Among the core strategies of aggregate planning, level production, chase production and hybrid approaches, level production stands out as a pivotal method for managing operations and aligning with business objectives.
The “level production strategy“, which offers a promising solution for businesses seeking to maintain consistency in their product output.
By implementing this approach, businesses can ensure a steady production rate that caters to market demands and optimizes operational efficiency.
This blog post will explain what level production strategy is, how it works, and its advantages, and disadvantages. It also explains the factors to be considered in this production strategy.
Evaluate level production strategy using our online Level production strategy calculator
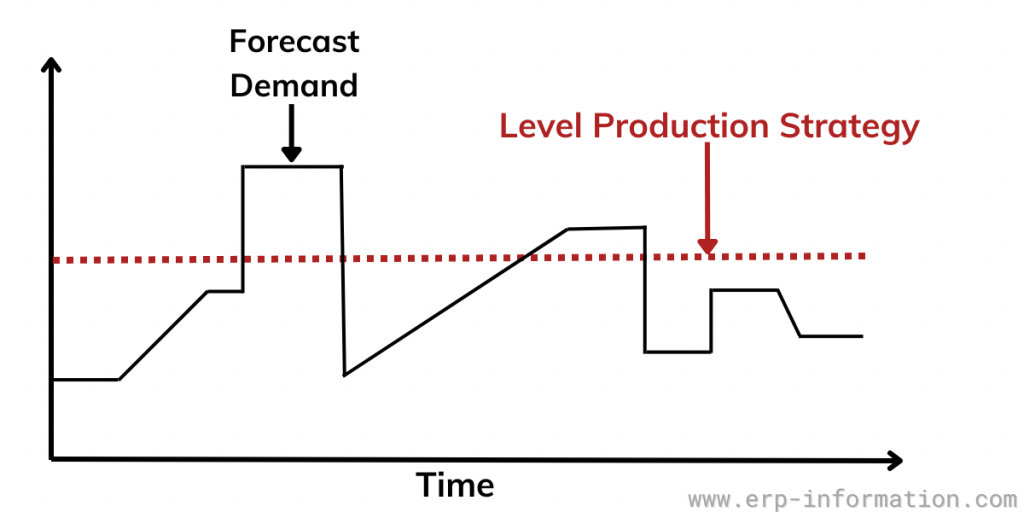
What is Level Production Strategy?
The level production strategy involves consistently manufacturing a set quantity of products at a steady rate. This approach is commonly employed by businesses dealing with a diverse range of products, making it applicable to both manufacturing and service industries alike.
How Does It Work?
The essence of the level production strategy lies in maintaining a uniform product output. To achieve this, businesses must determine their daily production requirements and establish a reliable schedule.
This schedule should possess the flexibility to adapt to fluctuations in demand while ensuring the steady creation of a consistent product.
Level Production Formula
Here’s a closer look at the core formulas that facilitate this strategy:
1. Production Required
Production Required=Total Demand−Beginning Inventory
This formula calculates the total production needed for a period by considering the initial inventory and the demand.
2. Minimum Production Per Month
Minimum Production Per Month=Total Demand/Number of Months
It distributes the total demand evenly across the available months, ensuring a steady production rate.
3. Workers Required
Workers Required=Minimum Production Per Month/Units Produced by Worker
This formula helps determine the number of workers needed to meet the minimum production requirements based on the productivity per worker.
4. Actual monthly production
Actual Monthly Production=Number of Workers×Units Produced by Worker
Reflects the actual production capacity based on the workforce and their individual output levels.
5. Ending Inventory
Ending Inventory=Beginning Inventory+Regular Production−Demand
Calculates the inventory at the end of the period by considering what was initially available, produced, and sold.
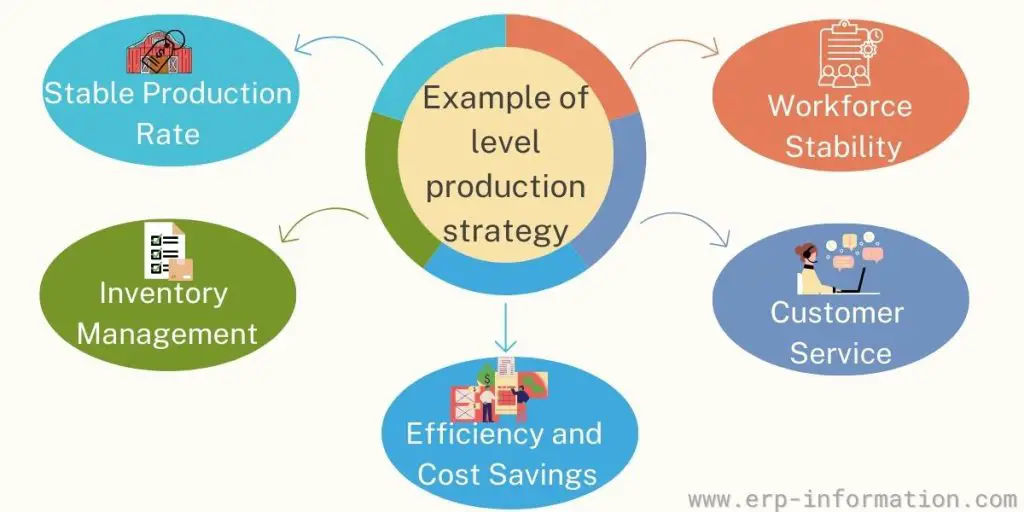
Example of level production strategy
We will have in-depth knowledge of the work of production strategy with this example.
