You may have heard of “Lean Warehouse Management” but do not know what it means or How it can help your business.
It is a system that can help you streamline your warehouse operations and improve efficiency.
This blog post will explain lean warehouse management, how it can benefit your business, and some of the best practices for implementing it.
What is Lean Warehouse Management?
Lean warehouse management is a system that helps you optimize your warehouse operations by reducing waste and improving efficiency.
It aims to help you save time, money, and other resources by streamlining your processes and eliminating wasteful practices.
The main goal of lean warehousing is to streamline the flow of materials and products through the warehouse to reduce or eliminate waste.
What are Lean Principles in Warehousing?
Some of the fundamental lean warehouse principles that can be applied in warehouse settings to improve efficiency and productivity include:
1. Eliminating waste
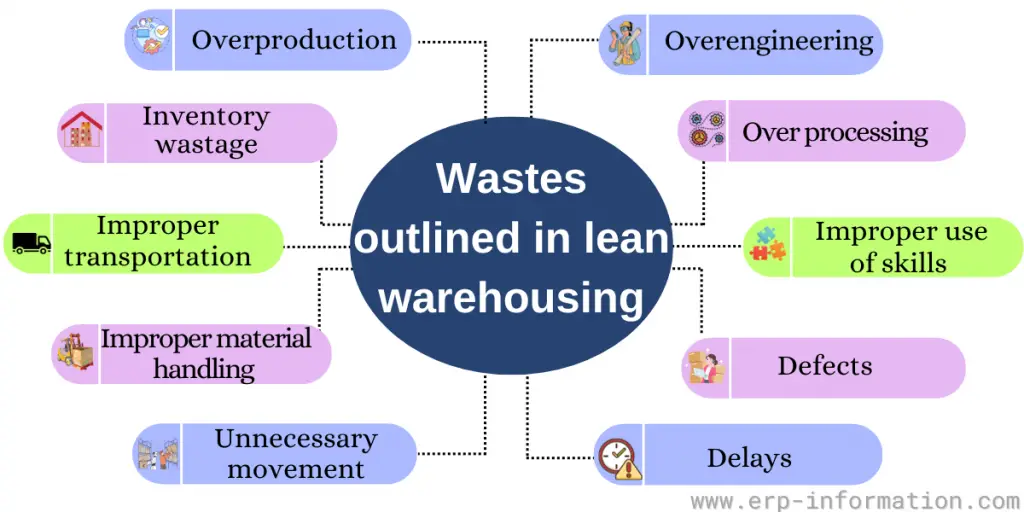
One of the core principles of lean is eliminating waste throughout the manufacturing process without compromising productivity. The following are the wastes outlined in lean warehousing.
- Overproduction – It means producing more products than necessary and results in storage costs.
- Inventory – This includes both work-in-progress inventory and finished goods. Inventory wastage leads to congestion in the yard area.
- Transportation – It includes moving equipment unnecessarily without loading any materials within the facility.
- Material handling and storage – This includes improper methods for material handling and improper placing of materials (storing materials in the wrong place).
- Movement – This is employees’ wasted time and effort as they move around the facility.
- Delays – This is wasted time waiting for materials, information, or approvals.
- Defects – This includes rework or scrap resulting from errors or faults.
- Skills – This is the wasted potential of employees who have not utilized it to their fullest potential.
- Overprocessing – It includes doing unnecessary activities that are not needed.
- Overengineering – This includes unnecessary usage of complicated processes or methods, even if it can be done with simple processes.
2. Increasing utilization
Another fundamental principle of lean is maximizing the utilization of all assets within the manufacturing process. This could involve ergonomic design principles in a warehouse setting to optimize pick paths and reduce travel time.
Areas for Implementing Lean Warehouse
It is crucial to make improvements in the following areas for the success of lean warehousing. Unfortunately, the areas look overlap with each other.
Warehouse layout
While constructing the warehouse, layout design is essential. Plan for good gateways for the free movement of vehicles. Have a proper plan for shelf arrangement. Racks should be easily reachable for workers while picking them. That helps to reduce the movement of workers.
Inventory management
Along with the warehouse layout, managing inventory is also crucial for ‘lean.’ That means what items to store, how to store, where to store, and how to pick and pack; These things must be clearly defined, and the same thing must be followed.
Material-handling
Selecting the proper material-handling equipment, such as carts and pallet trucks, matters. To balance the variations dynamic approach is required.
