In a dynamic supply chain environment, getting your products to customers quickly and affordably is crucial. That’s where Distribution Requirements Planning (DRP) comes in. But understanding DRP isn’t easy. It takes a strategic approach tailored to your business.
DRP focuses on the distribution side of the supply chain. This includes everything from the distribution center and production schedules to supply chain and customer demand.
Several factors go into a successful distribution requirements plan, and it can be challenging to get it all just right.
This blog post will discuss the definition, methods, process, and some of the most critical aspects of DRP and how to optimize your distribution network for maximum efficiency.
What is Distribution Requirements Planning?
Distribution Requirements Planning (DRP) is an organized process and part of supply chain management to optimize the distribution of goods.
DRP ensures that the right amount of manufactured goods is shipped to each distribution center based on customer orders. This information is then translated into purchase orders.
The main objective is to avoid goods shortages and reduce the ordering, transporting, and holding costs.
The key elements of DRP in supply chain are
- Current inventory levels
- Target safety stock
- Forecast demands
- Recommended replenishment quantities
- Replenishment lead times
- Customer orders
Terminologies Related to DRP
A few related terms you need to know before proceeding are,
Production schedules
It is a business term used in operations management that refers to manufacturing or assembling products in a factory according to a specific timetable.
Supply chain
It is the network of organizations involved in creating and efficiently delivering a product or service.
Customer demand
It is how much of a product or service customers are requesting.
Distribution center
It is a facility that receives, stores, and distributes products to retailers or other businesses.
DRP Methods
DRP works in 2 methods. Push and pull method. Let us look into each method.
Pull method
Imagine you’re at a restaurant and you order a burger. The restaurant doesn’t start cooking until you place your order. Similarly, in the pull method of DRP, goods move through the distribution network when there’s a demand for them.
This ensures greater availability for consumers because local management controls the availability of goods. However, managing distribution inventory can be challenging because each order is new to the supplying location as demand flows up the network.
This phenomenon is known as the “bullwhip effect,” where small changes in consumer demand lead to significant swings in demand higher up the network.
Push method
Imagine a bakery that bakes a batch of bread every morning regardless of how many customers come in. They bake based on a forecast of how much bread they think they’ll sell.
In the same way, the push method involves sending goods down through the network. This approach typically incurs lower costs because shipments are planned globally and stored centrally. However, service levels may suffer if central planning is too distant from the actual demand.
The Distribution Requirement Planning Process
We can summarize the process into the following steps:
Forecasting the demand
The very first step is analyzing past sales, market trends, and customer behavior to forecast demand. By doing these, businesses can make educated guesses about future demand.
These forecasts help to stock the right amount of products in the distribution network, ensuring customers get what they want when they want it.
Inventory analysis
Businesses need to know what they already have, what they’re running low on, and what’s flying off the shelves. By crunching numbers on current inventory levels, safety stock requirements, and pending orders, companies can spot trends and plan for replenishment effectively.
Replenishment planning
Businesses use demand forecasts and inventory analysis as their playbook and strategically plan when and how much to reorder to keep their inventory levels in check.
In this way, they need to have a balance between enough stock and demand without excess inventory.
Optimization of distribution network
Distribution network optimization is about ensuring that products move swiftly and efficiently from the central warehouse to regional hubs and, finally, to customers.
By optimizing the flow of goods, companies can minimize transportation costs, reduce delivery times, and keep customers happy.
Collaboration and Execution
It’s all about teamwork—sales, production, and logistics should work together towards a common goal.
The department should share real-time data, use automated systems, and have clear communication to hold everything together, which ensures the DRP plan is executed flawlessly and adjustments are made when needed.
Key Considerations While Implementing DRP
Implementing Distribution Requirements Planning requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure success:
Reliable data and accurate forecasting
DRP heavily relies on data accuracy and forecasting precision. Gathering reliable data on inventory levels, customer demand, and market trends is crucial. Investing in forecasting tools helps to do accurate forecasting and determine the right amount of products to distribute.
Use our Single Exponential Smoothing Forecast Calculator to do an accurate forecast.
ERP system integration
DRP integration with an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is essential for seamless information flow. An ERP system consolidates data from various departments like sales, inventory, and production, providing a unified view of the supply chain. This integration ensures real-time data sharing and facilitates informed decision-making.
Continuous evaluation and monitoring
Implementing DRP is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Continuous evaluation and monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover, fill rates, and order accuracy are necessary.
Regularly assessing the effectiveness of the DRP strategy allows for adjustments and improvements to optimize distribution processes.
Good relationship with suppliers
Building and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is vital for DRP success. Collaborating closely with suppliers ensures timely delivery of raw materials and components, reducing lead times and enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Scalability and flexibility
DRP must be flexible enough to adjust to evolving business requirements and market conditions. The distribution network should be capable of accommodating growth or fluctuations in demand without significant disruptions.
Flexibility in adjusting inventory levels, production schedules, and distribution routes enables agile responses to market changes and customer requirements.
