Environmental issues continue to take center stage, it is common for conversations to delve into the realm of “cap and trade” or “emission trading.” These terms have increasingly become part of our lexicon when discussing actions against climate change.
But what do those terms mean? And why are they important tools in reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Here we’ll explore how cap and trade works, its successes, challenges, and potential for helping reduce global warming. Learn more about this promising tactic for curbing greenhouse gas emissions!
What are Cap and Trade?
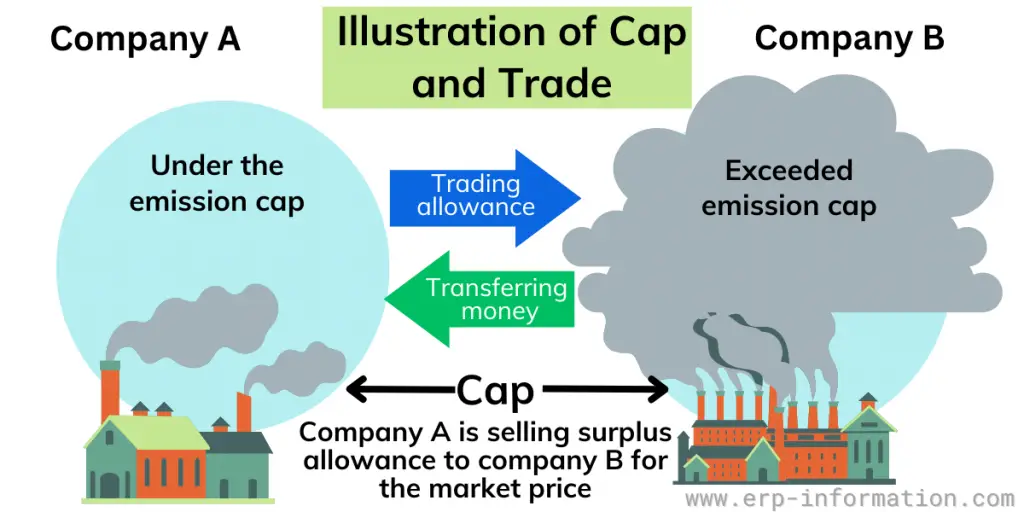
Cap and trade is an environmental policy used to limit greenhouse gas emissions. It works by placing a “cap” on the total amount of certain pollutants emitted yearly, allowing companies to buy or sell emission allowances in a market-based “trade” system.
Under this policy, companies must either reduce their emissions below the cap or purchase additional credits – from other entities that have achieved reductions in emissions.
The result is reduced overall pollution and increased costs for those producing the dirtiest energy sources.
Cap and trade is a system the government created to control the amount of pollution caused by industries. It limits how much certain greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, can be released into the air. It is also known as” Emission Trading.”
The United States government created the first cap-and-trade program in 1990 to help control sulfur dioxide pollution. In 2005, they created another one called the Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR), which also works to reduce both sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
It is an important part of California’s plan to reduce gases that cause global warming. It works with other plans to make sure California cost-effectively meets its goals.
Carbon emission trading is a way to reduce pollution. It works differently than the government commands the citizens to reduce carbon emissions.
Cap and trade let the market decide how much it will cost to reduce emissions. This means empowering the market to establish a carbon price, fuel investment choices, and inspire groundbreaking market advancements with cap and trade.
It differs from a tax because with cap and trade, you can be sure how much pollution will be reduced, but not how much it will cost. Governments with specific goals for reducing emissions usually use cap and trade instead of taxes.
More about Cap and Trade policies
Govt limits the amount of pollution
This program is when the government limits the amount of pollution that companies can create. They will give out a certain number of permits each year. The permits say how much carbon dioxide and other pollutants that cause global warming can be released. Smog-causing pollutants can also be limited with this program.
Govt gives allowances
The government puts a limit, called a cap, on how much pollution companies can make. The cap is split into pieces called allowances, like tickets. Each allowance lets the company put out one ton of emissions. The government gives these allowances to companies for free or makes them buy at an auction.
Govt reduces the number of permits every year
The government reduces the number of permits that can be used for emissions. That means fewer companies can pollute. As a result, permits become more expensive. This encourages sustainable environmental technologies since it will cost less than buying more permits.
Companies must pay tax
Companies must pay taxes if they release more pollution than their permits allow. They may even have to pay a fine if they break the rules. Companies that produce less pollution can sell their extra allowance, called trading, or save it for later.
Advantages
Provides extra economic benefit
The cap and trade system is like a marketplace. It sets a value for emissions that companies release. Companies can make money by selling their emissions credits. This gives them an extra economic benefit.
Offers cleaner technologies to companies
People who support a cap and trade program say it encourages companies to spend money on environmentally good technologies. They won’t have to buy permits, which will cost more yearly. Companies can also use their money to look for new energy sources.
Income source for government
The government can make money by auctioning emissions credits. This money can be used to fix roads and bridges, help people in need, pay for new technologies to help the environment, or even fill the government’s budget.
Provides an option to customers
Cap and trade is a system that lets people buy and sell things without taxes. Customers can pick which companies are trying to be cleaner and reduce pollution.
Benefits taxpayers
This system can help taxpayers. The government sells emissions credits to businesses that need them. This money helps the government pay for things taxpayers have already paid for.
Disadvantages
Set high allowed emission levels
The government may set too high a limit for allowed pollution. This could mean that it would take longer to make energy cleaner.
Cleaner technologies are expensive
Emissions credits are usually cheaper than changing to cleaner energy sources, like fossil fuels. This means that companies don’t have a reason to switch to cleaner energy if they can buy emissions credits instead. Cap and trade don’t give them any extra incentive to do this.
Companies may sell credits
Sometimes, companies do not follow the “trade” system for emissions credits. They may sell them to the highest bidder or even give them away for free. This means that companies don’t need to spend money if they want to increase their emissions.
Companies may cheat
Many businesses do not have machines that measure how much pollution they are giving off. This makes it easier for them to lie about their pollution numbers.
Expensive investment effect on consumable products
Renewable energy resources are new and cost more money. Companies have to follow the rules when making products from renewable energy resources, which makes them more expensive for consumers. That means products and services become very costly for end users.
Examples of Cap and Trade users
The below-listed countries started using the cap trade program given this example by referring to a nonprofit organization, “Center of Climate and Energy Solutions(C2ES).”
- In Europe, some countries have had a cap-and-trade program since 2005. This means they set a limit on how much greenhouse gas can be produced by certain companies.
- China has also done this in some cities and provinces since 2013 and is now making this law for the whole country.
- Mexico started its cap-and-trade program on January 1, 2020.
- In the United States, eleven states joined in 2009 to create a program called RGGI (Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative). It is called cap-and-trade, and it helps reduce air pollution.
- In 2013 California started its cap-and-trade program that works with a similar one in Canada. There was an effort to make this same program across the US, but it did not pass through the Senate after passing through the House in 2009.
FAQ
What is the difference between the carbon tax and cap trade?
A carbon tax means companies pay money for each ton of pollution they make. A cap and trade program lets people buy “allowances” to make pollution. The allowances can be bought or traded, which sets a price on the pollution.
Conclusion
Cap and trade or emission trading is an effective tool for curbing environmental pollution. It works by setting a ‘cap’ on certain types of emissions identified as sources of pollution and then setting up a trading system that lets companies buy and sell permits related to those emissions.
Some challenges associated with emission trading schemes due to economic uncertainty and other pressing political issues must be addressed before they can succeed.
Despite these challenges, cap and trade systems offer a powerful way to address global climate change and promote sustainable energy policies.