Wastage of resources
Utilizing resources is crucial to lean warehouse management. For example, if there is a delay in picking the items from racks is also named a waste of resources.
That means that delay leads to a waste of time of labor. Wastage of resources is interconnected with warehouse layout, material handling, etc. Hence to eliminate resource wastage, the other areas need to be optimized.
Management Information System
Implementing lean management requires a robust, integrated, and actionable Management Information System (MIS) that utilizes data from sourcing to processing to decision-making.
Although most firms have some form of MIS, developing an effective system is essential for successfully implementing lean philosophies.
Lean Warehouse Examples
Lean warehouses are distribution facilities designed and configured to minimize waste and maximize efficiency. Several examples of lean warehouse techniques are there to achieve efficiency, including but not limited to the following:
- Using gravity to move products downhill instead of using machines or workforce to move them uphill
- Eliminating unnecessary steps in the process of getting products from one place to another
- Creating lean storage zones that allow workers to find and access the products they need easily
- Installing conveyor belts and other transportation systems that move products through the warehouse quickly and efficiently
Best Practices for Implementing Lean Warehouse Management
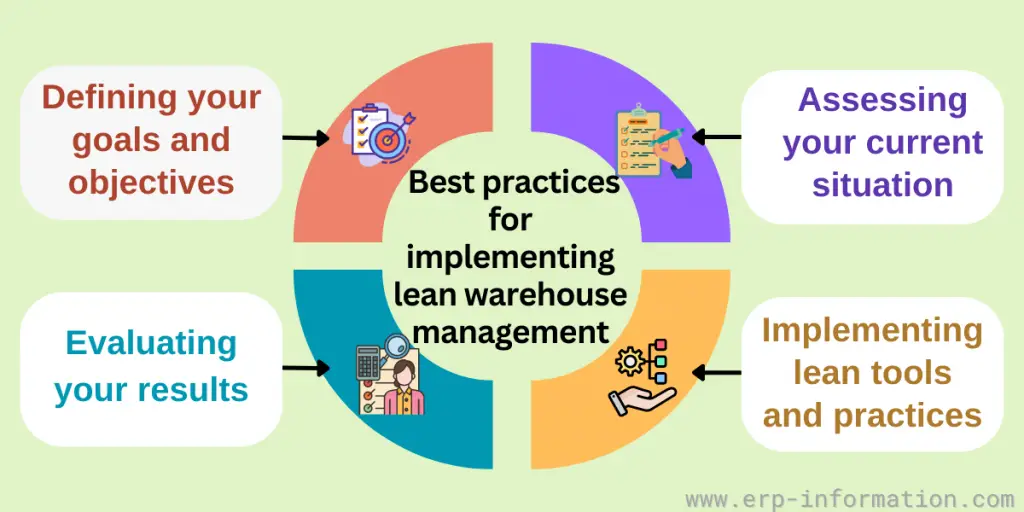
If you’re interested in implementing lean warehouse management in your business, there are a few best practices to keep in mind.
Some of these include:
Defining your goals and objectives
Before you start implementing lean warehouse management, it’s essential to have a clear idea of what you hope to achieve. That will help you plan and choose the right tools and practices for your business.
Assessing your current situation
Once you’ve defined your goals, it’s time to look closely at your existing warehouse operations. That will help you identify areas where you can improve and make changes to streamline your processes.
Implementing lean tools and practices
There are many different lean tools and methods that you can use to improve your warehouse operations. These include 5S, Kanban, value stream mapping, and continuous improvement.
Evaluating your results
Once you’ve implemented it, taking a step back and evaluating your results is essential. That will help you determine whether or not your efforts are having the desired effect and make changes as needed.
5S Methodology of Lean Warehousing
Lean tool 5s is a methodology that helps improve warehouse operations by creating and implementing standard work procedures and removing waste. The five steps in the 5s method are:
- Sort – Remove everything from the workspace that is unnecessary to perform the task. That includes tools, materials, or other objects that do not contribute to the task.
- Set in Order – Arrange the sorted items logically, making them easy to find and use. It may include labeling shelves or cabinets, organizing tools by type or size, and arranging materials in an order that makes sense for the task.
- Shine – Clean the workspace and its contents so it is tidy. That includes sweeping, dusting, and organizing items, making them easy to find and use.
- Standardize – Create standard work procedures for regularly performed tasks, such as creating checklists, setting up assembly lines, or labeling storage containers.