Distribution Resource Planning and Distribution Networks
DRP is crucial for making sure that companies can meet customer orders. Distribution resource planning includes ensuring enough resources for the distribution network, including distribution centers, transportation networks, and labor. It’s also essential to maximize product availability at a lower cost.
A distribution network collects disbursement centers and other cooperations to serve buyers. Therefore, companies must carefully plan the disbursement network to ensure that they can deliver finished goods on time.
How Does a Distribution Center Work?
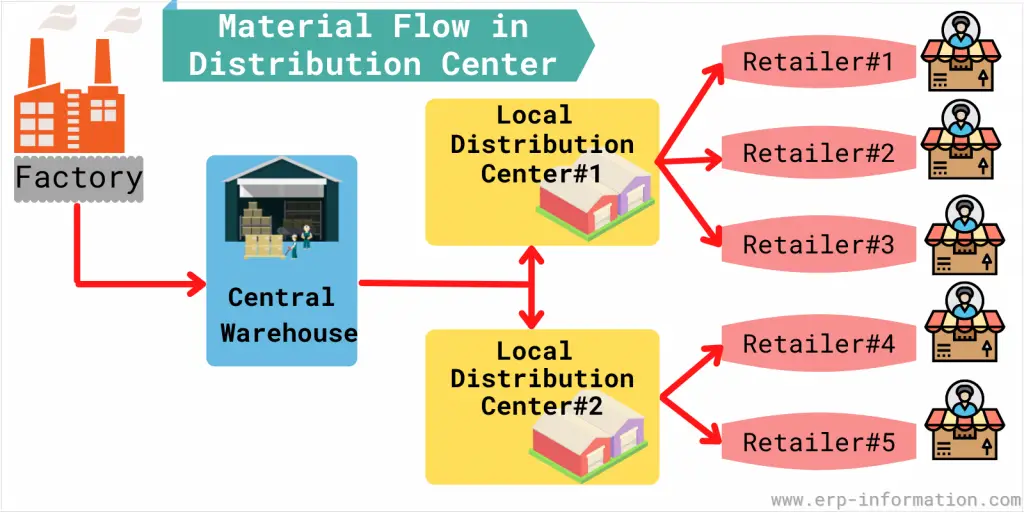
A distribution center is a facility that receives, stores, and distributes finished goods to retailers and other businesses. It is the backbone of the logistics network, and it is essential to have one or more delivery centers to serve consumers effectively.
Many factors go into choosing the optimal locations for centers. Some of the most important factors include:
- The distribution network map includes the distribution centers, suppliers, and buyers. Therefore, it should be easy to identify where each entity is located and connected.
- The customer base is essential to consider where most of your customers are located. This will help you determine how many locations for holding goods you need and how far apart they should be.
- The distribution network topology – This is how the locations are connected. There are three main topologies: radial, star, and mesh. It can also be a tree-like structure.
- The distribution requirements include the number of products, the weight and dimensions of products, and the delivery time.
- The transportation network includes the modes of transportation (road, rail, water, and air), the distance between warehouses, and the delivery time.
- Labor availability – It is vital to ensure enough workers are available at the allocation center when it opens.
- Cost – The warehouse should be located where the price is the lowest.
Supply Chain Planning and Strategies for DRP Success
Key supply chain planning and optimization strategies can help ensure DRP success.
One is to have accurate and timely data regarding market requirements. This information is used to create the distribution plan, so it must be as precise as possible.
An effective distribution center (DC) network is also essential for getting products to customers quickly and efficiently.
Finally, having a well-run inventory management system is critical for ensuring that products are available when customers need them while minimizing shortages.
Six must-consider ideas while making supply chain optimization strategies are,
- Adjusting the warehouse locations
- Planning production schedule
- Allocating resources to meet disbursement demands
- Minimizing shortages and maximizing customer satisfaction
- Set safety stock levels
- Considering disbursement requirements in inventory control
The supply chain strategies should try to achieve the following.
- Distribute products quickly and efficiently
- Minimize shortages
- Follow key tips for success
Distribution Requirements Planning Tools
A few software solutions that enable DRP are,
- Microsoft Dynamics AX
- Oracle EBS Distribution
- Infor Distribution Planning
- Plex Demand Caster
- Batch Master
- Manhattan SCALE
Each software tool has its strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to choose the one that will work best for your organization.
Some of the benefits of using this software include:
- Increased data accuracy and timeliness of data
- Improved network design
- More effective inventory control
- Easier compliance with government regulations
FAQs
What is demand forecasting in DRP?
Demand forecasting is the process of predicting future customer demand for a product. This information is used to create the allocation plan, so it must be accurate. This information will help us meet forecasted demand.
What are current inventory levels?
The current inventory levels are the number of products currently available for delivery. This information is used to create the allocation plan.
Conclusion
Distribution requirements planning is a complex process that can be difficult to get right. However, it is essential to optimize your distribution network for maximum efficiency.
DRP optimizes distribution networks by considering inventory levels, demand forecasting, and replenishment planning. It operates through pull and push methods, each with benefits and challenges.
This blog post has discussed some of the most important aspects of logistics requirements planning. By following these tips, you can optimize your business.