercial and open-source variations.
Some of the open-source APS software systems available for the supply chain are
Most modern cloud ERP solutions are either available with APS functionalities or integrated with external APS systems. The vendors are
- Oracle
- IBM
- Microsoft
- Katana
A few popular software systems available for Advanced Planning and Scheduling are
- PlanningForce
- Cybertech,
- Dynasys
- Ortames
- Orchestrate
- Optessa
- Delfoi.
Uses
APS will easily integrate with the ERP system. The software helps the people in the planning team save their time during the updation of production schedules, inventory plans, and priorities.
- It generates enhanced scheduling that balances delivery performance and efficiency of production.
- It helps to maximize resource usage to improve the company’s revenue.
- Accompany the demand and supply to decrease the inventories.
- It allows you to visualize the capacity available throughout the organization.
- Validate the scenario-based data for decision-making.
- It helps upgrade the production process to the next level with increased efficiency.
FAQs
How does APS differ from traditional production planning?
Traditional production planning often relies on manual processes and experience-based decision-making, whereas APS uses sophisticated algorithms and real-time data to optimize schedules. APS can handle complex and dynamic production environments more effectively than traditional methods.
Conclusion
APS is a methodology that helps organizations remain on schedule for their projects. As the name implies, it provides advanced planning and scheduling tasks to ensure they are completed on time.
It allows companies to plan more effectively by identifying all activities upfront, so there are no surprises during execution.
It also ensures that everything gets done by its due date, decreasing project risks significantly because you’ve already planned for any potential delays or bottlenecks before they happen.
This lowers risk exposure while increasing efficiencies on-schedule delivery times increase customer satisfaction with better quality work products!