Each organization has certain demands for goods and services. Managing this demand is necessary for an organization to become successful and meet its goals.
Demand management is a way to ensure that the demand for something stays the same as the available amount. Companies can optimize resources and improve operational efficiency by understanding and managing demand.
This post will explore demand management and its different components, objectives, advantages, best practices, processes, challenges, and tools. It will also discuss the difference between demand management, demand planning, and capacity planning.
What is Demand Management?
Demand management is a process businesses use to predict, understand, and meet customer needs effectively. It involves gathering data about what customers want, analyzing that data to identify real demand, and then planning how to create and deliver products or services to satisfy that demand.
It is also popularly known as consumption management. It is the connection between suppliers and customers. The key factors determining demand management are Pricing, Purchasing, and Supplier.
What is demand management in logistics?
Demand management in logistics is the process of planning, analyzing, and controlling the movement of goods between vendor and consumer.
It helps to analyze customer demand and adjust supply chain operations to meet that demand. It involves identifying customer needs, forecasting shipment needs, and managing inventory to ensure the right products are available for customers when they want them.
What is the role of demand management in the organization?
Demand management is an important planning methodology organizations use to forecast and plan how to meet the demand for services and products. It is a part of supply chain management.
The role of demand management is to understand, anticipate, and influence customer demand for services.
This includes activities such as
- Making effective forecast models based on demand patterns and trends in the industry
- Supervising a team of demand planners in all the demand planning activities of an organization
- Overseeing daily activities of the team and guiding as needed
- Supporting management with risk analysis and forecasting decisions
- Ensuring that all process activities are being performed
The Demand Manager manages the process and ensures all activities are completed on time. They also work with customers to meet their needs and collaborate with vendors to ensure they have what they need.
By using this methodology, organizations can better manage their resources and ensure they cost-effectively meet customer demands.
Check our blog post on ITIL Demand Management and Demand Management in SAP
What is the purpose of demand management?
Demand management initiative aims to forecast, realize, and determine customer demand.
This enables companies to satisfy customer needs better, helps them identify trends, and spends wisely. This is done through various statistical techniques such as trend analysis and time series forecasting.
Companies can also use demand management in developing a well-balanced project portfolio management by the following:
(1) Balancing the company’s product mix (to meet key demand drivers)
(2) Managing inventory levels at stores or warehouses (ensuring that they are not undersupplied nor overstocked), and
(3) Target promotions to maximize customers’ response rates without saturating their market share.
Calculate demand forecasting using our online calculators.
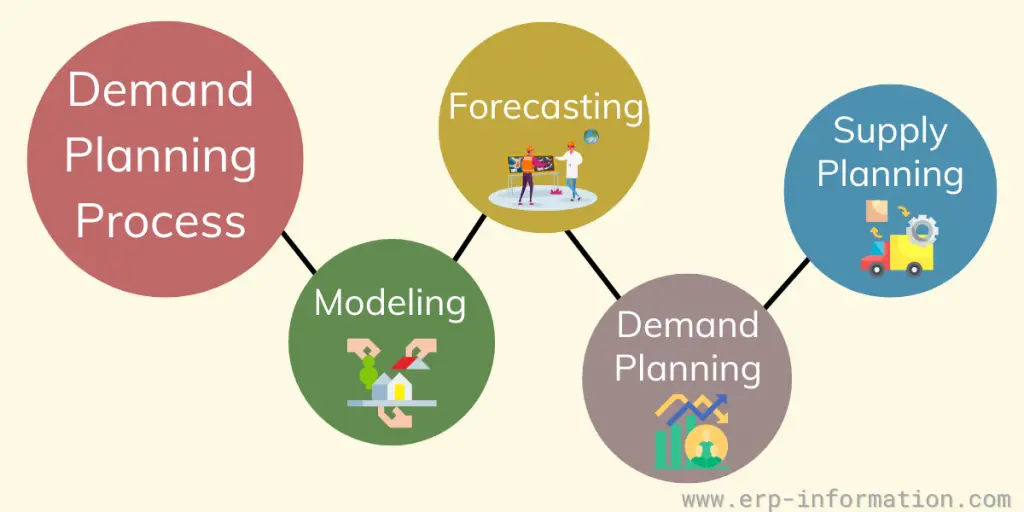
Components of Demand Management and Process
The process of managing demand is a crucial aspect of supply chain management that ensures a balance between demand and supply. Modeling, forecasting, and demand planning are linked to supply planning.
