Imagine a scenario in which your aerospace company receives an order for a spacecraft component. This component needs to meet stringent performance standards and exact specifications, and it can’t be satisfied with off-the-shelf solutions.
This is where Engineer to Order (ETO) manufacturing steps in. In ETO, each product is meticulously engineered and tailored to meet the unique demands of the customer. It thrives in industries like aerospace, defense, and healthcare, where customization is non-negotiable.
It is a manufacturing process where the customer specifies what they want, and the manufacturing company designs and makes it.
This blog post will discuss the definition of Engineer-to-Order, its manufacturing process, advantages, disadvantages, best practices, and differences between ETO and MTO.
What is Engineer-to-Order?
Engineer-to-Order is a term used in manufacturing. It refers to a process in which a custom or unique product is designed and manufactured specifically. It is often used when customers have requirements that are hard to meet using regular products.
It can be a more expensive production process than traditional manufacturing, allowing customers to customize products for their specific needs.
It also allows manufacturers to produce smaller products, which can be important for niche markets or custom applications.
ETO Manufacturing Process
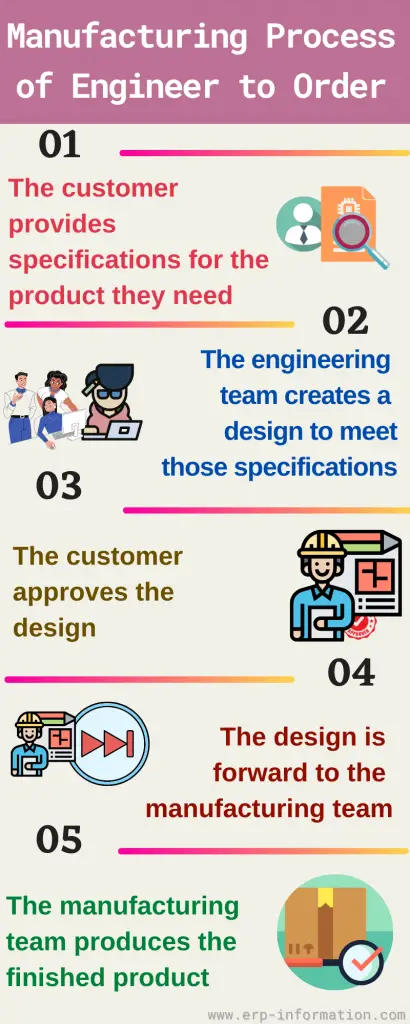
The following steps make the engineer-to-order manufacturing process easier:
Product specification
First, the customer provides specifications for the product they need. The customer will typically give a product requirements document (PRD) that outlines their specific needs.
That is often done through a Request for Quotation (RFQ) or Request for Proposal (RFP).
The engineer will then look at the Product Requirements Document (PRD) and decide if the product can be made using standard components or if specialized and dedicated components need to be designed and made.
Design creation by the engineering team
The engineering team creates a design to meet those specifications. The engineer will design a product that meets the customer’s requirements. That may involve creating custom components or modifying existing features to meet the customer’s needs.
The engineer will also create a Bill of Materials (BOM) for the product, listing all parts and quantities.
Design approval by the customer
The customer will review and approve the design or provide feedback for changes.
The engineer will move to step four if the customer approves the design. If not, the engineer will change the design based on the customer’s feedback.
Forwarding design to the manufacturing team
The engineer will send the design to the manufacturing team. The manufacturing team will create a product plan based on the engineer’s BOM. That may involve creating and procuring custom components or machinery. Hence inventory management is critical in this process.
The manufacturing team will also do an automated production scheduling for producing the product, considering how long it will take to make each component and assemble the product.
Once the manufacturing team has created a plan, they will send it back to the engineer for approval.
Production of the finished product
The manufacturing team will deliver the product according to the plan they created in step four. This may involve producing custom components or machinery, which can take time and be expensive.
The manufacturing team will assemble and test the product to meet its requirements.
Best Practices for Engineer to Order

Along with an accurate change management system, the following are the best practices for Engineer-to-Order manufacturing:
Develop good communication
In the ETO process, customer involvement is significantly more critical than in Make-to-Stock (MTS) or Make-to-Order (MTO) processes.
