In an era where digital transformation and the rapid expansion of technology have become integral to business operations, the importance of safeguarding sensitive information cannot be overstated.
An Information Security Management System serves as a comprehensive framework designed to protect an organization’s critical data assets, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The blog post discloses the information security management system, including its working, benefits, best practices, implementation tips, and top frameworks.
What is Information Security Management System?
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a systematic and structured approach to managing and protecting an organization’s sensitive data, information assets, and IT infrastructure.
The primary objective of this system is to limit the impact of security breaches and make sure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data by implementing risk management processes, security controls, and policies.
How Does It Work?
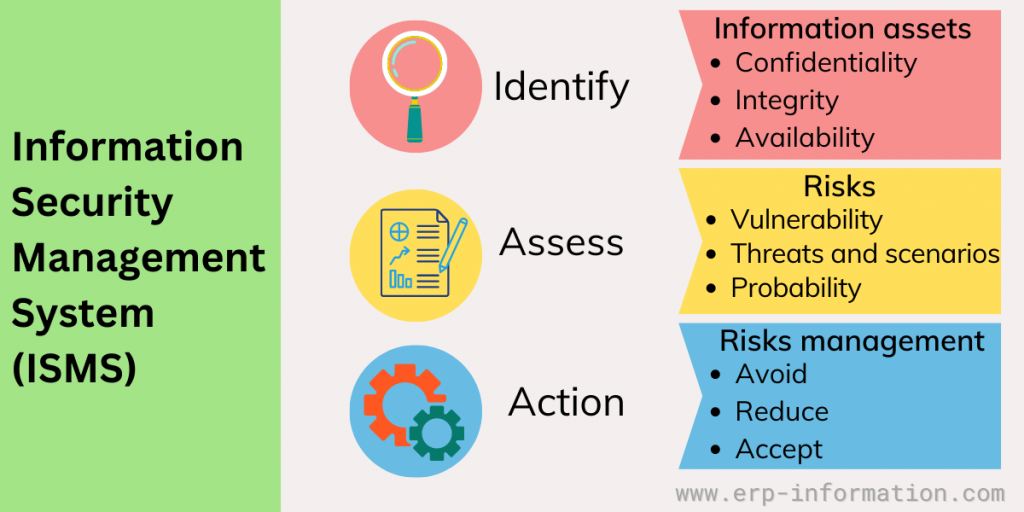
ISMS offers a well-structured method to manage the information security of the organization. It involves a continuous cycle of planning, implementing, monitoring, reviewing, and improving the organization’s information security posture. The way of working is as follows.
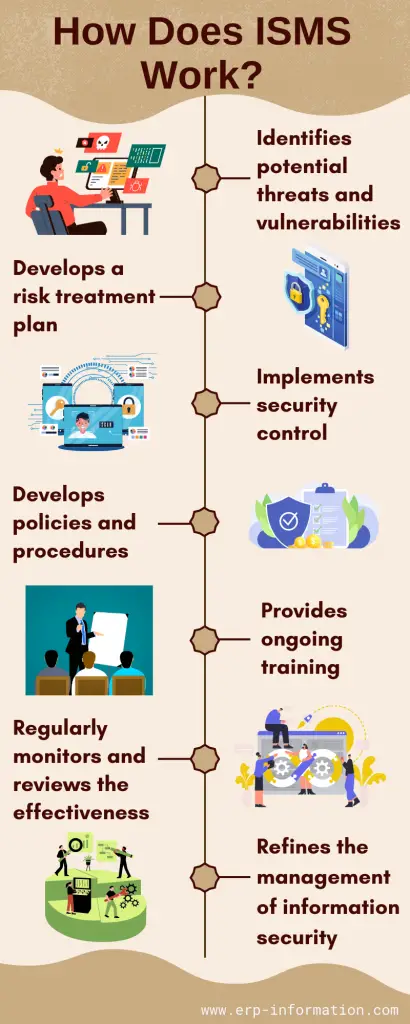
Identifies potential threats and vulnerabilities
It identifies the potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact the organization’s information assets. Evaluates the likelihood and impact of those risks materializing, considering factors such as asset value, existing controls, and threat actors.
Develops a risk treatment plan
Develops a risk treatment plan outlining the appropriate security controls and measures to mitigate identified risks. That may involve accepting, avoiding, transferring, or mitigating risks based on cost-benefit analysis and the organization’s risk appetite.