According to Feldman, there are four main steps in this process.
Modeling
It is the process of representing reality in a simplified way that allows us to understand and predict behavior. In other words, it is a means of understanding the past to anticipate the future better.
Demand forecasting
It is the process of predicting future events based on past data. This data can come from many sources, including historical sales.
Demand planning
Making a demand plan requires the right tools, information, and operation. Depending on its strategic objectives, product positioning, and inventory needs, it may be different for each organization.
Supply planning
It determines the correct quantity of materials, parts, and products to produce or procure to meet customer demand. It ensures an organization has the proper inventory to meet customer demand while maximizing profits.
Objectives
- Enhanced customer services: Demand management helps understand and manage customer needs, satisfy the customer, and improve services.
- Accurate forecasting: Future prediction helps business owners to make decisions accurately.
- Improvement of existing products and excels at new products: Helps business owners to line up the products and group them using customer feedback.
- Decreased costs: Accurate forecasting helps to keep optimal inventory and minimizes unwanted stock.
Best Practices
Have the right ERP software
While implementing Enterprise Resource Planning software in your organization, ensure that it can handle forecasting reporting and confirm that it provides transparency and realistic forecast data.
Collect and prepare data
It gives real-time visibility to look at inventory movements to identify the areas to be improved.
Define the process
A well-defined process with accurate data and information helps improve overall performance. To define the process, follow the below steps.
- Construction of data
- Initial forecasting
- Integration of market intelligence
- Review of sales objectives and financial reports
- Rectify the final forecast
- Monitor the performance
Monitor the demand planner
Based on the historical data and expressive analytics, design a demand planner and have a dedicated team to design the plan, execute it, and monitor it.
Advantages and Functionalities
Advantages
- Helps to build a foundation for merchandising, budgeting, and logistics processes.
- Monitor supplier transactions and check for growth or decline, respectively.
- Monitor all related expenditures.
- Build a strong relationship with customers and suppliers. Also, ensure that relationships last with reasonable pricing and other offers.
- Allows you to boost supply chain operations.
- It helps to create more revenue.
Functionalities
- Point out the critical delivery dates.
- Make out the future needs.
- Point out the frequency of demand.
- Link the requirement to the budget.
- Based on past spending and future demands, analyze the expenditure.
- It integrates with strategy, procurement, requirement, and market analysis.
- In the case of strategic purchases, manages industry analysis and commodity analysis.
Challenges
While implementing demand management, organizations face some fundamental challenges. They are
- Lack of knowledge about automated algorithms.
- Maintaining balance for sales and retailers to generate demand design to find the timing, level, and location.
- Lack of organized data structure for receiving, storing, and retrieving the point of sale information from retailers.
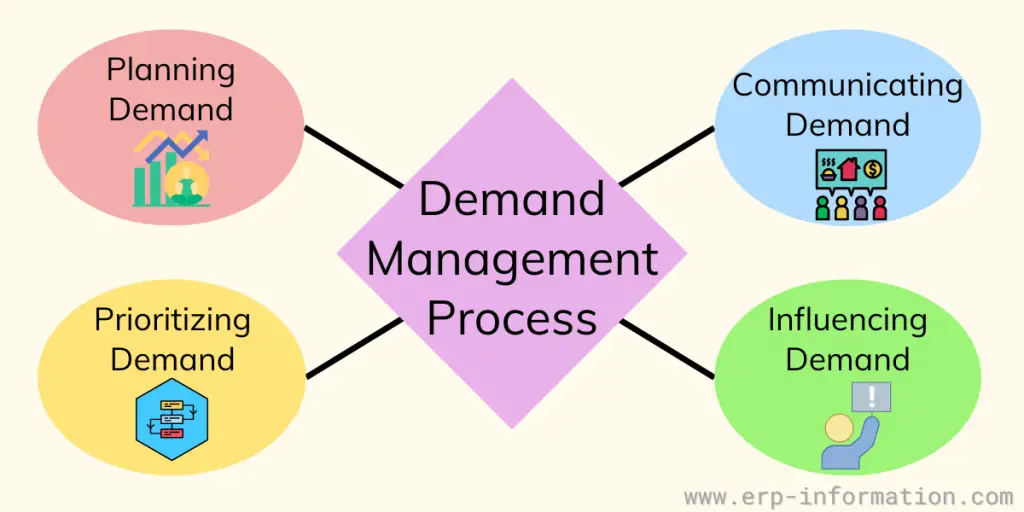
Demand Management Process
1. Planning demand
This process analyzes customer requirements in advance and forecasts IT resources. Built primarily for IT administrators, this component analyzes, evaluates, and projects customers’ future requirements within an IT environment.
