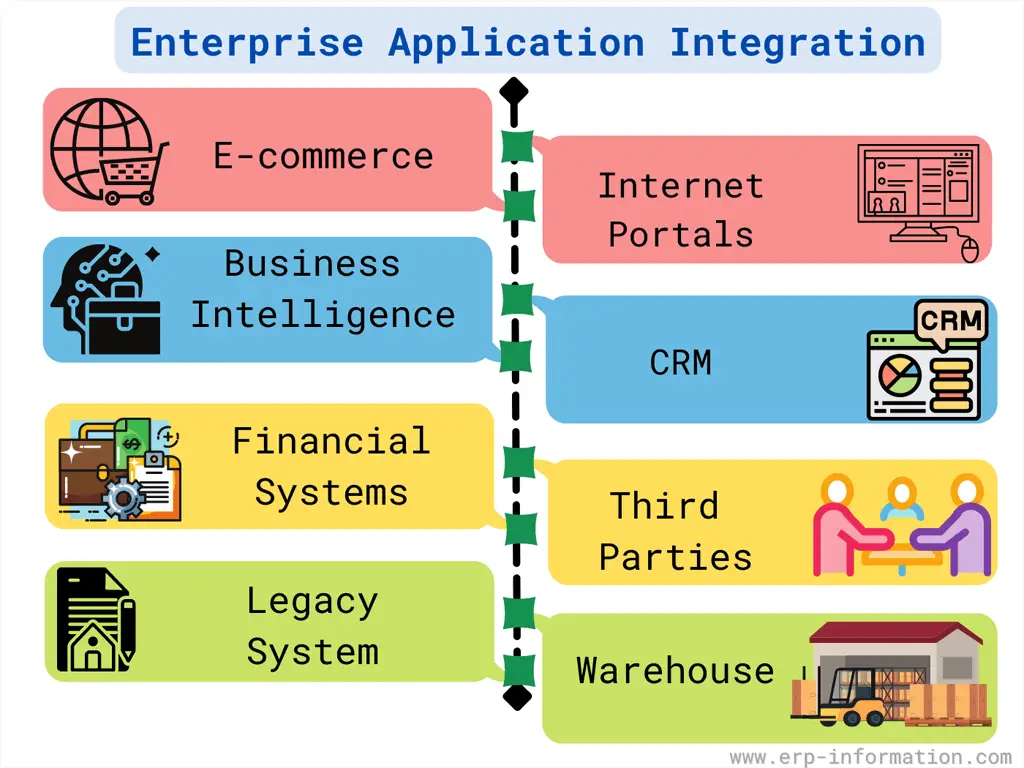
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) shares data and business processes between an organization’s different applications.
It’s more than just connecting two applications to share data – it’s about integrating business processes and systems to work together harmoniously.
This is most needed where inventory control, human resources, sales automation, and database management are designed to run separately, without interaction.
This blog post will explore enterprise application integration, its categories, importance, objectives, components, advantages, and disadvantages. Stay tuned!
EAI Definition
Enterprise application integration connects different databases and workflows used by business applications.
This is done so that the business can use information consistently and changes to core data made by one application are correctly reflected in others.
It eliminates redundant data entry, reduces errors, and promotes seamless communication between systems.
Companies can integrate one system with another through many different methods, including messaging protocols, middleware, or database replication.
Data may also be shared using databases that store data in multiple locations, requiring synchronization techniques when changes to the same record at each site.
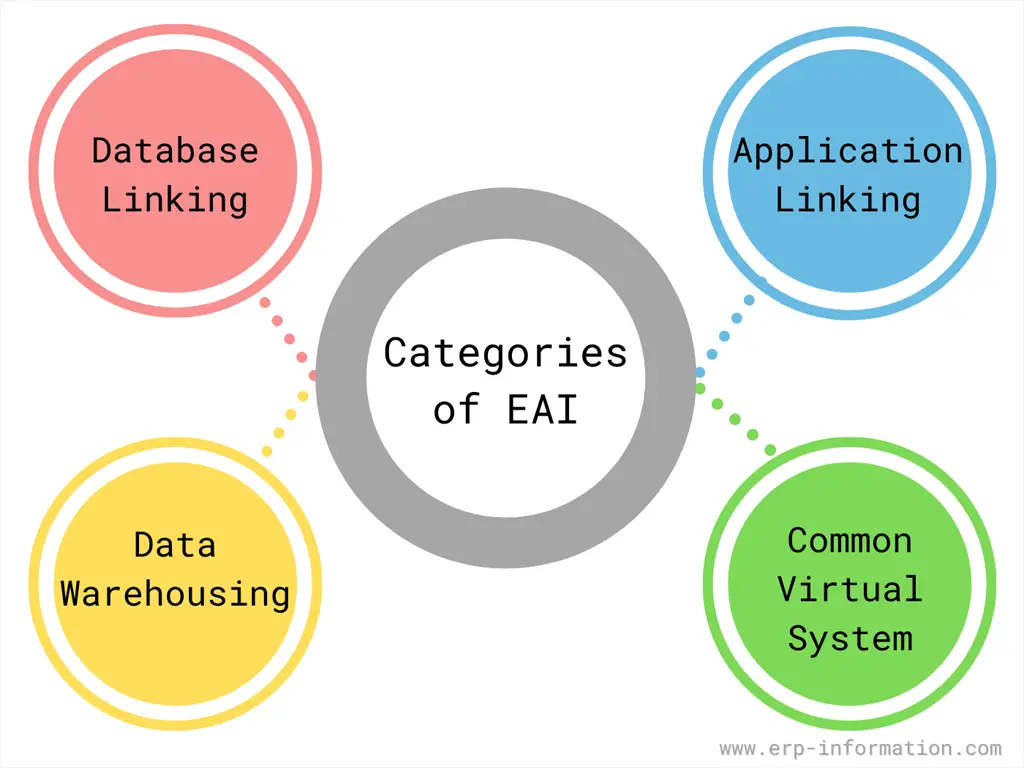
Categories
There are four major categories.