Implements security control
Implements security controls by putting the selected security controls, which can be technical, administrative, or physical. Examples include firewalls, access controls, encryption, security policies, and staff training.
Develops policies and procedures
Creates and maintains comprehensive information security policies, procedures, and guidelines that outline the organization’s security expectations, responsibilities, and compliance requirements.
Provides ongoing training
Provides ongoing education and training for employees to foster a security-conscious culture and ensure they understand their role in maintaining information security.
Regularly monitors and reviews the effectiveness
Regularly monitors and reviews the effectiveness of the implemented security controls, policies, and procedures. That may involve audits, vulnerability assessments, and performance metrics to identify areas for improvement.
Refines the management of information security
Uses the findings from monitoring, reviews, and incident management to refine the ISMS, update risk assessments, and improve security controls and processes.
By doing all these things in a cyclical manner, an ISMS enables organizations to maintain a robust information security posture that adapts to the evolving threat landscape and addresses the unique risks and challenges they face.
Benefits
An Information Security Management System benefits organizations in the following ways,
Protects information assets
It protects organizations’ sensitive data, including paper-based and digital information. This information may include customer, financial, and personal information.
Reduces risk
It helps identify and mitigate potential threats and vulnerabilities, reducing the likelihood and impact of security incidents.
Meets legal and regulatory compliance
By adhering to a standard such as ISO/IEC 27001, ISMS helps organizations demonstrate compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry-specific requirements related to information security.
Enhances reputation
Implementing an ISMS signals to stakeholders, customers, and partners that the organization takes information security seriously, which can boost trust and confidence in its ability to protect sensitive data.
Provides business continuity
By identifying critical assets and ensuring their protection, an information security system contributes to the organization’s resilience and ability to maintain business operations in the face of security incidents.
Saves costs
Proactively addressing information security risks can result in significant cost savings by preventing data breaches, avoiding regulatory fines, and minimizing the impact of security incidents on the organization.
Improves company culture
It provides a structured approach to the entire organization’s risk management, security, and asset management. It encourages the employees to learn about the risk associated with the organization’s information assets.
It fosters a security-conscious culture by providing ongoing training and raising employee awareness about their role in maintaining information security.
Increases efficiency
By streamlining processes and implementing standardized security controls, the system can help organizations operate more efficiently and reduce the likelihood of costly security breaches.
Provides continuous improvement
It promotes a cycle of continuous improvement, ensuring that the organization’s information security posture adapts to evolving threats and emerging technologies.
ISMS Best Practices
By following the below practices, organizations can implement the information security system easily.
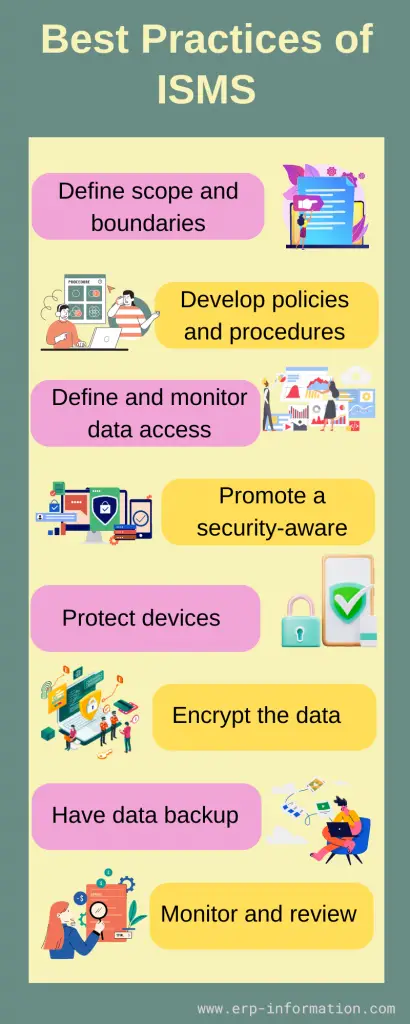
Define scope and boundaries
Clearly define the scope and boundaries of the ISMS, including the organization’s information assets, business processes, departments, and any relevant legal or regulatory requirements.
Develop policies and procedures
Establish clear and comprehensive information security policies, procedures, and guidelines that reflect the organization’s security objectives and compliance requirements.
