A manufacturer wants to determine the number of machines and workers that are required to produce products on a certain day.
What do you think can help them plan and manage their resources, tasks, time, and manpower?
It is here that capacity planning can be implemented and achieve great profits, reduce overspending, and have happy customers. It plays a major role in the success of growing industries.
This blog post will help you understand how to plan for how much work your business can do. In addition, you will learn capacity planning strategies, goals, process steps, types, best practices, tools, systems, and who is involved in capacity planning.
Evaluate Capacity Planning using our Capacity Planning Calculator.
Capacity Planning Definition
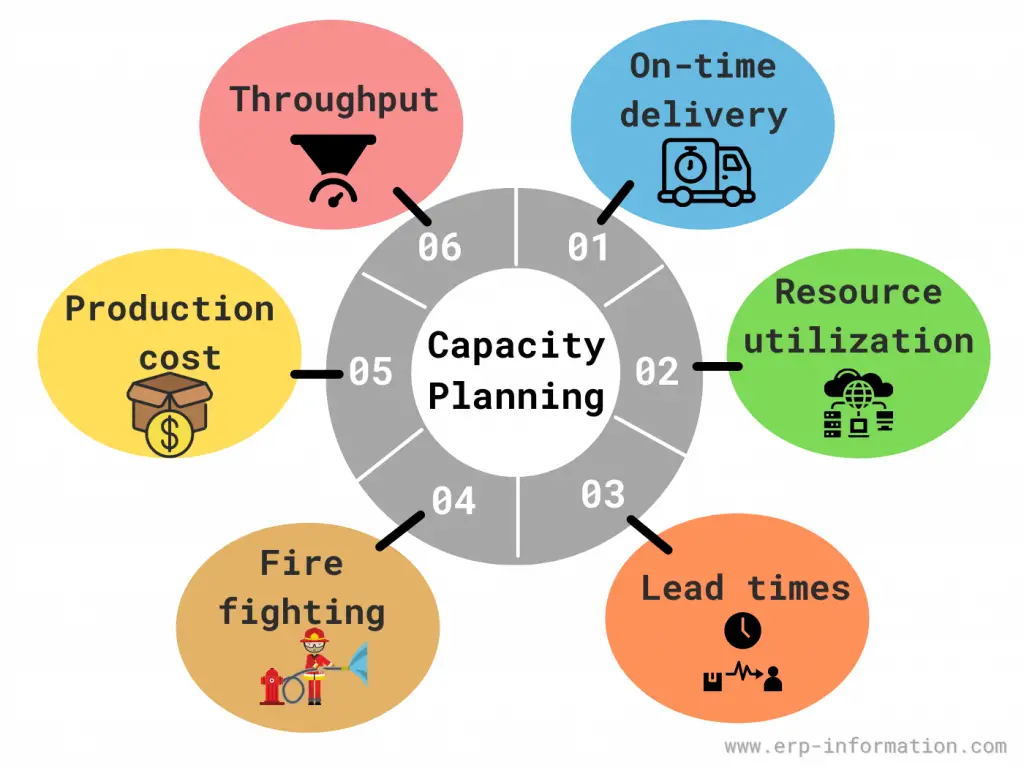
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products or services.
It involves assessing current capacity, forecasting future demand, and planning for the necessary resources to ensure that the organization can efficiently and effectively meet those demands.
This includes managing resources such as labor, equipment, and facilities to avoid overproduction or underproduction, optimizing costs, and maintaining a balance between supply and demand.
Capacity planning is integral to resource management because it helps a company meet demand without going over or under budget.
The capacity planning process is crucial in project management. It is related to project management knowledge areas like:
- Work Management
- Resource Management
- Time Management
- Team Management
The Goal of Capacity Planning
- Assessing how much capacity an organization currently has.
- Predicting how much capacity will be needed in the future.
- Ensuring the necessary resources are available when needed.
A few related terms that we need to know before proceeding are:
Resource Planning and Resource Management
Resource capacity planning is forecasting future resource needs and allocating current resources to meet those needs.
It includes forecasting the demand for people, money, materials, and machines and then assigning those resources in a way that will meet projected requirements.
Resource management is the process of managing resources in an enterprise. It ensures the enterprise has enough resources to meet its current and future needs.
Different Capacity Planning Strategies
What is strategic capacity planning?
