Annual physical inventory is an essential process in businesses of all sizes. It allows business owners and managers to track the quantity and value of inventory on hand and identify discrepancies between actual and recorded inventory levels.
You can use a few methods and procedures for annual physical inventory, so choosing the right approach for your business is essential.
Companies must regularly monitor their inventory levels to stay within IRS and GAAP guidelines. Yearly physical counts or periodic cycle counting are two popular methods to achieve this goal.
Keeping an accurate stock count helps organizations remain compliant while ensuring they have the resources necessary for successful operations.
This post will provide an overview of the annual physical inventory process and tips for effectively completing it.
Define physical inventory
Annual Physical Inventory is the process of personally checking the stocks to ensure appropriate accounting of the materials and physical existence as recorded in the company books.
This process helps the business to understand the accuracy of the company stock.
It helps in planning the delivery of goods to the customers on time. In addition, it further enhances the inventory management system by tracking the existing materials and understanding which ones need to be ordered for smooth and non-stop production.
Thus the overall business decisions are taken with the help of this process.
The process is suitable for small and medium-sized organizations that have fewer products. However, this process will not be ideal for large organizations with more products in inventory.
Large organizations cannot shut down for a long time to take physical inventory. Therefore, annual physical inventory is to be done once a year.
Steps to perform annual physical inventory
Following are a few crucial steps to perform the annual physical inventory process.
Process planning
- Decide the proper method to count the physical inventory. That will be the periodic or perpetual method.
- Determine the intervals between the counts.
- Find out the number of days or time required to count by taking the stock’s draft of a list of inventories.
- Schedule the date for processing the inventory count. Make sure the days you choose will negligibly affect your typical work process.
- Assign at least two people to do this process—an experienced person familiar with the warehouse person to count and another to record the quantity.
- Train the staff if they are new to the inventory counting process.
- Inform the outside partners and staff in the company in advance. Share the scheduling date and time with them.
- If you assign more employees to do the process as your inventory is more, make teams, so each group contains a new person and experienced employees.
- Arrange the necessary stationeries and equipment to perform the process.
- If you use apps or software for the counting process, upgrade them to the current version.
- Check the instrument’s accuracy if you use an electronic instrument to count.
- Find out and assign some extra space for counting if required.
- Instruct the employees who perform the process of handling some situations in writing.
- Avoid data entry in the inventory management software during the counting process.
- Stop the receiving and issuing of inventories during the process.
- Instruct the employees to record the counts correctly to avoid double counts.
- Utilize this time to clean your warehouse and organize it.
- Record the procedures that you have followed during the process.
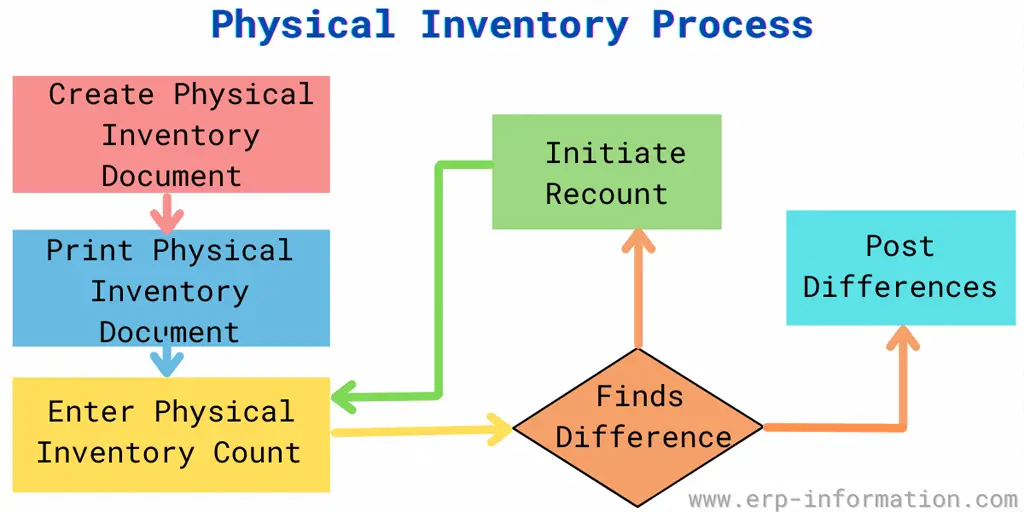
Process execution
- The authorized person froze all the activities related to inventory items.