- Sustain – Maintain the cleanliness and order of the workspace regularly. That includes setting up a cleaning schedule, performing regular maintenance on equipment, and stocking shelves with needed materials.
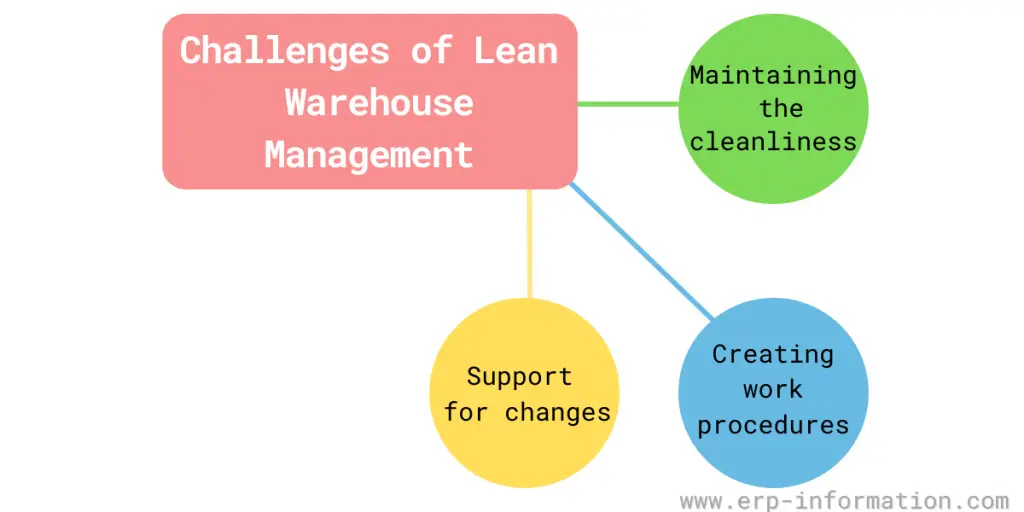
Challenges of Lean Warehouse Management
1. Maintaining the cleanliness
One challenge of it is maintaining the cleanliness and order of the workspace. That requires regular cleaning and maintenance of the area.
2. Creating work procedures
Another challenge is creating standard work procedures for tasks that are performed regularly. That can be difficult to do if the job is not well-defined or changes often. You need to have systems and procedures to ensure that your gains are not lost over time.
3. Support for changes
Finally, sustaining the improvements made through it can be difficult if all levels of the organization do not agree to and support the changes. Everyone needs to be on board with the changes that are being made to make the transition smooth.
Reasons to Implement Lean Warehousing
Lean warehousing benefits in many ways. Some of them include:
Reduced costs associated with waste and inefficient processes
Lean warehousing helps in cutting down unnecessary expenses. By eliminating waste and streamlining processes, you can save money on labor, storage, and resources.
Improved customer satisfaction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, shorter lead times are the norm. Lean warehousing helps you to reduce shipping delays and errors ensuring you meet customer demands in a timely manner.
Increased number of perfect orders
Implementing lean principles leads to improved accuracy and efficiency, resulting in a higher rate of error-free orders. This boosts customer satisfaction and minimizes returns or corrections.
Multiple delivery channels management
With the growth of e-commerce, businesses often need to juggle multiple delivery methods. Lean warehousing facilitates the efficient management of diverse delivery channels.
Increased number of SKUs management
As your product range expands, lean warehousing helps you organize and handle a larger inventory without overwhelming your storage and staff.
Reduced the need for storage space
Space is often at a premium in warehouses. Lean principles optimize space utilization, ensuring that every inch of your warehouse is put to productive use.
Control over seasonal and fluctuating demands
Many businesses face seasonal fluctuations in demand. Lean warehousing enables you to scale your operations up or down efficiently, aligning with changing customer needs.
FAQs
What is the meaning of Lean in Warehouse Management?
In warehouse management, lean refers to practices or techniques that help optimize the storage and movement of goods within a warehouse facility. That could include optimizing the warehouse layout, streamlining processes such as picking, and packing, and reducing waste such as inventory that is not being used.
What is Lean Inventory Management?
Lean inventory management is a business strategy that aims to reduce the waste of time, money, and resources in producing and distributing goods by optimizing the stock of materials and finished products.
Conclusion
Overall, lean warehouse management is a beneficial way to improve your business operations. It can help reduce costs and increase efficiency in many ways.
However, some challenges need to be considered when you implement. You can overcome these challenges with careful planning and commitment from all levels of the organization.
References: