You’ve decided it’s time for your company to implement an ERP system, but you’re unsure where to start.
Implementing an ERP system is a big step, but it’s only the beginning. You still have a lot of work ahead of you.
This comprehensive guide to ERP implementation will take you through every step of the process, from choosing the right system to post-implementation support. Our expert methodology ensures that your implementation goes as smoothly as possible.
Before knowing about ERP implementation, let us learn about ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning).
ERP Implementation Methodology
Any business seeking to implement an ERP system must select an appropriate methodology. The three most common methodologies are waterfall, agile, and hybrid.
The waterfall is the traditional approach, and it entails completing all requirements for one phase before moving on to the next phase.
Agile is a more modern approach that emphasizes flexibility and rapid delivery.
Hybrid is a combination of the two, and it enables businesses to tailor their methodology to their specific needs. However, selecting the right methodology is essential for a successful ERP implementation.
For ERP projects to be successful, there needs to be an ERP implementation methodology that guides all aspects of ERP deployment, including,
- Planning & Preparation
- Designing business processes
- Building data warehouse architecture
- Testing systems functionality before going live with them (UAT testing) etc., so they work as intended once implemented into the production environment (going “live”).
- ERP implementation life cycle is how ERPs are installed, deployed, and managed over time. An ERP system can take anywhere from six months to three years, depending on size and complexity, so it’s vital for companies looking into implementing a solution.
Cloud ERP Implementation Life Cycle
The ERP implementation lifecycle is the sequence of activities required to successfully implement ERP software in an organization.
ERP implementations are complex processes that involve multiple stakeholders from different departments within a company and can take anywhere from six months to two years or more, depending on the size and complexity of the project scope.
ERP Implementation Steps
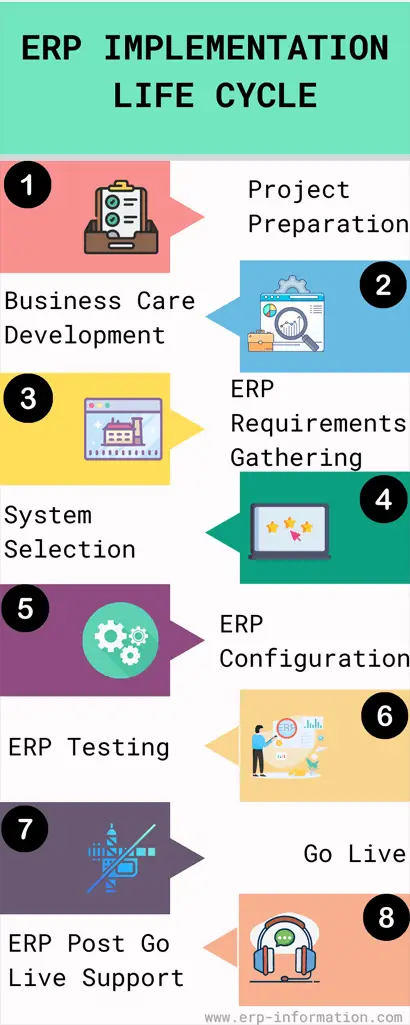
The below infographic shows the ERP implementation process.
Project preparation
ERP implementation is a complex process requiring rigorous planning and coordination between stakeholders.
Therefore, ERP projects should have clear goals, objectives, deliverables, and timelines for completion. Hence, everyone knows what they are working towards during the ERP life cycle.
Business case development
The ERP business case explains why an organization needs to implement ERP software. It shows how the company can save money or make more money over time.
The case also demonstrates the risks of not implementing ERP. If the company does not implement ERP, it might lose its competitive advantage in today’s marketplace.
ERP requirements gathering
In the Enterprise Resource Planning requirements gathering phase, the business and its functional areas work with ERP consultants to document their current processes.
This process usually takes several months, as there can be a lot of back and forth between stakeholders until everyone agrees on what should or should not be included in the new ERP system.
System selection
Once the ERP requirements have been gathered, the system selection process begins by reviewing different Enterprise resource planning software packages that meet those needs and budget restrictions.
In this stage, vendors typically hold demonstrations to see how their software works and if it is a good fit.
ERP configuration
ERP software is not a one size fits all solution. Therefore, most packages require customization (or tailoring) to meet specific needs. The configuration stage takes place with the help of ERP consultants who have expertise in the particular package that has been selected.
ERP testing
ERP testing is conducted in two phases – system testing and user acceptance testing. System testing verifies that the ERP software functions as designed, while user acceptance testing ensures that end-users meet their workflows and requirements.
Go live
ERP go-live is the official launch of the new system and marks the end of the ERP implementation life cycle.
User training must be completed before going live, and a solid change management plan should be in place to ensure a smooth transition from the old system to the new one.
ERP post-go-live support
Post-go-live support provides ongoing assistance to users after they have gone live on the new system. This can include troubleshooting problems, providing updates/patches, and answering any questions or concerns.