- A list of inventories and required equipment will be provided to the employees.
- Employees count the stocks that are assigned to them.
- Employees record the physical count in a spreadsheet or a standard sheet.
- The manager or supervisor compares the count data with the actual data in the system.
- The supervisor asks the employees to recount the inventories in case of a mismatch.
- Employees submit the changing data if any.
- Again manager/supervisor validates the data. If all are ok, they send that to the accounting department.
- An authorized person in the accounting department re-checks and approves the inventory count.
Advantages of annual physical inventory
Ensures precision and Responsibility
Helps businesses to begin each year with a clean slate, ensuring the precision and responsibility of their inventory.
By manually tallying and verifying the actual stock against the inventory system, any discrepancies can be promptly identified and rectified.
Detects and Addresses losses
Provides an opportunity to uncover and address potential losses caused by theft, breakage, or unforeseen circumstances.
By reconciling the physical count with recorded inventory levels, businesses can pinpoint any unaccounted-for discrepancies, shedding light on areas where pilferage or damage may have occurred.
Enables effective planning
Accurate inventory records are essential for effective planning and forecasting. Performing an annual physical inventory count ensures alignment between the inventory system and the actual stock on hand.
Compliance and Audit preparedness
For businesses operating in regulated industries or subject to internal and external audits, it plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance.
By meticulously documenting the inventory counting processes and results, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to accuracy, transparency, and meeting regulatory requirements.
Boosts customer satisfaction
Accurate inventory management directly impacts customer satisfaction levels. An annual physical inventory count assists businesses in maintaining precise stock levels, reducing the chances of stockouts and associated delays in order fulfillment.
By promptly and reliably meeting customer demands, businesses can elevate customer satisfaction, strengthen their brand reputation, and foster long-term customer loyalty.
Disadvantages of annual physical inventory
Time-consuming
Even though there are several benefits of using the Annual Physical Inventory, the biggest issue of this process is that it takes a lot of time for the personnel to count and check every item individually.
It also unnecessarily adds up to the human resources costs lost in actual production and, simultaneously, is invested in checking the stock.
Chances of inaccuracy
No company can perform this activity often. They might do this once every quarter or a year. Once the stock is checked, it is adjusted per the existing records.
But the critical point is that inaccurate data prevails during the rest of the year, making this system inefficient.
Best practices for effective physical inventory counts
Here are a range of invaluable pointers to boost your staff’s counting precision:
Embrace modern technology
Leveraging barcode scanners or innovative stock counting technologies can drastically enhance the accuracy of your inventory count.
Select attentive counters
Ensure your staff possesses a keen eye for detail and can focus on the task at hand. Attention to detail is the linchpin of a successful count.
Swiftly tackle discrepancies
When discrepancies surface during the inventory count, address them immediately. Proactive resolution prevents errors from compounding.
Rehearse with a mock count
A mock count during the planning phase can help your team familiarize themselves with the process, iron out any kinks, and bolster confidence.
Shield cost information
It’s crucial that the cost of items being counted is not visible during the count to prevent bias and maintain objectivity.
Pause operations
Conducting a complete physical inventory warrants undivided attention. Temporary cessation of regular operations during this process ensures a meticulous count.
Secure the stock area
Prior to the inventory day, take measures to secure the stock area, ensuring its integrity and preventing unauthorized access.
Determining the timing for a physical inventory check
The frequency at which you should conduct physical inventory counts hinges on various contributing factors, such as:
- The Volume of SKUs in Your Inventory
- The quantity of distinct Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) within your inventory plays a pivotal role in deciding how often you should perform inventory checks.
- Daily Sales Volume
- The number of items sold on a daily basis is another determining factor in the frequency of inventory assessments.
- Use of Inventory Technologies
- Incorporating modern inventory technologies like Point of Sale (POS) systems or barcode scanners can streamline the counting process, potentially affecting the frequency of checks.