- Database linking – databases share information and duplicate information as needed;
- Application linking – the enterprise shares business processes and data between two or more applications;
- Data warehousing – data is extracted from a variety of data sources and channeled into a specific database for analysis; and
- Common virtual system – the pinnacle of EAI; all aspects of enterprise computing are tied together to appear as a unified application.
Why does Enterprise Application Integration Important?
We know that large companies use a lot of different apps. For example, one app manages the supply chain, and another for human resources. But, of course, different businesses have other apps too.
It is good to divide the enormous responsibility into small modules. It benefits the organization also. It also helps those who handle the individual modules focus on growth and stability.
But the problem is there will be no connectivity between these applications. Hence sharing critical information across the organization will not happen.
Enterprise application integration helps solve this problem by integrating applications and sharing the data across the organization.
Objectives
- Vendor independence: Rules of specific business applications or business policies need not be re-implemented even if one of the business applications is replaced with a different vendor’s application
- Data integration: Ensures consistent information in multiple systems
- Common facade: Users need not learn different software applications because it provides a compatible software application access interface
Benefits of Enterprise Application Integration
- It increases the speed of communication between Enterprise apps.
- The organization can host it on-premise with its data center or be hosted in a private cloud server.
- EAI allows information to flow between the different software programs within a company. Thus it integrates data and avoids the repetition of collecting and storing data.
- It helps to take less time to search for complete, up-to-date information.
- It allows individuals and departments to collaborate effectively.
- EAI helps to automate the process. For example, a company can integrate the information in the CRM with Email management to send messages to the customer based on the demand.
- It enables new applications to work effectively with already existing applications.
- It enables the organization to identify and react quickly to opportunities.
Drawbacks
- It fails when the person who manages the implementation of EAI is not dynamic.
- It needs more technical and skilled people.
- It is not a tool; it is a system and should be implemented as a tool.
- There will be a chance of losing details.
- Because of a lack of consent on interface design, you need to put extra effort into mapping between systems data requirements.
- It is necessary to have clear accountability because all departments have different requirements.
What is Application Integration?
Application integration links two or more software applications to share data and work together. That can be done in many ways, such as through APIs, web services, or file transfers.
Application integration can be challenging because it requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the various applications work together seamlessly.
However, application integration can provide several benefits when done correctly, such as increased efficiency and productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Application Integration Tools
Many application integration tools are available in the market. Some important tools are
- Mulesoft
- Tibco software
- Informatica
- Dell Bhoomi
- Workato
- Celigo
- Cloud Elements
- InterSystems
- OpenLegacy
- IBM
- Boomi
What are Enterprise Applications?
An enterprise application is a type of software businesses use to help them run their operations. They typically include payroll, accounting, inventory management, and customer relations management (CRM).
Typical enterprise applications are Microsoft Office 365, SAP ERP, and Oracle Database. Many businesses find that using enterprise applications helps them become more efficient and productive.