Therefore, maintaining clear and transparent communication with procurement, engineering, sales, and manufacturing teams, as well as with customers, is essential. This ensures alignment and meets the specific requirements of each custom project effectively.
Coordinate engineering and manufacturing capabilities
The ETO process entails new and customized product production, necessitating close coordination between engineering and manufacturing teams.
This collaboration is critical to ensure that the manufacturing team comprehends how the product integrates with existing manufacturing capabilities and to effectively manage the Bill of Materials (BOM) and associated costs.
Maintain accurate records
The Engineer-to-Order process is known for producing unique, custom-made products, which inherently come with extra responsibilities, including adhering to safety requirements and regulations.
Ensuring precise documentation from the start to the finish of the process is essential. Furthermore, effective inventory management plays a crucial role in maintaining robust and comprehensive documentation throughout the ETO process.
Use automated tools
In today’s manufacturing scenario, effectively managing costs and reducing waste, along with maintaining a robust workflow, are essential for enhancing the sales experience.
To achieve these objectives, manufacturing units should leverage advanced automated tools such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems. ERP systems, in particular, facilitate improved outcomes by managing various critical functions, including:
- Inventory Management
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Human Resources (HR)
- Accounting
- Supply Chain Management
Why is there a need for ERP in ETO?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is indispensable for Engineer to Order (ETO) manufacturing due to the complex, customized nature of ETO projects. ERP systems enable precise control over every facet of the project lifecycle.
They facilitate the management of intricate design specifications, procurement of unique materials, and the coordination of skilled labor, all critical in ETO scenarios.
Moreover, ERP offers real-time visibility into project progress, ensuring better project control, cost management, and on-time delivery to satisfy customer requirements.
It aids in accurate resource allocation, minimizing waste, and optimizing resource utilization. Without ERP, ETO manufacturers risk operational inefficiencies, errors in project planning, and inaccurate cost estimates.
The system aids engineers, production teams, and project managers in seamless collaboration and execution, ensuring the successful delivery of highly customized projects, customer satisfaction, and profitability in the ETO manufacturing sector.
Engineering to order process in SAP enterprise resource planning
The flow of orders for individual items if they are not in the store are as follows:
- Receiving the order
- Checking the availability of materials
- Creating the bill of materials
- Planning the production order
- Confirming the production order
- Producing the product
- Inspecting and shipping the product
Benefits
There are several advantages to using Engineer-to-Order instead of off-the-shelf products:
Customized products
In today’s global manufacturing environment, customized products are getting more and more traction. It allows manufacturers to create products specifically tailored to the customer’s needs. This can include features, dimensions, and even colors unavailable in off-the-shelf products.
Customers may need a unique size or shape for their product that is unavailable from the manufacturer.
Niche markets
Small quantities of products are often crucial in niche markets with insufficient demand to justify producing large items. It allows manufacturers to create smaller quantities of products, which can help them tap into these markets.
A company that makes custom cabinets may use ETO to produce a limited number of cabinets in different colors and styles.
Small quantities
It allows manufacturers to produce smaller products, which can be important for niche markets or custom applications. In addition, it helps reduce inventory costs and keeps specialized production line processes flexible.
A company that makes custom parts may use ETO to produce small quantities of components unavailable from the manufacturer.
Faster time to market
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, it does not require developing a new mold or tooling for each new product. This speeds up the time it takes to get a new product to market.
A company that makes custom medical equipment may quickly use ETO to produce new products for its customers.
Disadvantages of ETO Manufacturing
The following are the main disadvantages of Engineer to Order production:
Increased costs
First, producing customized products can be more expensive than having standard products. That takes longer and requires more resources to create a design that meets the customer’s needs.
A company that makes custom cabinets may have to spend more time and money on research and development to create a new design for each customer.
Need for both engineering and manufacturing capability
ETO requires established company capabilities for both engineering and manufacturing. This can be a challenge for companies that do not have in-house resources.
A company that makes custom medical equipment may need to partner with another company to produce the finished product.
Limited availability
Customized products are not always available due to limited production capabilities. This can lead to backorders and frustrated customers.
A company that makes custom cabinets may only have a certain number of cabinet styles and colors available at any time.
Limited selection
Products produced using Engineering-to-Order usually have a limited selection. This is because products are not based on standard inventory and need more time to plan and create.
