An Application Platform as a Service is a type of cloud computing that provides users with on-demand access to preconfigured application environments.
With it, you can quickly and easily deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. That makes it an excellent choice for businesses wanting to get up and running quickly without investing in their IT infrastructure.
This post provides complete details about aPaaS, including its definition, benefits, working, and associated risks.
What is aPaaS?
It is a term used for software platforms that provide a cloud-based environment where users can develop, deploy and manage application services without the burden of handling the infrastructure and platform layers.
It is classified by two features.
- Low code development tools
- Rapid application development (RAD)
How does it work?
It is a cloud computing platform that provides web developers with on-demand access to calculate resources, such as memory, storage, and CPU cycles. It helps them deploy their applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Application platforms typically include an operating system, a database management system, middleware, and programming languages.
In addition, they offer services such as debugging and testing tools, backup and disaster recovery capabilities, load balancing, and scalability features. Some platforms also offer pricing models that allow customers to pay for only the resources they use.
Benefits
Reduced time to market
Applications can be deployed more quickly with APaaS than if they were developed and deployed on traditional infrastructure.
Increased efficiency
Developers can focus on developing applications rather than configuring and managing the underlying infrastructure. That can lead to faster development times and improved application quality.
Scalability and flexibility
Applications can be scaled up or down as needed and easily adapted to changes in demand.
Cost savings
This can often be less expensive than building and maintaining an in-house application development platform.
You can pay only for what you use with aPaaS, so there are no upfront costs or long-term contracts. This can save you a lot of money in the long run.
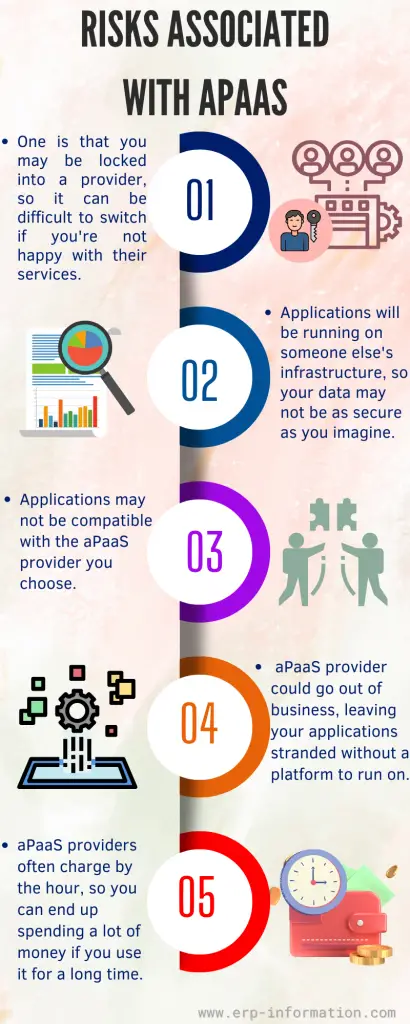
Risks
- One is that you may be locked into a provider, so switching can be difficult if you’re unhappy with their services.
- Your applications will be running on someone else’s infrastructure, so your data may not be as secure as you imagine.
- Your applications may not be compatible with the Application Platform as a Service provider you choose.
- There is always the risk that the Application Platform as a Service provider could go out of business, leaving your applications stranded without a platform to run on.
- aPaaS providers often charge by the hour, so you can spend a lot of money if you use it for a long time.
Popular Vendors
The most popular providers are
- IBM
- Microsoft Azure
- Google App Engine
- Salesforce
- ServiceNow
- Mendix
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk
- Force.com
- OpenShift
- Apache Stratos
- Magento Commerce Cloud
- Appian
- OutSystems
aPaaS vs PaaS
PaaS offers a complete application development and operations environment, including everything from the operating system to middleware and application frameworks.
On the other hand, aPaaS focus exclusively on the Application Development Platform as a Service layer of the cloud computing stack. That includes providing tools and services for developing and hosting web applications.
So, in summary, PaaS offers a more comprehensive platform for developing and running applications, while aPaaS aims to provide tools and services for developing web applications.
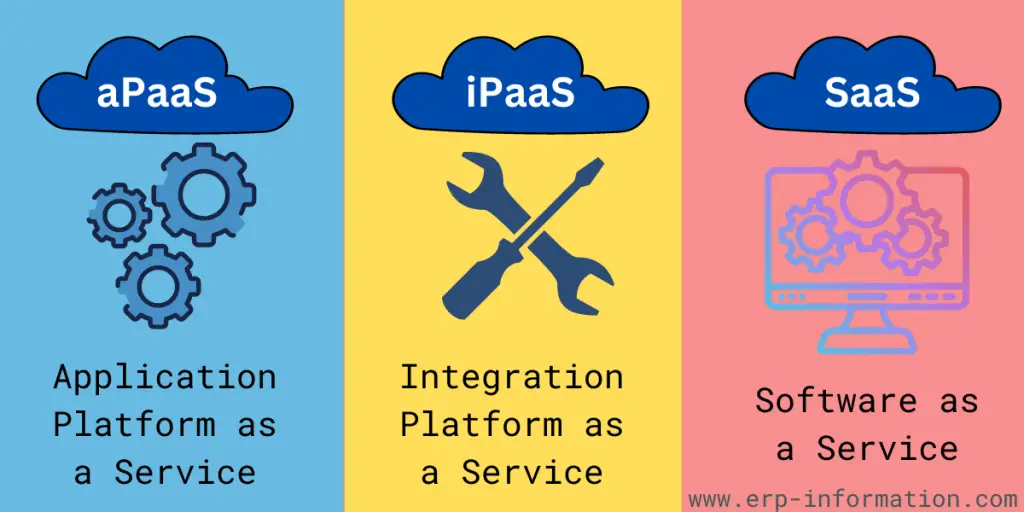
Difference between aPaaS, iPaaS and SaaS
| aPaaS | iPaaS | SaaS |
| It enables rapid application development and provides a cloud environment for deploying, designing, and maintaining business applications. This platform offers high productivity, a quick way to build apps, and high control. It also automates the application life cycle. | iPaaS is a cloud-based, multi-tenant integration platform hosted by a vendor on-premise. With this platform, applications on the cloud or on-premise can have data flow between them for integration. | Vendors host SaaS applications. It provides applications in the form of ready-to-use to meet organizational needs. Customers can get applications over the internet. |
| Examples: ServiceNow Mendix, Outsystems, SalesForce | Examples: Zapier, Segment, Jitterbit, IBM App Connect | Examples: Google Apps, Dropbox, Concur, Cisco WebEx |
FAQs
What are the common features of aPaaS?
Elasticity: Scale up or down as needed.
Autoscaling: Automatically add or remove resources based on load.
Multi-tenancy: Serve multiple customers/tenants on a single platform.
API management: Control access and usage of APIs.
Platform services: Run common functions like storage, computing, and networking.
What are low-code development tools?
Low code development tools allow business users to create custom applications without learning to code. These tools typically use a visual interface, so you can drag and drop different components to create your application.
Low code development tools are a great option for businesses that need custom applications but don’t have the resources or time to learn to code.
What is rapid application development?
Rapid application development (RAD) is a software development methodology that emphasizes speed and agility. RAD tools and techniques allow developers to create applications more quickly and efficiently than traditional methods.
Conclusion
aPaaS is an excellent solution for businesses that need to deploy applications quickly with minimal management. It offers scalability, flexibility, and cost savings, and most providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
However, some risks are associated with using it, including being locked into a provider and data security risks. Before choosing the provider, be sure to do your research and compare prices and features.