Enterprise Architecture is an essential framework for modern businesses striving to align their IT infrastructure and business processes with their strategic objectives.
It provides a structured approach to documenting and visualizing the current state of an organization’s IT assets and processes, facilitating a clear path towards a desired future state that supports overarching business goals.
This blog post will discuss what EA is, the benefits it can provide, its goals, its process, and the types of frameworks you can use to get started.
Definition
Architecture involves identifying and mapping out the various IT systems, applications, and processes within an organization.
It plays an important role in modeling business capabilities and pinpointing opportunities for optimization.
This structured approach helps in standardizing processes and reorganizing IT infrastructure to ensure alignment with the organization’s goals.
Overview
Why Enterprise Architecture is Important?
- Managing Technological Advancements: It helps businesses keep up with rapidly evolving technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT, ensuring they fit into the overall strategy.
- Bridging Business and IT: It creates a common language for business and IT teams, fostering better collaboration and alignment.
- Clarifying Organizational Structure: This architecture makes critical interdependencies visible, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
- Guiding Strategic Planning: It provides a clear picture of the current and desired future state, aiding in strategic planning and goal achievement.
- Optimizing IT Investments: It ensures IT investments align with business objectives, maximizing return on investment and resource efficiency.
Benefits
It offers numerous benefits that enhance both IT and business operations. Here’s a breakdown of these benefits, presented in a concise and clear format for better understanding and engagement:
- Resilience and Adaptability: It helps organizations quickly adapt to changes and disruptions, ensuring they remain resilient in the face of challenges such as supply chain issues or market shifts.
- Managing Supply Chain Disruptions: By providing a structured approach to IT and business processes, EA aids in managing and mitigating the impacts of supply chain disruptions.
- Staff Recruitment and Retention: Architecture supports creating a structured and efficient work environment, which can enhance employee satisfaction and retention while attracting new talent.
- Improved Product and Service Delivery: This architecture streamlines processes, leading to more efficient product and service delivery, ultimately improving customer satisfaction.
- Tracking Data and APIs: It enables better tracking and management of data and APIs, improving data quality and accessibility.
- Support for Redesigns and Reorganization: During major changes like mergers or acquisitions, EA provides the necessary support for effective redesigns and reorganizations.
- Standardizing and Consolidating Processes: This architecture introduces discipline into the organization by standardizing and consolidating processes, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
- Improved IT Investment Decisions: It helps in making better IT investment decisions, ensuring resources are allocated effectively to support strategic goals.
- Enhanced Service-Orientation via APIs and Cloud: By leveraging APIs and cloud services, this architecture enhances the service orientation of IT systems, leading to improved flexibility and scalability.
- Rationalized and Cost-Effective Application Portfolios: This architecture rationalizes application portfolios, reducing costs associated with maintaining unsupported or redundant technologies.
- Improved Information Management and Security: This architecture strengthens information management and security, protecting organizational data and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Reusing Existing IT Assets: It promotes the reuse of existing IT assets, maximizing value and reducing the need for new investments.
- Better Performance and Resilience: It enhances overall system performance and resilience, ensuring business continuity and efficient operations.
- Faster and More Successful Implementations and Updates: It supports quicker and more successful implementation of new systems and updates, keeping the organization up-to-date with technological advancements.
- Improved Business Insights: It provides better business insights, aiding in strategic decision-making and improving overall business performance.
- Alignment of Capabilities with Strategy: This architecture ensures that business capabilities are aligned with strategic objectives, driving better business outcomes.
- Enhanced Compliance and Risk Management: This architecture improves compliance and risk management, helping organizations adhere to regulations and mitigate risks effectively.
- Improved Business Processes and Collaboration: It enhances business processes and fosters better collaboration between different functions within the organization.
- Increased Business Agility and Continuity: This architecture boosts business agility, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to changes while ensuring business continuity.
- Faster Time to Market and Innovation: EA accelerates time to market and fosters innovation, keeping the organization competitive and responsive to market demands.
Goals
Enterprise Architecture is designed to align an organization’s IT infrastructure and business processes with its strategic objectives. Let’s delve into the key goals and why they are essential for modern businesses.
1. Aligning with Business Requirements
This architecture is driven by the organization’s business needs. It provides a blueprint for how information, business, and technology interact.
This alignment is crucial for businesses to stay competitive, especially with the rapid emergence of technologies like cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and machine learning.
Key Benefits
- Ensures that IT initiatives support business goals.
- Helps businesses adapt to technological advancements.
- Facilitates digital transformation by integrating new technologies smoothly.
2. Providing a Holistic Enterprise View
Unlike traditional frameworks that may rely on rigid documentation, It offers a comprehensive view of the entire enterprise.
This perspective considers the viewpoints of different stakeholders, including owners, designers, and builders, to create a unified understanding of the organization.
