In the ever-evolving landscape of product customization, ‘Configure to Order’ has emerged as a pivotal strategy, allowing businesses to cater to unique customer demands efficiently.
Configure-to-order is a business process that allows customers to configure the features and options of products or services to their specific needs.
That can be done through an online interface, talking to a customer representative, or both.
Configuring products and services gives customers more control over their purchases and results in higher satisfaction.
This blog post will discuss its definition, process, benefits, disadvantages, and examples.
What is Configure-to-Order?
Configure-to-order is a business model that allows customers to configure their product and deliver it directly to them. This business model differs from traditional manufacturing, which produces products in bulk and then sells them to retailers or distributors.
With this, businesses make products only after being ordered by a customer, which helps reduce inventory costs.
Steps involved in the Configure-to-Order process
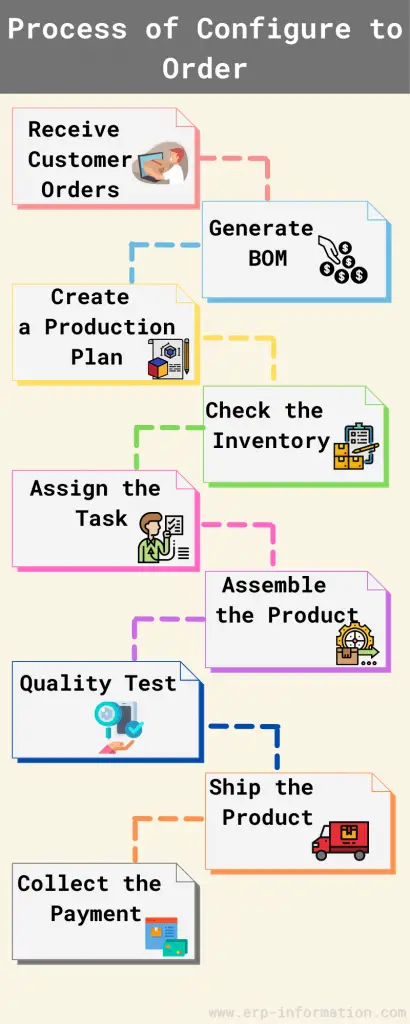
The following are the steps involved :
- First, receive customer orders through various methods such as online, by phone, or in person.
- Once the order is placed, the software will generate a bill of material (BOM) for the product. This document lists all the components needed to build the product and their quantities.
- The next step is production planning. The production plan determines how many products can be made per hour/day and what resources are necessary to produce them.
- Inventory must be checked to ensure enough components are on hand to meet customer demand. If not, the company must contact new suppliers or order additional inventory.
- In the next step, the assembly line is set up. That includes organizing the workstations and determining who will do what tasks.
- Assembly workers must be trained on how to assemble the product and where each component goes.
- Quality control testing must also be done to ensure that products meet customer specifications.
- Ship the product to the customer.
- Collect payment from the customer.
Additional Tips for Implementation
- Replace an existing product line with configure-to-order versions of those products
- Start producing new products through CTO
- Offer configurable options on current products
- All these methods have advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to weigh them carefully.
Configure To Order and Inventory Management
CTP is a hybrid process that includes both make-to-stock and made-to-order. In this process, a set of components is manufactured for stock, and finished goods are assembled on customer demand.
Inventory management at the component level ensures that only the necessary inventory is maintained.
Moreover, postponing the final product assembly until an order is received offers a degree of product customization flexibility and optimizes the utilization of existing component stock.
This approach aids companies in minimizing the expenses associated with carrying inventory, enhancing inventory control, and reducing time-to-market.
Hence, it is an excellent business approach that offers bulk customization and rapid order fulfillment.
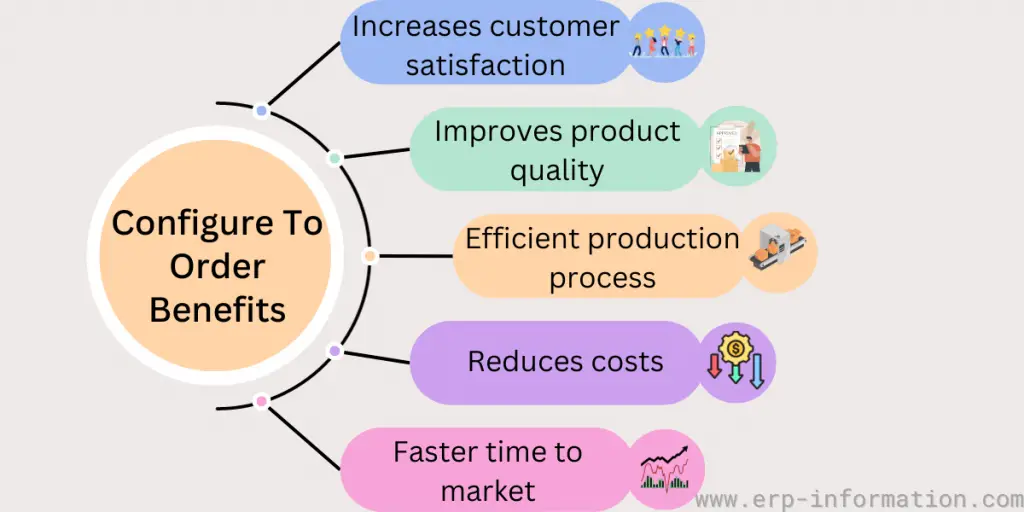
Benefits
Increased customer satisfaction
Configuring products and services to meet specific needs gives customers more control over their purchases, leading to higher satisfaction.