A company that makes custom medical equipment may only offer a few different products.
Longer lead times
Engineer-to-Order products typically have longer lead times than off-the-shelf products. This is because it takes time to receive the order, check the availability of materials, create the bill of materials, plan the production order, and produce the product.
A company that makes custom cabinets may need up to two weeks of lead time to produce the cabinets.
A few more disadvantages
- The process can be more complex than the traditional production method.
- It requires specialized knowledge and skills.
- Product quality can be more challenging to ensure.
- Product testing and validation are essential.
- Customer involvement is essential.
- This task requires a lot of coordination between different groups. For example, you will need the engineers, the people who make the product, and the salespeople to work together to make this happen.
- It requires a high degree of standardization to be effective.
- It may not be suitable for all products or applications.
- Requires a high level of commitment and investment to be successful.
Engineer to Order examples
Engineering-to-Order Model stands out among manufacturing techniques due to its complexity and cost. Specifically, this process is employed when a company receives complex and costly special orders from governments or large corporations.
This process allows Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor production trends so defects can be caught early on.
This ensures that costs remain low and quality does not suffer. In particular, the ETO process is widely used in the following areas.
- Defence
- Commercial HVAC equipment
- Industrial cranes
- Electrical switchgear
- Power plant boilers
- Security industry
- Aerospace manufacturing
- Energy industry
- Helthcare
Engineer to order vs Make to order
ETO and MTO are the two most common production methods, which have some differences, as listed below.
ETO
- It involves creating highly customized products tailored to specific customer requirements. Each order often results in a unique product design.
- The process starts with detailed customer specifications. Engineers then design the product from scratch or make significant modifications to existing designs.
- It projects generally have longer lead times due to the extensive design and engineering work required before manufacturing can begin.
- Examples include specialized machinery, custom-built equipment, and large-scale infrastructure projects.
MTO
- It involves producing standard products but allows for some customization based on customer preferences. The base product design remains the same, with variations in features or components.
- The process begins once an order is received. The manufacturing team assembles the product using pre-designed components and modules, incorporating any customer-specific adjustments.
- MTO typically has shorter lead times than ETO because the basic design work is already completed, and only minor modifications are needed.
- Examples include customized furniture, personalized electronics, and tailored clothing.
What is Engineer to Order Manufacturing Software?
Engineer to order manufacturing software is designed specifically for businesses that produce custom or highly-engineered products, such as industrial equipment, machinery, and complex systems.
ETO manufacturing software helps businesses manage the entire process of designing and building these products, from initial concept through final delivery.
The software typically includes features such as project management tools, engineering design modules, bill of materials (BOM) management, and production scheduling capabilities.
It also offers real-time visibility into production processes and allows businesses to track and analyze costs associated with each project.
With ETO manufacturing software, businesses can streamline their operations by automating many manual processes involved in custom product design and production. That can help reduce errors, improve quality control, increase efficiency, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction.
Below is the list of software
- S2K Enterprise
- JOBSCOPE
- ABAS ERP
- ShopVue
- Decision Builder
- BatchMaster ERP
- IFS Cloud
- SCP 4.0
- Infor LN
- Expandable ERP
FAQs
What is Engineer to Order manufacturing, and how does it differ from other manufacturing processes?
It is a manufacturing approach where products are custom-designed and engineered to meet the unique requirements of each customer.
It differs from make-to-order (MTO) manufacturing, where products are standardized and then customized post-production.
Can I use Engineer-to-Order for all my products?
No, not all products are suitable for this. It would help if you had a clear idea of what you are selling before putting a price on it. It may not be appropriate for mass-produced products or have a relatively short life cycle.
Whether or not it is suitable for a particular product depends on several factors, including the customer’s needs and the product’s complexity.
Conclusion
Engineer-to-Order process is a vital approach in manufacturing that enables the creation of highly customized products tailored to specific customer needs.
While it can be more complex and costly than traditional manufacturing methods, the benefits of producing unique, high-quality products that meet exact specifications are significant.
Effective ETO processes require close collaboration between engineering and manufacturing teams, precise documentation, and the use of advanced tools like ERP systems to manage resources and workflows efficiently.
By embracing ETO, manufacturers can cater to niche markets, reduce waste, and deliver exceptional value to their customers, ultimately enhancing satisfaction and fostering long-term business success.