Key Benefits
- Encourages collaboration across departments.
- Provides a clear picture of how different parts of the business interact.
- Supports strategic decision-making with a broader understanding of the enterprise.
3. Enhancing Agility
One of the primary goals of EA is to foster agility within the organization. A robust architecture strategy helps companies navigate complex and rapid changes, positioning them to thrive in turbulent times.
This has been especially crucial during recent events like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key Benefits
- Increases the organization’s ability to adapt to market changes.
- Supports agile practices and methodologies.
- Enhances resilience against disruptions.
A survey by Bizzdesign found that organizations with mature EA programs were three times more likely to exhibit organizational agility.
However, only a small percentage reported that their EA programs facilitated faster innovation and time to market, highlighting a significant area for improvement.
4. Supporting Innovation and Integration
A successful EA strategy takes into account the latest innovations in business processes, organizational structures, information systems, and technologies.
It promotes the use of standardized language and best practices across the organization, making it easier to integrate or eliminate processes as needed.
Key Benefits
- Drives innovation by keeping up with the latest technological trends.
- Streamlines business processes for greater efficiency.
- Enhances the reliability and timeliness of business information.
5. Ensuring Executive and Stakeholder Buy-In
Implementing this architecture strategy requires the support of executives and stakeholders. Their buy-in is important for ensuring that the strategy is adopted across the organization and that it has the necessary resources for successful implementation.
Key Benefits
- Facilitates alignment between IT and business leadership.
- Ensures adequate funding and resources for EA initiatives.
- Promotes a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
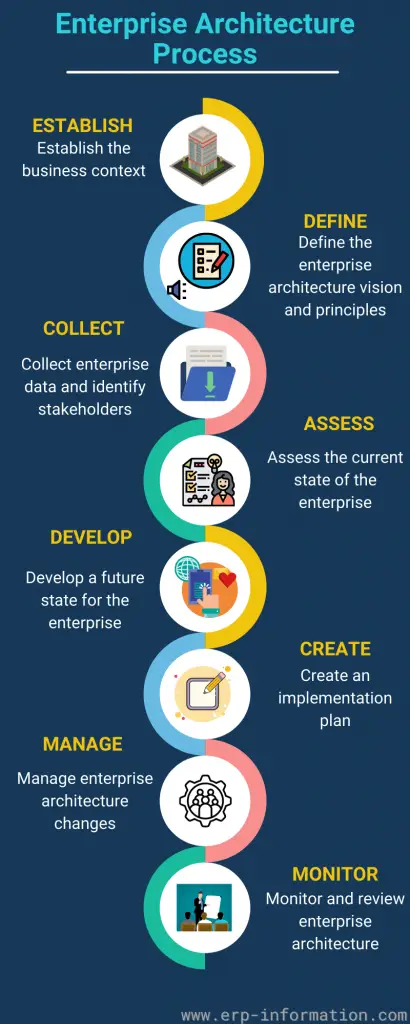
Steps
There are eight steps in the process:
Viewpoints
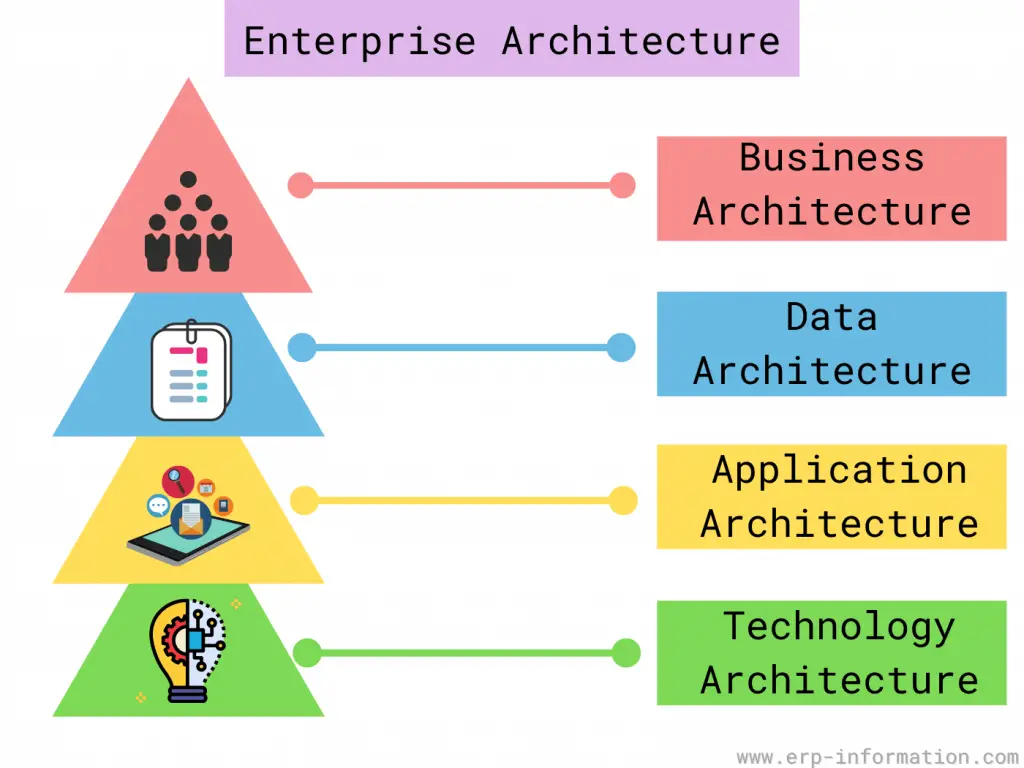
It contains four viewpoints. They are
- The business perspective defines day-to-day processes and standards of business.