Improved product quality
Businesses can produce products only after they are ordered, which helps ensure that products meet customers’ specific requirements.
More efficient production processes
Configuring products to order can help streamline production by reducing waste and eliminating unnecessary steps.
Reduced manufacturing and inventory costs
Producing goods only when ordered reduces the inventory that must be kept on hand, leading to manufacturing and storage cost savings.
Faster time to market
Configuring products to order helps businesses get new products to market faster since there is no need to wait for a product to be manufactured in large quantities.
Disadvantages
- Extra charges for addressing customer complaints and refunds
- A significant amount of time is needed to create products
- There is a high risk of inventory shortages
- It can be difficult to predict customer demand
- Products may not meet all of the customer’s specifications
Configure to Order vs Engineer to Order
Engineer To Order
ETO
- With Engineer to Order (ETO), an order is placed for a product before the manufacturing process has even begun.
- In this approach, production begins only after receiving customer drawings or specifications outlining the required product features.
Configure To Order
CTO
- This type of manufacturing makes products after receipt of customer orders.
- In this approach, base products exist before an order is received, but they’re configured according to the customer’s specific needs and requirements.
- That allows for greater customization and flexibility, which can be important for businesses that need to meet the unique needs of their customers.
- In addition, CTO is more common than ETO because it places less risk on the manufacturer.
FAQs
What is the difference between build-to-stock (BTS) and CTO?
Produce products only after being ordered by a customer, which helps reduce inventory costs. In contrast, BTS companies make products in bulk and then sell them to retailers or distributors.
It helps them keep their costs down by reducing the need for storage space and allows them to take advantage of economies of scale.
However, it also means that they may not be able to respond as quickly to changes in demand. Therefore, CTO businesses are better suited to industries where product demand is relatively stable, while BTS businesses are more appropriate for highly cyclical sectors.
What are the examples of configure to order?
The following are examples of configure to order products.
1. Customized Laptops
Major brands like Dell and HP have mastered the art of Configure to Order. When a customer visits their websites to purchase a laptop, they are presented with a variety of options.
These options typically include:
Processor: Customers can choose from different CPUs, such as Intel Core i5 or i7, tailored to their performance needs.
Memory (RAM): Options range from 8GB to 32GB or more, accommodating users who need laptops for basic tasks and those who require high-performance capabilities.
Storage: Choices include traditional hard drives, solid-state drives, or a combination of speed and storage capacity.
Graphics Card: Customers can select integrated graphics or dedicated GPUs for gaming or graphics-intensive work.
Display: Options for screen size, resolution, and touch capability cater to different preferences.
Customers assemble a laptop that aligns with their specific requirements, whether it’s for gaming, graphic design, or everyday productivity.
2. Fast-Food Restaurants
Even in the fast-food industry, Configure to Order plays a significant role. Many fast-food chains, like Subway, allow customers to build their meals by choosing various components.
Customers can customize their sandwiches by selecting the type of bread, protein, vegetables, sauces, and additional toppings.
3. Custom-Made Furniture
Businesses like IKEA offer Configure to Order options. Customers can personalize their furniture by choosing:
Size: Adjustable dimensions to fit specific room layouts.
Materials: Selections range from different types of wood, fabric, or metal.
Design and Features: Choices for shelf placement, drawer configurations, or additional add-ons.
Finishes: Varied finishes or colors to match individual aesthetics.
These examples illustrate how Configure to Order benefits both businesses and customers by offering tailored solutions within predetermined parameters.
This CTO strategy not only provides customers with tailored solutions but also streamlines the manufacturing process for the company, reducing excess inventory and waste.
What is the difference between Make to order and configure to order?
Make-to-order (MTO) means that a product is created based on a customer’s specific demands, involving extensive customization.
On the other hand, configure-to-order (CTO) focuses on assembling orders from pre-existing components, eliminating the need for re-engineering. These pre-made components allow for the creation of a customized product within the primary process, leading to greater convenience and predictability.
Conclusion
Configure-to-order is a business model that allows customers to configure the features and options of products or services to their needs.
That differs from traditional mass production, where products are made in large quantities according to a set design and then customized after purchase.
Businesses can offer consumers more variety and choices while maintaining efficient production processes. In addition, configuring products to order can increase sales by choosing the exact product they want.
Configurable products might be the answer if you want a more customizable shopping experience.