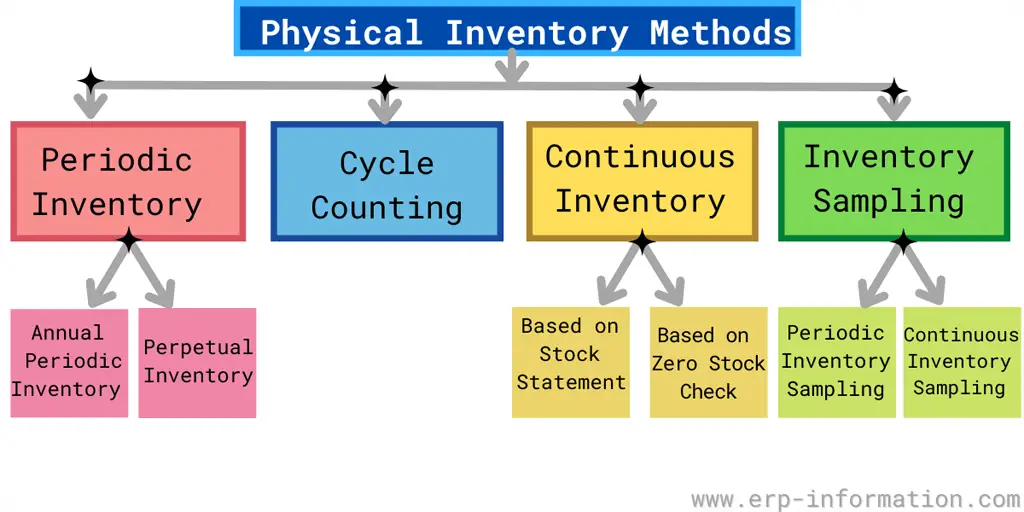
Physical inventory methods
The Annual Physical Inventory system comprises the essential phases: planning, execution, and report analysis.
The best-suited alternative to this procedure is the inventory cycle count, where the materials are checked on a specific day for a particular location. But, again, ABC analysis can be utilized here to make counting more efficient and reliable.
Cycle counting
Cycle counting is one more method of counting inventory. It is a never-ending counting process. In this process, a small stock set is measured in a particular place on a specific day.
Using this method, You can daily check your physical inventory. Generally, it suits large organizations where inventory is extensive.
Following are the few benefits of the cycle count method over annual physical inventory.
- Less down disturbance in work while performing this method.
- It saves money and the workforce because only one person can perform this process.
- This process is not difficult and complex as the annual physical inventory. You can do this process without any confusion.
- It increases the accuracy of the inventory and gives a clear idea of each line of products or inventories.
- It gives a vision to the buyers into which component to be ordered to stock.
- It helps to recognize missed sales opportunities.
Continuous inventory
Continuous inventory is one of the physical inventory methods where all materials are counted at some month or point in the year. So, for example, a bicycle spare part manufacturing company can count some materials in May and some in September.
In this method, counting inventories takes place throughout the year. The company has to ensure that all the materials are counted physically at least once that year.
Inventory sampling
In this procedure, physical counting happens only for randomly picked materials. Any differences found when compared with the balance sheet. Then the other materials are also counted.
What is the difference between annual physical inventory and cycle counting?
Annual physical inventory
- In the Annual physical inventory count, businesses temporarily freeze operations and devote their attention to counting up an abundance of stock-keeping units( SKUs).
- To keep track of inventory, operations are paused until the count is completed; this gives us a moment to take stock and ensure our warehouses remain in order.
- The business has to shut down while doing inventory counting temporarily.
- You can finish your stock counting, make the required corrections, and start with new inventory quantities.
Cycle counting
- Cycle counting is how to stay organized and on top of inventory levels all year round.
- An efficient system allows you to easily divide your project into manageable units based on location or type for a smooth operation.
- Businesses can run their operations seamlessly while conducting inventory checks – a great way to keep productivity high.
- Cycle counting helps you to keep track of every item in your inventory at least once a year, which makes your list more accurate.
FAQs
What is physical inventory?