It uses statistical analysis, best practices, and current demand cycles to evaluate future customer needs. It also serves as an input to capacity planning to provision required IT resources based on current and expected future demand.
2. Communicating demand
Communicating demand is an essential component of demand management. Therefore, management will implement qualitative methods to forecast the market and share with the stakeholders.
Once the firm understands the demand, it is vital to make it known to several aspects of the business to ensure they leverage the production accordingly.
3. Influence demand
As part of supply chain management (SCM), Businesses should focus on retaining customers, service levels, and supplier relationships.
Companies should build additional policies to face sudden changes in demand and supply.
4. Prioritizing demand
Identifying and prioritizing projects forms an essential part of the demand management process.
Organizational capacity, risk assessment, financial value, and implications must be carefully assessed while forming policies.
Demand Management Example
Imagine a company that produces office supplies, such as pens, notebooks, and binders. They’ve observed an increasing number of conversations online and in the media about environmental sustainability and reducing plastic waste. Employees and businesses alike are showing interest in greener practices and products, yet this buzz alone doesn’t confirm an actual market demand for eco-friendly office supplies.
To determine whether there’s genuine demand for sustainable office products, the company can employ demand management techniques. Here’s how they might go about it:
Data collection
The company conducts surveys and interviews with existing customers, business partners, and office supply retailers. They also analyze sales data for any existing eco-friendly products they offer and monitor social media and environmental forums for insights.
Demand analysis
Through this research, the company discovers that there is significant interest in products made from recycled materials, as well as a willingness to pay a premium for sustainable options.
They also note specific product features customers desire, such as biodegradable pens and notebooks made from recycled paper.
Prototyping and Testing
With this information, the company develops prototypes of eco-friendly office supplies. They use recycled plastics for pens, biodegradable materials for binders, and 100% recycled paper for notebooks. These prototypes are then tested with focus groups comprising environmentally conscious consumers and office managers.
Operational strategy
Confirming the demand, the company devises an operational strategy. This includes sourcing sustainable materials, optimizing the supply chain to reduce the carbon footprint, and training their design team to create products that meet eco-friendly standards.
Production and Launch
The company begins full-scale production of the new eco-friendly office supplies. They launch a marketing campaign emphasizing the environmental benefits and the quality of their sustainable products. They also collaborate with large corporations and office supply stores to promote bulk purchases.
Factors that Affect Demand
Many factors will influence demand. Here we are listing a few factors.
External factors
- Market situations: It is a significant factor that directly affects the demand—for example, recessions and strikes.
- Competitor’s step: If your competitor starts giving the same product or services with good quality at less price, then there will be a chance of a sudden reduction of demand for your product or service.
- Seasonality: Some products’ demand increases or decreases depending on seasons. For example, ice cream, woolen cloths, umbrellas, school bags, etc.
- Trends: Market trend is one of the major factors that increases or decreases demand.
Internal factors
- Pricing approach
- Maintenance
- Customer relationship
- Promotion and advertisement for products/services
- Product alteration
Demand Management Tools
The following are the popular software tools for demand management systems.