Define and monitor data access
Clearly define the data access control policies, including who can access sensitive data. Carefully monitor who is accessing the data by tracking logins and authentications.
Promote a security-aware
Provide ongoing training and awareness programs to ensure that employees understand their responsibilities in maintaining information security and fostering a security-conscious culture.
Protect devices
Ensure that all the devices of the organization are protected from physical damage and hacking attempts. Some tools like Google Workspace and Office 365 help secure the device. Hence make sure all devices are installed with those tools.
Encrypt the data
Data encryption is the best way to prevent security threats, and it helps to prevent unauthorized access. Make sure all information assets of the organization are encrypted before implementing ISMS.
Have data backup
Before implementation, have a data backup that helps prevent data loss. It is better to have a backup on both on-premise and cloud.
Monitor and review
Monitor and review the effectiveness of security controls, policies, and procedures through audits, vulnerability assessments, and performance metrics. Make adjustments as needed to address emerging threats and changing circumstances.
Implementation tips
Define the objectives
Determine the reasons to protect the assets. Outline the scope and boundaries of the ISMS, including the organization’s information assets, business processes, departments, and any relevant legal or regulatory requirements.
Identify the assets
Identify the list of assets that need to be protected, including hardware, software, databases, and information.
Identify risks
List out the risk factors associated with the assets. Establish a consistent methodology for conducting risk assessments, including identifying risks, evaluating their likelihood and impact, and prioritizing them for treatment.
Develop a risk management approach
Establish a consistent methodology for conducting risk assessments, including identifying risks, evaluating their likelihood and impact, and prioritizing them for treatment.
Create a risk treatment plan
After considering the risk assessment findings, develop a plan outlining the appropriate security controls and measures to mitigate identified risks.
Monitor and improve
Regularly monitor and review the effectiveness of the implemented security controls. Use the findings from monitoring, reviews, and incident management to refine the ISMS, update risk assessments, and improve security controls and processes in a continuous improvement cycle.
Top ISMS Frameworks
ISO/IEC 27001
It is an internationally recognized standard for Information Security Management Systems. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), it provides a comprehensive set of requirements and best practices for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an organization’s ISMS.
The primary objective of ISO/IEC 27001 is to ensure the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of the information by applying a risk management process and assuring stakeholders that the organization’s information security risks are being adequately managed.
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
It is a service management approach with a dedicated ISM (Information security management) component. It ensures effective management of information security by aligning IT and business security.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies)
It is an IT-centered framework showing the importance of asset and configuration management in information security and ITSM.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of the ISMS?
The ISMS aims to protect the overall organization by providing guidance in managing security risks in the enterprise. It also contains procedures addressing information security risk assessment and management.
How can organizations get ISO/IEC 27001 certificates?
Organizations seeking to achieve ISO/IEC 27001 certification must have an independent audit by an accredited certification body. This audit assesses the organization’s ISMS against the standard’s requirements, ensuring that it effectively manages information security risks and demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement.
By implementing an ISMS aligned with ISO/IEC 27001, organizations can show others about their commitment to information security, build trust with stakeholders, ensure compliance with relevant regulations, and protect their valuable information assets from potential cyber threats.
What are the three principles of an information security management system?
Three major PRINCIPLES are
Confidentiality: Ensuring information can only be seen by certain people and nobody else can see it.
Integrity: Data integrity means that the data is safe. No one changes it without permission. The data can only be changed when people upload or store it in a database.
Availability: Only authorized users can get information when they need it. Computers, security, and communication must work well for the system’s availability. Special systems like medical equipment, power plants, and safety systems have extra rules so they can stay working if something bad happens.
What is the difference between ISMS and ISO/IEC 27001?
The difference is as follows.
ISMS is a framework or system used by organizations to manage information security risks, including policies, procedures, and controls to manage information security risks within an organization.
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard that outlines the requirements and best practices for implementing and maintaining an ISMS. It provides a comprehensive set of best practices and guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an organization’s ISMS.
Conclusion
Information Security Management System is vital to modern organizations, providing a structured and systematic approach to managing and protecting sensitive information assets.
By adhering to best practices and recognized standards such as ISO/IEC 27001, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to information security, ensure compliance with relevant regulations, and foster stakeholder trust.
We hope that the post provided valuable information about ISMS.
Reference