Strategic planning is the proactive part of capacity planning, ensuring that the enterprise has the resources to meet its long-term goals.
There are four common capacity planning strategies: the lead strategy, the lag strategy, the match strategy, and the adjustment strategy.
Lead strategy
Lead capacity planning is when you increase your capacity ahead of anticipated future demand to meet that demand as soon as possible.
In lead strategy, you can either add resources to your current system or expand your system. Adding resources is the most common way to increase capacity. However, you can do it as part of resource planning.
Example
A popular ice cream company that experiences a surge in demand every summer. To ensure they can meet this seasonal demand, they use a lead capacity planning strategy.
In the spring, before the summer rush, the company decides to increase its production capacity. They do this by hiring additional workers and extra ice cream machines. This proactive approach ensures that when summer arrives, they can immediately meet the higher demand without delays.
Lag strategy
The lag strategy is when you delay expanding capacity until after experiencing demand.
A lag strategy can be problematic since you may find yourself in a situation where demand has increased, and there’s no capacity to meet the demand.
Example
Imagine a trendy coffee shop that has become very popular, attracting more customers. The owner waits to see consistently high demand before expanding the seating area and hiring more staff, using a lag strategy.
As a result, the coffee shop struggles to keep up with the increased demand, leading to long wait times and overcrowding. This delay causes the shop to potentially lose customers and damage its reputation until it finally increases its capacity to meet the demand.
Match strategy
The match strategy is adding capacity only after the ongoing capacity matches the current demand. This is the best for budgeting because you will only be buying capacity when needed.
However, this strategy does not work well with fast-changing demand. If the whole industry is changing, your capacity might not be enough to meet that change in demand, and you will have a bad customer experience.
Example
Imagine a popular online clothing store using a match strategy for its inventory, waiting until stock matches demand before ordering more. This budget-friendly approach works well unless fashion trends change rapidly.
If a style suddenly becomes popular, the store might run out of stock before it can restock, causing customers to turn to competitors and resulting in lost sales and a poor customer experience.
Adjustment strategy
The adjustment strategy is gradual changes to either capacity or demand based on past performance.
For example, if you notice that you come close to or exceed your capacity during your busiest months, you will adjust by increasing your capacity in preparation. This strategy is an excellent method because it’s gradual and doesn’t have a lot of negative consequences if it fails.
Some more strategies
Forecasting
Forecasting is a common capacity planning technique used by many organizations to help anticipate future needs and plan for changes in demand.
By analyzing past trends and considering predicted future events, organizations can build models that help them predict more accurately how much they need to produce.
Anticipation model
A technique used for capacity planning is anticipation modeling, which focuses on forecasting future demand using historical data and then adjusting existing resources in advance of actual requirements to ensure smooth operations when demand increases suddenly or decreases substantially.
Outsourcing
In some industries, outsourcing is becoming an increasingly popular capacity planning strategy.
Typically, companies will identify the services and processes critical to their success and then leverage an outside vendor or partner who can execute those processes more efficiently than they currently do.
Demand management
A related approach is demand management, which focuses on reducing expectations for a product or service to decrease overall demand and thus reduce capacity requirements.
While this may seem counterintuitive, many companies find that it improves customer satisfaction because lower-quality products delivered at a lower cost lead to more satisfied customers than higher-quality products delivered at a higher price.
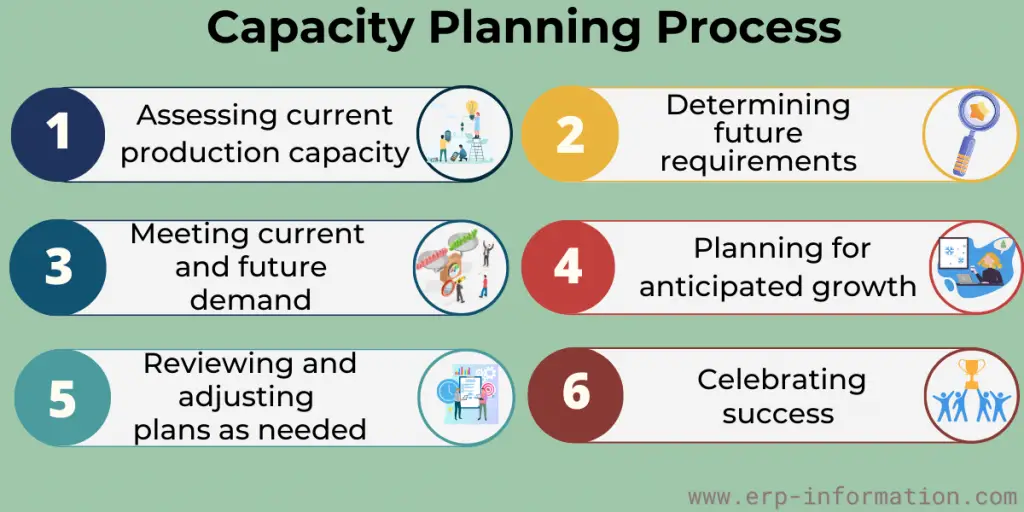
6 Steps in the Capacity Planning Process
Effective capacity planning involves the assessment of existing capacity and the identification of later requirements. It also includes developing plans to ensure that sufficient resources are available when needed.