- SAP Advanced Planning
- Infor Demand Planning
- Logility Demand
- Kinaxis RapidResponse
- NetStock
Demand Management vs Demand Planning
| Demand Management | Demand Planning |
| It is the process of understanding, anticipating, and managing customer demand. | It is designing and building a plan to meet desired customer demand at a minimal cost. |
| It includes forecasting future demand, setting targets for meeting that demand, and ensuring that the necessary supplies are available when customers want them. | It usually includes determining what products to make, how much of each product to make, when to make them, and where to make them. |
| Considers customer demand in the short term | Considers customer demand in the long term |
Demand Management vs Capacity Planning
| Demand Management | Capacity Planning |
| It mainly focuses on anticipating future customer demand and preparing an organization to meet it. | It looks at internal resources to determine how much demand the organization can take on. |
| It requires a data-driven approach to predicting customer needs | It involves analyzing company operations and assessing capabilities. |
| It influences customer behavior. | It focuses on understanding what resources are available internally, such as technology, labor, equipment, warehouse space, etc., and how businesses can use them more effectively. |
| It involves evolving effective forecast models based on demand patterns and industry trends. | It examines capacity utilization and evaluates potential tradeoffs between utilization rates while maintaining service quality. |
| It utilizes mathematical techniques such as time series analysis and other predictive models to make forecasts. | It mainly uses scenario-based or simulation modeling techniques to find practical solutions for decisions regarding resource allocations. |
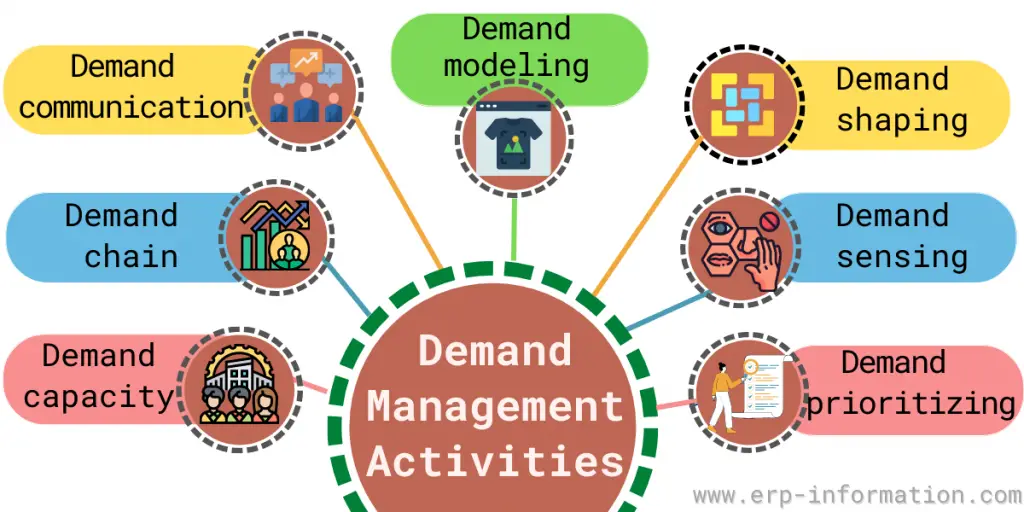
Demand Management Activities
The organization needs demand management activities to develop and implement effective supply chain management plans. The activities are as follows.
1. Demand capacity
Demand management helps organizations organize capacity demands. Capacity demands refer to the number of resources needed in terms of capacity and capability to meet customer demand.
That can include physical space, machines, labor, and knowledge. Capacity demands can vary from one customer to another depending on their specific needs or the number of products they are ordering.
Organizations must monitor their capacity demands to meet customer needs while utilizing existing resources. Capacity demands should be evaluated regularly so adjustments can be made if necessary.
2. Demand chain
The demand chain is the shift from a traditional supply-based model to one that focuses on customer demands. This model involves analyzing customer needs and using those insights to create satisfying products or services.
By doing this, businesses can keep up with customers’ evolving needs while still being efficient in their operations and responding quickly to any changes in demand.