- The application perspective defines relations between organizational processes and standards.
- The information perspective defines raw data like databases, images, files, etc.
- The technology perspective defines hardware and software, such as operating systems, networking tools, etc.
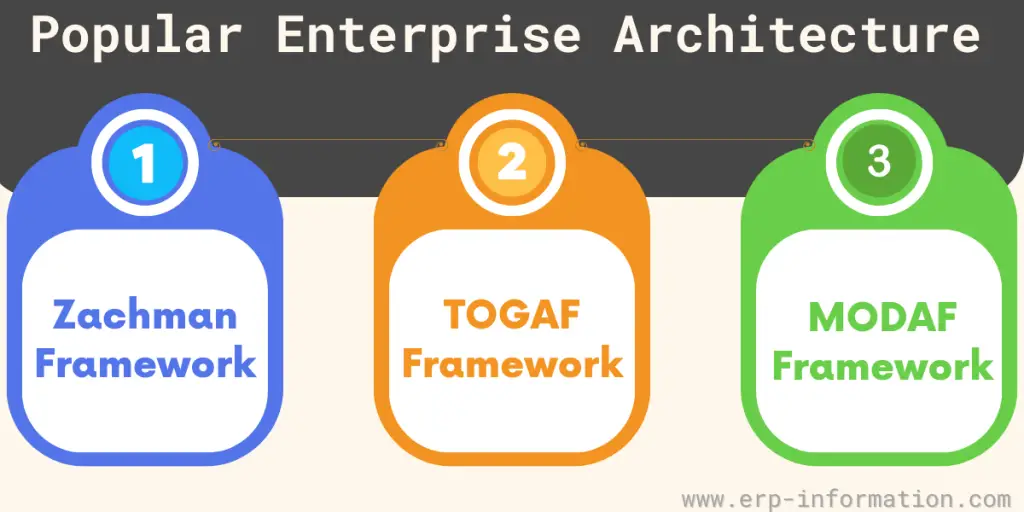
Framework
A variety of EA frameworks can be used for enterprise architecture. More popular frameworks include the Zachman Framework, the TOGAF Framework, and the MODAF Framework.
Zachman Framework
The Zachman Framework consists of six steps:
- Define the problem or opportunity
- Generate alternative solutions
- Select a preferred solution
- Develop a blueprint or model of the preferred solution
- Implement the blueprint or model
- Monitor and adjust the implementation as needed
TOGAF Framework
The TOGAF Framework consists of seven steps:
- Define enterprise goals and objectives
- Create an enterprise framework
- When designing or redesigning your enterprise architecture, you need to think about the different business processes, information systems, and infrastructure that will be necessary.
- Develop a detailed design for the components identified in step three. Then, consider how each component should work individually and interact with other enterprise components. Be sure to include any relevant non-functional requirements such as security, scalability, or performance requirements—document things like data models, user interface designs (UI) specifications, etc.
- Develop a transition plan that identifies what needs to change from the current state to the future described in the target enterprise architecture model.
- Implement the enterprise architecture plan.
- Validate enterprise architecture by checking that what was designed and implemented meets enterprise goals
MODAF Framework
The MODAF Framework consists of five steps:
- Define what is to be modeled
- Construct the enterprise model
- Model elements and relationships within the enterprise model
- Derive system requirements from the enterprise model
- Implement the system requirements
Enterprise Architecture Vendors, Tools, and Certifications
| Vendors | Tools | Certifications |
| Orbus Software | Ardoq | TOGAF 9 Certification |
| Software AG | Atoll Group SAMU | Evolution |
| Planview | Avolution Abacus | Axelos ITIL Master certification |
| Avolution | BOC Group ADOIT | Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert |
| Sparx Systems | BiZZdesign HoriZZon | Google Professional Cloud Architect |
| Capsifi | Virtualization Council Master Infrastructure Architect certification | |
| Capstera | CISSP Information Systems Security Architecture Professional (ISSAP) | |
| ServiceNow | CISSP Information Systems Security Architecture Professional (ISSAP) | |
| Oracle | Red Hat Certified Architect | |
| Orbus Software | EC Council Certified Network Defense Architect (CNDA) | |
| Sparx Systems | Salesforce Certified Technical Architect (CTA) | |
| Software AG | AWS Certified Solution Architect | |
| Avolution | Dell EMC Cloud architect training and certification | |
| MEGA HOPEX | ||
| Erwin | ||
| BiZZdesign | ||
| Planview | ||
| SAP | ||
| BOC Group |
Who Should be Involved in Enterprise Architecture?