The most common types of enterprise applications are as follows.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Enterprise Messaging System
- Payment Processing
- Email marketing platform
- Service desk applications
- Customer relationship management (CRM) tools
- Content management system
- Business continuity planning
- Business analytics and intelligence platform
- Accounting system
- Automated billing system
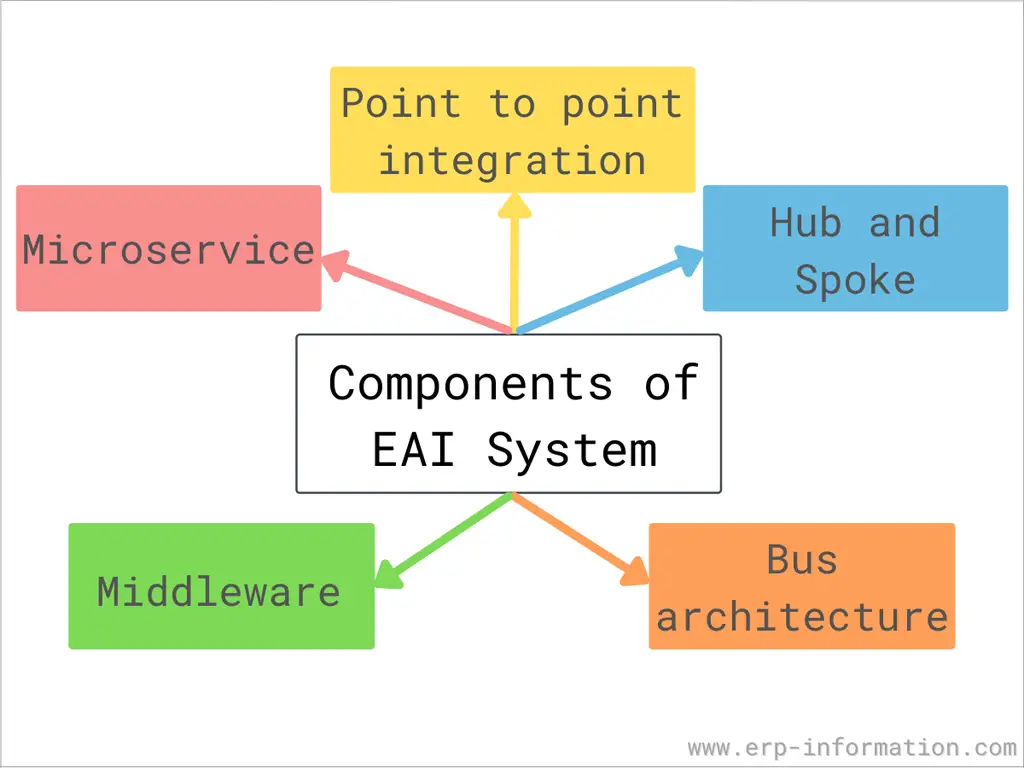
Components of Enterprise Application Integration System
Many components have merged to initiate communication between enterprise applications. Hence there are no standardized components.
However, it has some methodologies to transfer data and facilitate communication between software programs.
- With the small number of applications, point-to-point integration is effective. But when the number of applications increases, it is difficult to program and maintain the protectorate to integrate the system properly.
- All the enterprise applications and captures are connected to a central hub in a hub and spoke model. It re-formats and decides where that data should be distributed.
- A new model evolved to run away from the problems caused by the hub-and-spoke approach. That is bus architecture. It runs without workforce interference.
- A middleware framework is a tool that sits between the operating system and the application user interface.
- Microservice is the latest and standard EAI that is deployed in the cloud.
The Future
The future of EAI is rapidly evolving and growing as the need for companies to connect their backend systems becomes more prevalent. In addition, with the advent of big data, SOA, and cloud-based solutions, EAI is becoming more critical than ever before.
The EAI future looks promising. Here are three reasons:
First, the explosive growth of big data and the Internet of Things (IoT) drives the need for enhanced integration capabilities. Organizations must quickly and easily integrate data from many sources to make timely and informed decisions.
Second, EAI platforms are becoming more agile and easier to use. This makes them more accessible to a broader range of users, including business analysts who might not have had coding experience in the past.
Third, companies increasingly look for EAI platforms to accommodate hybrid environments as they move towards cloud-based solutions.
FAQs
What are things to consider when choosing an EAI tool?
When choosing an EAI tool, you should consider the following factors:
The size of your company – If you are a small or medium-sized company, you will likely need a more affordable and user-friendly tool.
Your budget is essential to finding a tool that fits your budget.
The features you need – Ensure the tool has all the features, including communication, project, and task management tools.
Ease of use – Make sure the tool is easy to use to get up and running quickly.
Customer support – Ensure the tool has good customer support if you have any questions or problems.
What are the types of EAI?
1. Message-oriented middleware (MOM): MOM is software that helps integrate two or more applications by handling the communication between them in messages. In MOM, each application is represented by a process that sends and receives messages.
2. Data-level integration involves moving data between different applications and databases. For example, it can populate a database with data from another source or consolidate multiple sources into a single database.
3. Application-level integration: This type of integration uses software to combine the functionality of two or more applications into one system.
Conclusion
Enterprise Application Integration merges applications to create a more efficient system.
It can be used for anything from synchronizing data between systems to integrating enterprise-level software like ERP and CRM with other business applications, such as Salesforce or Marketo.
The goal of EAI is not just integration but also coordination so that all parts work together seamlessly.
Reference