3. Demand communication
Demand communication is a collaborative approach used to manage and forecast market demand. It involves collecting, analyzing, and sharing data between stakeholders in the supply chain.
It allows you to communicate your forecast demand to suppliers so they can adjust their production levels accordingly and ensure that the right amount of inventory is available on time.
Demand communication also helps identify potential risks in the supply chain and quickly address them before they cause delays or other problems.
4. Demand modeling
Demand modeling divides demand components into internal and external factors and explains how these factors affect future demand.
5. Demand shaping
Demand shaping is one of the crucial supply chain management strategies. Here, the organization offers some price drops, discounts for specific items, and some incentives that help to match the demand for a particular product/service.
6. Demand sensing
It is a mathematical technique that helps businesses to sense real-time demand for products/services. It also predicts who the customer is, what is selling, and how the product impact demand.
7. Demand prioritizing
Demand prioritizing identifies and organizes projects based on their potential impact and urgency.
It’s an important part of demand management, which involves understanding customer needs, analyzing market trends, mitigating risks, managing resources, and evaluating requests to maximize output while minimizing cost.
Advanced Technologies in Demand Management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are helpful in demand management. These are the top future technologies that can be used in SCM. Each of these is discussed further below.
Machine learning in demand forecasting
Some businesses rely on their sales staff to anticipate consumer demands. Unfortunately, this frequently results in over-or understocking, which can cause shortages or surpluses.
Machine learning may help you make more accurate forecasts and reduce the uncertainties in demand prediction.
The company can use machine learning in demand forecasting by incorporating data from different sources such as social media, news feeds, and on-site activities on shopping portals.
In addition, machine learning has been found effective for demand forecasting in cases where forecasting is prone to human bias.
For example, a case study on high-street fashion retailers demonstrated reduced forecast errors by 10% using machine learning compared with traditional methods.
Companies may also use social media insights to derive demand forecasts. For example, social media mining techniques are used for unstructured text data analysis and can enhance time series analysis leading to accurate demand forecasting.
It can derive insights from customer conversations, analyze product satisfaction levels, and forecast future demands. Sentiment analysis may be conducted using natural language processing techniques such as speech tagging, parsing, and sentiment lexicons.
Artificial intelligence
AI systems rely on learning algorithms to predict demand patterns in different situations. For example, the AI can predict demand patterns based on past data, recommend optimum inventory levels maintained at warehouses, and determine when to replenish stocks.
In a study, a company used artificial intelligence with machine learning techniques to forecast sales of fashion apparel items to choose the right quantities to order from the supplier. This study indicated that machine learning techniques with artificial intelligence could aggregate demand forecasts at multiple levels and reduce forecast errors.
FAQs
What are the components of demand management?
Demand management comprises three main components: forecasting, pricing, and promotion. Forecasting helps businesses anticipate consumer demand, while pricing and promotion help encourage consumers to purchase goods and services. By understanding and utilizing all three components of demand management, companies can help ensure their success and stability.
What is an example of a demand management strategy?
One example is adjusting prices to raise them if you have too much inventory or lower them to move things out faster.
Another option is to change your marketing mix to emphasize selling products well and downplay those that aren’t.
You can also adjust your production schedule to meet changing demand levels.
Ultimately, the goal is to match supply with demand as closely as possible to minimize wasted resources and maximize profits.
Who uses demand management?
Typically organizations use it to make decisions about price, promotions, product mix, and inventory.
And also, every department, such as production, quality control, logistics, R&D, marketing, and sales in the organization, utilizes demand management.
The information flow from all these departments affects customer service, order fulfillment, customer relationship, and product development.
Conclusion
Demand management is a process that ensures the supply and demand of your products stay in balance.
Any company needs to have some strategy for it. Still, it can be beneficial if you’re dealing with customers who need specific types or quantities of goods on an ongoing basis.
An excellent way to start is by looking at each sale funnel step and using tools like forecasting software to simulate forecast scenarios. Hence, you know what could happen when new product launches, promotional campaigns go live, or inventory levels change over time.
We hope this post has been informative enough about how robust demand management strategies work and where they fit into the broader scope of business operations.
References