The steps involved in capacity planning are:
1. Assessing current production capacity
Current production capacity assessment is the first step in any capacity planning process. Next, you need to understand what resources you have at your disposal and how they’re currently used in resource planning. This can include everything from people and equipment to office space and data storage.
2. Determining future requirement
It may seem daunting, but planning for growth is essential. Whether your business is expanding or anticipating more traffic on your website, you need to know what capacity you’ll need down the road.
3. Planning for anticipated growth
It is essential, but it’s also important to be realistic about potential needs. It’s better to overestimate than underestimate, so don’t be afraid to think big!
4. Meeting current and future demand
It is the ultimate goal of capacity planning. Of course, you want to ensure you have enough resources available at all times, but it’s also important not to waste money on excess capacity.
5. Reviewing and adjusting plans
Reviewing and adjusting plans as needed will help your business grow steadily instead of haphazardly. No matter what kind of changes come up — whether they’re related to growth or anything else — you should always be willing and able to adapt!
6. Celebrating success
It may seem like an odd part of a process that requires so much focus and attention, but everyone deserves recognition after doing such hard work.
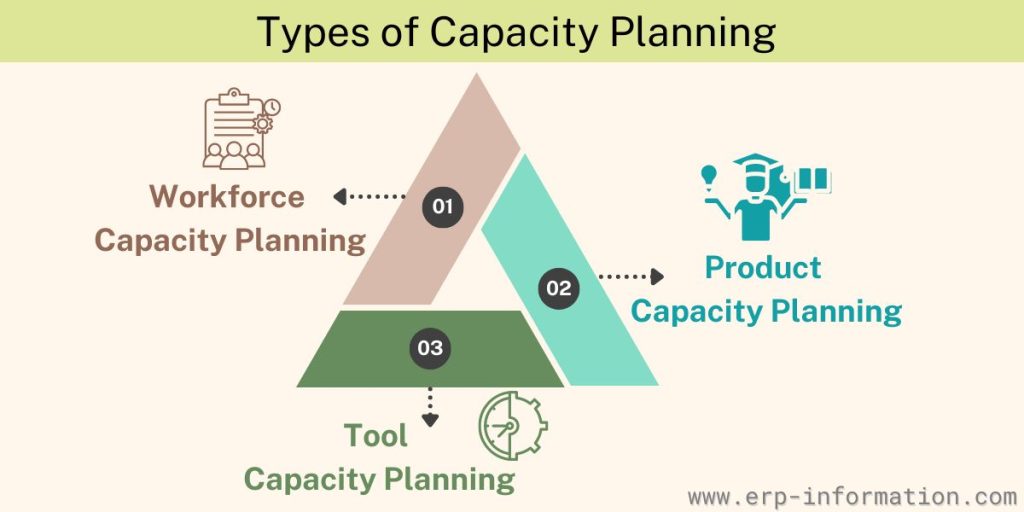
Types of Capacity Planning
There are three types of capacity planning.
Workforce capacity planning
Workforce capacity planning focuses on managing your human resources to ensure you have the necessary workforce to meet demand effectively. It helps you determine how far in advance to initiate hiring or downsizing, ensuring you have the right number of employees to complete tasks efficiently.
Product capacity planning
Product capacity planning ensures you have the production capability to meet varying product demands. It allows you to adjust production levels by securing the necessary materials and labor to align with market demand fluctuations.
