We all know preserving the environment is important, but we must figure out what steps to be taken. Even if you’re trying your best, it can be tough to figure out if your efforts are making a real difference.
Carbon neutral and net zero sound the same. But there is a slite difference between them.
The blog post explains carbon neutral vs net zero. Let us look into the difference between carbon neutrality and net zero.
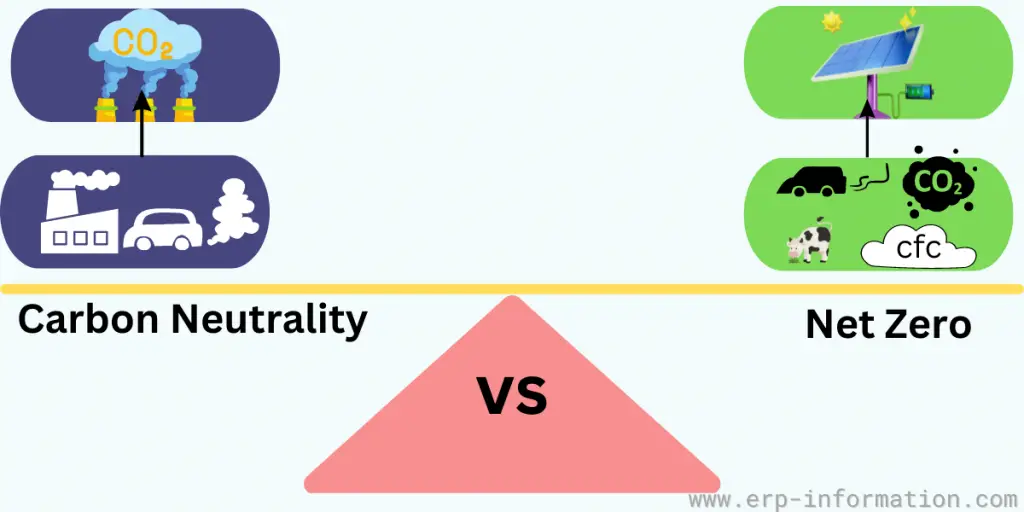
You can erase your carbon footprint and become carbon neutral by offsetting your carbon emissions. Net zero goes one step further by offsetting emissions and creating more renewable energy than you use. That makes your home or business completely net zero emissions.
Evaluate carbon emissions using our Carbon emission calculator online
What is carbon neutrality?
Carbon neutrality is the state of being carbon neutral, which is reached when an individual or organization’s net carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) are zero.
In other words, Carbon neutrality is the state in which an equivalent amount of removal balances out any carbon dioxide released by a company through its activities.
Carbon neutrality can be achieved in various ways, including reducing energy consumption and capturing and sequestering CO2.
What is net zero?
Net zero is the same as carbon neutral, but it is broader in scale, which means it is not only the removal of carbon dioxide.
It is the state where the amount of greenhouse gases(GHGs) entering and leaving an environment is in equilibrium. In other words, the net emissions from a particular activity or group of activities are zero.
This can be accomplished by reducing energy consumption or carbon offsetting with renewable energy. Net zero carbon dioxide emissions can also be achieved by sequestering carbon dioxide.
(The Paris climate agreement is an international agreement negotiated in 2015 and concluded in November 2016. It sets out a global plan to fight climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The objectives of the Paris Agreement are to keep this century’s global temperature increase well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and to put efforts to limit the temperature rise even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius. To achieve this, the Agreement asks all Parties to set national climate action plans, called Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), and to report on their progress every five years.)