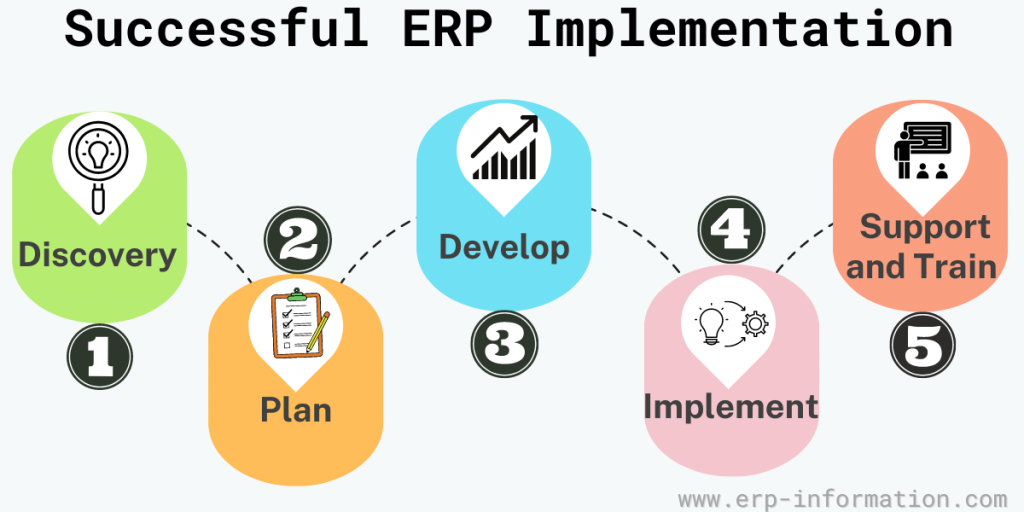
The ERP implementation life cycle is a necessary process to follow to ensure a successful ERP deployment. By taking the time upfront to document your requirements and selecting an ERP package that is a good fit for your business, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying all the benefits it offers.
Additional Tips for Successful ERP Implementation
- While implementing, keep the prospects of the business too. Customizing the system later may take more effort than doing it initially.
- Get a clear idea about the total cost of the project. Don’t forget to consider training and future support costs. The vendor may charge an additional cost for additional features if you ask for them later.
- On-premises deployments usually cost more, and even the maintenance cost is high.
- Since the new system involves a learning curve for its end users, people continue doing how they have always been. Therefore, emphasis on change management is essential.
- Don’t buy functionalities that are not needed for your business. It makes training difficult and increases the price.
ERP Implementation Strategy
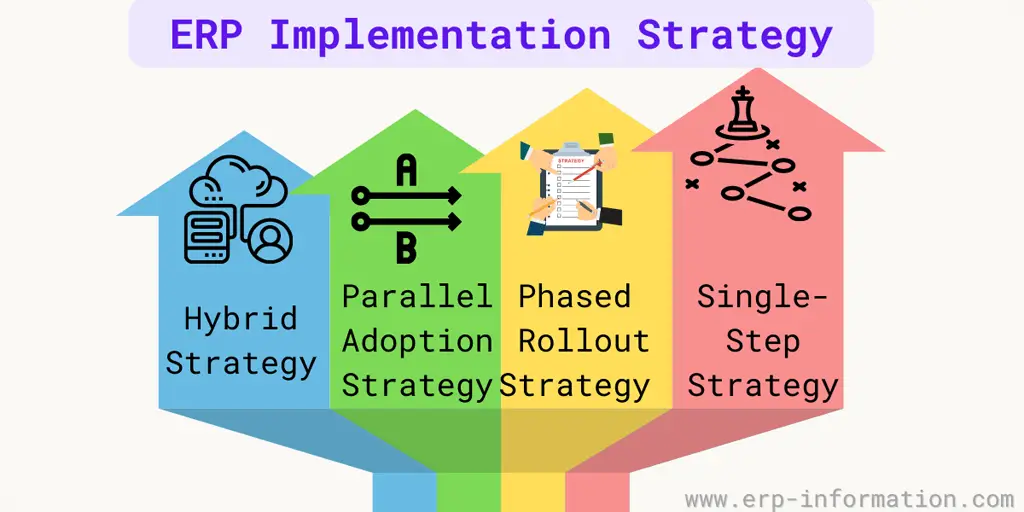
Below are a few proven strategies for implementing an ERP system. But, of course, all methods have their pros and cons.
1. Single-step strategy
All company users will simultaneously proceed to the new ERP system.
The important thing is you have to finish all the arrangements and testing of the new system with proper training for the users before the actual date of using the new system.
The pros are that you will immediately experience the new system’s benefits, such as increased productivity, reduced operating costs, etc.
The cons are minor errors that impact employees, customers, and business partners.
2. Phased rollouts strategy
Here, the deployment of tools, components, and features will occur in one or two weeks or a month. In this approach, the risk is less compared to the single-step method.
The disadvantage of this method is you will get the benefits of the new ERP system a little late.
3. Parallel adoption strategy
In this approach, the company uses its inheritance system in parallel with the new ERP system for some specified time.
In this method, the risk is significantly less because the company can return to its inheritance system if any problem occurs in the new system.
It also helps the employees to get adjust to the new system gradually. However, this strategy’s drawback is that it is costly because it requires more human resources and resources to run two systems parallelly.
4. Hybrid strategy
This strategy is a combination of all the above methods. That means a company can implement an ERP system with the single-step approach and then launch other modules with phase strategies for its departments.
Conclusion
The ERP implementation process is complex that can be overwhelming for any business.
However, by following the steps outlined and using our recommended methodology, your organization can successfully implement an ERP system to improve efficiency and productivity.