A collaborative effort must be initiated involving enterprise architects, business analysts, enterprise IT personnel, and other stakeholders as per requirement.
Enterprise architects
They have a thorough understanding of enterprise architecture. They are in charge of developing and maintaining the company’s architecture framework, identifying components that need to be designed or redesigned, producing detailed designs for these components, and ensuring that the corporate architecture is adequate.
Enterprise IT personnel
They will implement it. Therefore, when designing this architecture, one should always consult with enterprise IT personnel to ensure that what is designed can be implemented and will meet enterprise needs.
Business analysts
They should be involved in this because they help define EA’s enterprise requirements to build their models.
Other enterprise stakeholders
People who should help create the architecture for an enterprise include enterprise architects, IT personnel, business analysts, and enterprise customers, suppliers, and shareholders whenever possible.
For example, while they may not be required to help build out the architecture’s components, such as business processes or enterprise applications, enterprise customers and enterprise suppliers can provide valuable feedback that should be considered by enterprise architects when designing the architecture.
Certifications
LeanIX Academy
Description
LeanIX offers comprehensive training and certification programs to help professionals gain a deep understanding of Enterprise Architecture. Their courses cover various aspects of this architecture, including best practices, methodologies, and tools.
The Open Group TOGAF 9.2 Certification
Description
TOGAF, or The Open Group Architecture Framework, is a globally recognized certification for Enterprise Architects. TOGAF 9.2 provides an in-depth understanding of Enterprise Architecture concepts and methodologies.
AWS Certified Solution Architect
Description
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a certification specifically for Solution Architects. While not solely focused on Enterprise Architecture, this certification can be highly relevant for those working with cloud-based architectural solutions.
Salesforce Certified Technical Architect
Description
Salesforce, a leading CRM platform, offers a certification path for Technical Architects. This certification is ideal for professionals designing complex enterprise solutions within the Salesforce ecosystem.
Axelos ITIL Master Certification
Description
ITIL is a well-recognized framework for IT service management. Axelos ITIL Master Certification provides certification that is relevant for professionals involved in IT and EA processes.
Zachman Enterprise Architect Associate Certification
Description
The Zachman Framework is a widely-used approach to Enterprise Architecture. Their certification program offers a deep dive into the framework and its application in the EA domain.
Associate Certified Enterprise Architect (ACEA)
Description
The Associate Certified Enterprise Architect (ACEA) certification provides a strong foundation in EA principles and practices. It’s ideal for those looking to start their journey in Enterprise Architecture.
FAQs
What is the Purpose of Enterprise Architecture?
The purpose of Architecture is to build a roadmap for a successful organization. It helps a company plan, organize, and improve everything it does. Think of it as a guidebook that ensures everyone is on the same page and working towards common goals.
What are Enterprise Architecture Tools?
These tools are like toolkits for architects. They’re software or applications that help professionals create, manage, and visualize their architectural plans. It’s like having a set of high-tech tools to design and build a better organization.
Why Should an Organization Do Enterprise Architecture?
Organizations should use this architecture to make their lives easier and their businesses stronger. It’s like having a blueprint for a house; it ensures that everything is well-organized and efficient. Here are some reasons why:
Efficiency: Architecture streamlines processes, making work faster and less confusing.
Cost Savings: It helps in smart resource allocation, saving money.
Better Decision-Making: It provides insights for informed choices.
Adaptability: It helps organizations change and grow smoothly.
Customer Satisfaction: It ensures businesses meet customer needs.
Competitive Edge: It keeps companies ahead in the market.
What is an EA Model?
This model serves as an extensive framework detailing the critical data and processes of an organization. It identifies significant business entities (BECs) and major business processes (BASs), offering a thorough overview of the core elements and operations that underpin the organization’s existence and functionality.
Conclusion
Enterprise Architecture is not just about managing technology, it’s about driving business success through thoughtful, strategic planning and execution.
Embracing this architecture allows organizations to navigate complexity, foster innovation, and achieve their long-term objectives in an ever-evolving digital landscape.