In this way, it helps you maintain a balance between supply and demand, optimizing resources and minimizing waste.
Tool capacity planning
This capacity planning ensures your business has all the essential tools, such as machinery, vehicles, assembly line components, and other resources, required to produce and deliver your products or services promptly and efficiently.
Capacity Planning vs Resource Planning
| Capacity planning | Resource planning |
| Capacity planning is a strategic way of finding the required production capacity for the organization to meet changing demands for its products. | Resource planning is a specific procedure assigning resources (like people, equipment, and materials) to project activities based on their availability and the needs of the project. |
| The objective is to ensure that there are enough resources (like equipment, space, and labor) available to produce the required amount of goods or services. | The main objective is to ensure that the right resources are available at the right time and place to complete project tasks efficiently. |
| It focuses on the overall capability of the production system and the overall process of the organization. | It focuses on optimizing the utilization of resources within the constraints of a project. |
| It involves forecasting demand, determining the production capacity needed, and planning for future capacity requirements. | It involves assigning specific resources to tasks, managing resource availability, and resolving conflicts over resource allocation. |
| It often has a longer-term perspective, looking at future demand and preparing for it months or even years in advance. | It typically has a shorter-term perspective, focusing on the needs of current or upcoming projects. |
| Commonly used in manufacturing and service industries to balance capacity with demand. | Commonly used in project management across various industries to ensure project deadlines are met and resources are used efficiently. |
Tools and Systems
Businesses can use various tools and systems for capacity planning. One standard tool is Microsoft Excel, creating graphs and tracking data. Another tool that planners can use is Microsoft Projects. Project managers can use this software to create timelines and track resources as project management.
Other capacity planning tools that project managers can use include:
- Capacity Planning Toolkit
- Performance Scorecard Builder
- Capacity Planning Template
- Capacity Planning Worksheet
- Capacity Planning Spreadsheet
- Performance Scorecard Template
- Portfolio Management Toolkit
- Project Resource Planner (for project management and resource planning)
The company can use several third-party software products for capacity planning. Here is an example of some common ones:
Datastage Capacity Advisor
IBM’s Capacity Advisor is a tool used to help with capacity planning. The Capacity Advisor can predict subsequent requirements and help prevent capacity issues. The Capacity Advisor also helps with the identification of excess capacity.
IBM InfoSphere Optim Solutions Enabler Capacity Manager
IBM InfoSphere Optim Solutions Enabler Capacity Manager is essential for capacity planning. It helps you to understand and optimize your resource utilization. The Capacity Manager feature provides information on the following:
- Present Capacity
- Meet Demand
- Resource Management
The Capacity Manager also helps you identify and plan for future requirements.
CA Technologies Workload Estimator
CA Technologies Workload Estimator is a tool that helps you plan for the future capacity needs of your enterprise. The tool uses historical data to make predictions, giving you a realistic estimate of your capacity needs.
The Workload Estimator considers workload growth, the number of users, and resource utilization.
Dell ClearApp Enterprise Edition
Dell ClearApp Enterprise Edition helps organizations manage their resources and capacity. The software can optimize the performance of applications by identifying and resolving potential resource contention.
Dell ClearApp also provides performance and capacity planning for virtualized and cloud-based environments. Dell ClearApp Enterprise Edition is a part of Dell’s Integrated Cloud Application and Infrastructure Management (ICAM) solution.
The list goes on and on, though! But, again, this is because so many different tools are available to help with capacity and project management.
This makes it easier to take advantage of the benefits of effective capacity planning strategies! However, it’s important to note that there is no “one size fits all” solution for capacity planning.
The best approach is to identify the tools that will work best for your specific situation and then use them to their fullest potential.
Who is Involved in Capacity Planning?
The roles involved in capacity planning can vary depending on the organization but typically include members from different enterprise areas, such as human resources, information technology, marketing, and manufacturing.
It is strategic planning that a company should regularly undertake to ensure the organization can meet its current and future demands.
Roles involved in it are :
Capacity Planner
Responsible for the collection and analysis of information, as well as for creating an actionable capacity plan. They work closely with business managers to understand their requirements and translate those into a technical context.
This includes identifying future demand patterns based on industry trends, sales forecasts, or any other factor that can help predict changes in resource usage (e.g., product growth, new initiatives, workforce increase).
The capacity planner gathers information throughout the organization to give decision-makers insight into current performance levels and what might happen in the future.