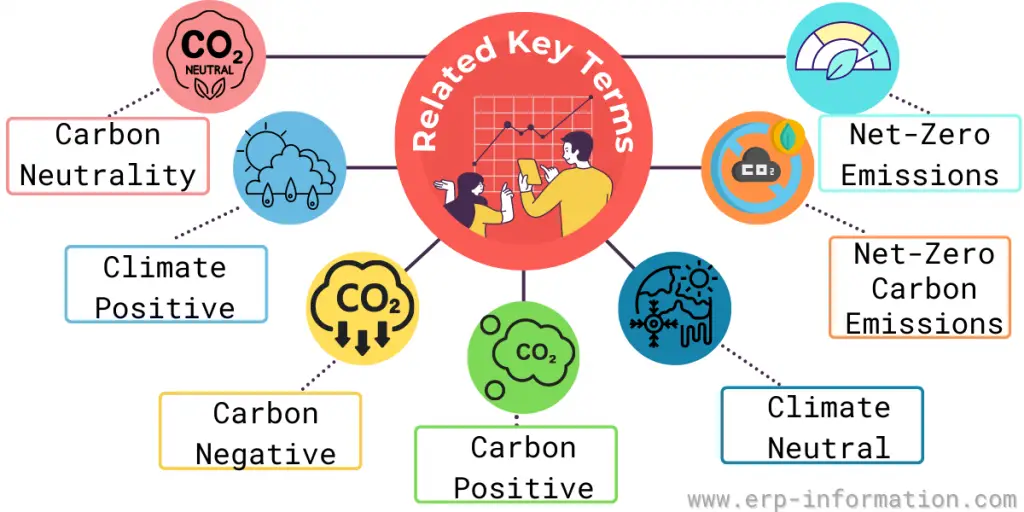
Related key terms
Carbon neutrality
Carbon neutrality is the state where an equivalent amount of removal balances any carbon dioxide released by a company through its activities.
Climate positive
Climate positive doesn’t only mean that action reduces net carbon emissions to zero. It also creates a separate environmental benefit by removing extra carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Carbon negative
Carbon negative and climate positive are similar terms. Carbon negative is a term that refers to reducing carbon dioxide emissions to a point where they are lower than what is being produced. This means that not only is the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere reduced, but the overall effect of climate change is positive.
Carbon positive
It is a term typically used by organizations to describe climate-positive and carbon-negative practices.
Climate-neutral
An organization must reduce all GHG emissions to zero and work to eliminate any other negative environmental impacts it may cause.
Net-Zero carbon emissions
When an activity has net-zero carbon emissions, it means that the same amount of carbon is being removed from the atmosphere as is being put in.
Net-Zero emissions
Net-zero emissions refer to a state where the total amount of greenhouse gas emitted into the atmosphere equals the amount removed.
Carbon neutral vs net zero
In this table, we are listing some of the important differences between carbon neutral and net zero.
| Carbon neutral | Net Zero |
| A carbon neutral means that the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from human activities is balanced by the amount of carbon they have sequestered or eliminated elsewhere. | A net zero strives not to emit greenhouse gases from on-site or off-site sources. It balances overall greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions produced and GHG removals by carbon sinks. |
| It is the goal to eliminate net carbon dioxide emissions. | This pathway to get there involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions and offsetting them with carbon removals. |
| It can be achieved in several ways | Here always requires some form of GHG mitigation. |
| Carbon-neutral strategies often include planting trees or investing in renewable energy projects. | Net zero strategies go beyond just reducing emissions – they also involve capturing and sequestering emissions from industries, transportation, and other sources. |
| It covers scopes 1 and 2, emissions | It covers scopes 1,2, and 3 emissions. |
| It is applicable to the organization, product, or service level. | It is applicable at national, international, and organizational levels. |
| It aims to balance emissions with offsetting measures. | It is more aggressive in reducing emissions. |
| It can be interpreted in several ways. | It is a specific goal. |
So, In summary, achieving carbon neutrality and net zero emissions are similar. The only difference is the scale and type of emissions removed.
FAQs
How does carbon neutrality help the environment?
Carbon neutrality is a way to stop global warming and help with energy. It can make the air cleaner, help nature get better, and make places more beautiful. It could be like an industrial revolution that helps people in many ways.
What are the benefits of net zero emission?
Net zero can help reduce bad weather like drought and flooding. Drought can make it hard to get water, grow food, and cause more wildfires. It also makes it harder for the land to store carbon.
Conclusion
There is a lot of uncertainty between the terms “carbon neutral” and “net zero.” In short, carbon neutrality means eliminating as many greenhouse gas emissions as possible, while net zero means producing no more carbon emissions than you offset.
Understanding these two concepts’ differences is important because they denote different approaches to mitigating climate change. This post briefly overviewed each term and the difference between carbon neutrality and net zero emissions.