A physical inventory is an inventory of the tangible assets of a company. It is a count of the items on hand, usually done at regular intervals, to ensure that the accounting records match the actual physical state of the company’s stocks.
The purpose of a physical inventory is twofold: first, it allows management to assess how much stock they have on hand, and second, it provides a snapshot of the company’s assets that can be used for financial reporting and taxation purposes.
The physical inventory process can also help identify discrepancies between accounting records and actual stock holdings (e.g., theft or misplacement).
What is yearly inventory?
An annual inventory is an accounting procedure whereby a business reviews the value of its assets and liabilities at the end of its fiscal year. This process helps ensure that the company’s financial records are accurate and up-to-date.
In addition, the results of the annual inventory can be used to inform critical financial decisions, such as whether or not to secure a loan or sign a new lease.
Typically, an annual inventory will involve physically counting the company’s assets (e.g., cash, equipment, property) and liabilities (e.g., accounts payable, loans). The totals from this count will be compared to the values listed in the accounting inventory records. If there are any discrepancies, they will need to be addressed.
What is a physical inventory plan?
A physical inventory plan is a plan for counting and verifying the number of items on hand to assess the adequacy of stock and identify discrepancies between what is physically present and what is recorded in the accounting system.
A physical inventory plan aims to ensure that the correct quantity of items is recorded in the accounting system and prevent or detect theft, fraud, or other errors.
A physical inventory plan typically includes the following:
-A schedule for taking periodic physical inventories
-A procedure for counting items and verifying quantities
-A procedure for investigating discrepancies between physical count and book balance
-A procedure for reconciling inventory balances with accounting records
What is the purpose of physical inventory?
There are a few reasons why businesses might conduct physical inventory counts. The most common cause is to ensure that the organization’s accounting records match the actual physical count of items in the warehouse or on the sales floor.
Another reason might be to perform a stocktake to identify and track slow-selling or discontinued items. A physical inventory also provides a “snapshot” of the organization’s stock at a given time, which can help forecast future inventory needs.
Finally, it’s also possible that an audit may require a physical count of items to verify that accurate records are being kept.
How to take inventory?
The first step is to develop a system for tracking your inventory. You can use a spreadsheet, database, or software program to help you keep track of what you have in stock and when it needs to be replaced.
Next, make sure you accurately count everything you have on hand. This includes the physical items themselves and the quantity and description of each item. If you have multiple items that are essentially the same (such as different sizes of the same garment), list them as one item.
Finally, review your inventory regularly and make changes based on what’s selling and not. Finally, update your tracking system as you always have an accurate picture.
What is the cycle counting method?
Cycle counting is auditing inventory by counting a selection of items periodically. Cycle counting aims to ensure inventory counts’ accuracy and identify any discrepancies.
The frequency of cycle counting depends on the size and complexity of the inventory but typically occurs every few weeks or months.
What is a continuous inventory method?
The continuous inventory method is an inventory management technique that strives to maintain an accurate count of all items in stock at all times.
In contrast, the periodic inventory method relies on periodic physical counts of items in stock, with adjustments made to account for any discrepancies between actual and book values.
The primary benefit of using the continuous inventory method is that it helps ensure that accurate information about quantities on hand is always available to decision-makers within the organization. This can help avoid stock-outs, overages, and other costly inventory management issues.
What is inventory sampling?
Inventory sampling is a process by which a representative sample of goods from an inventory is selected and counted to estimate the number of goods on hand.
This procedure avoids counting every item in an inventory, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Sampling can be done manually or using a computerized system. In either case, the company must use a statistically valid method to select the items for sampling.
The most common practice is random sampling, in which every item has an equal chance of being selected. Other methods include systematic sampling, where items are chosen based on a specific pattern, and stratified sampling, where items are divided into categories and samples are taken from each type.
Conclusion
Annual physical inventory is a process of counting the quantity and type of goods to determine their value. It’s an accounting practice that can be done at any time, but it usually happens once per year before the company closes its books for tax reporting.
This helps your organization stay on top of discrepancies between what you have and what you should have based on past transaction records.
A physical count also gives management insight into how much product they need to replenish or if more must be ordered from suppliers.