Operations Staff Member
An Operations Staff Member is an individual involved in the business’s day-to-day operations. They are responsible for ensuring that resources are available when needed and those production goals are met.
Business Manager
The individual is ultimately responsible for the success or failure of the business unit/department. Therefore, they must understand their capacity requirements to make informed decisions about future growth or initiatives.
Information Technology (IT) Staff Member
They are involved in supporting and managing the technology infrastructure within the organization. This includes evaluating current systems, recommending upgrades/changes, and working with vendors to procure necessary hardware/software.
In some cases, they may also be involved in designing and building new applications or modifying existing ones to meet organizational needs better.
Marketing Staff Member
Part of the organization that is responsible for marketing and brand development. They understand current demand patterns, evaluate how new initiatives may impact future capacity needs, etc.
Human Resources (HR) Team Members
They guide hiring plans/targets, training requirements, etc. Therefore, they need to be consulted when assessing future resource demands.
Benefits
Capacity planning allows businesses to forecast future production needs and ensure they have the resources to meet demand.
- It helps businesses optimize their resources and avoid costly overages or shortages.
- It enables businesses to plan for future growth and expansion.
- Effective capacity planning can help businesses manage their current resources more efficiently.
- It can help businesses react quickly to changes in demand.
Resource management software can automate much of the capacity planning process, making it easier and faster for businesses to accurately picture their current and future needs.
Best Practices
Among many best practices, we are listing effective practices.
- Ensure you have a clear understanding of your system requirements. That includes understanding your desired uptime, peak loads, anticipated growth, etc.
- Work with vendors to understand their capabilities and limitations. Make sure you know what they can provide regarding resources and assistance.
- Run load tests on your systems to get a realistic picture of performance under real-world conditions. That will help you identify potential bottlenecks and capacity issues before they cause problems in production.
- Utilize monitoring tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) in your production environments.
How Do You Determine Production Capacity?
The production capacity is the maximum number of units your company can produce in a given period. It includes all resources, including labor hours and machines.
To determine your production capacity, you must first understand your available resources. This includes understanding the amount of space you have, the number of workers you have, and the amount of equipment you have.
The steps are as follows.
- Assess Resources:
- Count your workers.
- Measure the available work hours.
- Evaluate your equipment.
- Calculate Time:
- Determine how long it takes to produce one unit of your product.
- Compute Capacity:
- Multiply the number of workers by the available work hours.
- Divide this total by the time it takes to produce one unit.
- Example Calculation:
- Workers: 5
- Work Hours: 8 hours per day
- Production Time: 2 hours per unit
- Calculation:
- Production Capacity = (5 workers × 8 hours) divided by 2 hours per unit = 20 units per day
You can calculate your Production capacity using our Online Production capacity calculator
Note: Production capacity is flexible. It can change based on product demand. If demand increases, you might need more workers or longer hours to boost capacity.
FAQs
What are the major problems of capacity planning?
One of the most critical challenges in capacity planning is determining when and how much capacity should be increased.
Increasing capacity too soon can lead to unnecessary costs, while doing it too late can result in lost sales and frustrated customers. So, getting the timing and the amount of capacity expansion right is essential for the success of a business.
If capacity planning is not done properly, it can lead to the loss of customers and business opportunities. This happens when a company doesn’t have enough capacity to produce what customers want, causing them to look for alternatives.
On the other hand, having excess capacity can be a drain on a company’s resources. It ties up money and other resources that could be used for more profitable ventures, such as new products or expanding into new markets.
How do you develop a capacity plan?
When developing a capacity and resource plans, consider several key factors to ensure effectiveness.
Assess Current Capacity: Evaluate available resources and how they can meet current and future demands.
Strategize for Adjustment: Develop strategies to expand or contract production based on demand. Be mindful that excess capacity can lead to inefficiencies.
Utilize Tools and Software: Use appropriate tools and software for accurate capacity planning.
Conclusion
Capacity planning is forecasting future business needs and ensuring that resources are available to meet those demands. It ensures that your enterprise has enough resources to meet current and future needs.
Capacity management involves a variety of capacity planning strategies, systems, processes, and input from various roles in the organization.
By doing strategic planning and considering factors such as production capacity, resource capacity, and impending requirements, you can create an effective capacity plan to help you meet demand now and in the future.