In the bicycle manufacturing industry, there are often seasonal fluctuations in demand. For instance, there might be a surge in demand during the spring and summer months when more people engage in outdoor activities like cycling. On the other hand, demand may decrease during the fall and winter months.
The company decided to implement a level production strategy to ensure a steady and consistent production rate throughout the year. Here’s how it works:
Stable Production Rate
The company establishes a constant production rate that remains relatively unchanged regardless of seasonal variations in demand. This means that, on average, the same number of bicycles are produced each month.
Inventory Management
During peak demand months, the company produces more bicycles than are immediately needed and builds up a surplus inventory. In contrast, during low-demand months, the company continues to produce at the same rate, using the accumulated inventory to meet customer orders.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
By maintaining a consistent production level, the company can optimize its manufacturing processes and achieve economies of scale. This results in cost savings as the production lines operate efficiently without the need for frequent adjustments or shutdowns.
Customer Service
Under the level production strategy, the company can promptly meet customer orders irrespective of the season, offering a consistent supply of bicycles throughout the year. This fosters customer satisfaction and builds loyalty.
Workforce Stability
Since the production rate remains relatively stable, the company can maintain a more consistent workforce. This avoids the need for frequent hiring and layoffs, contributing to employee morale and reducing the costs associated with fluctuating labor demands.
The bicycle manufacturing company’s adoption of a level production strategy helps it navigate through the seasonal variations in demand, optimize its operations, and provide a reliable supply of bicycles to customers throughout the year.
This approach not only meets customer needs but also enhances operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness for the company.
Factors to be Considered in Level Production Strategy
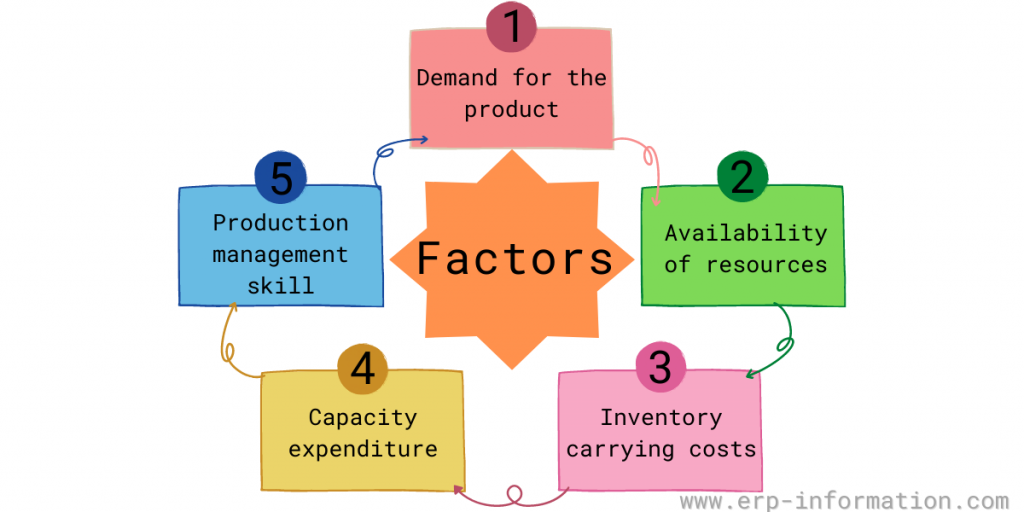
There are a few factors that businesses need to consider when using the level production strategy. These include:
The demand for the product
This is perhaps the most critical factor, as enterprises must ensure that they produce enough of the product to meet customer demand.
If demand is too high, there could be stockouts and disappointed customers; if demand is too low, businesses will end up with surplus inventory, which can tie up cash flow.
The availability of resources to produce the product
Businesses need to ensure that they have the necessary resources (e.g., raw materials, labor, etc.) to make the product. If resources are not available, then production will be delayed.
The inventory carrying costs
Businesses need to weigh the costs of holding the stock against the benefits of having inventory available to meet customer demand. Moving costs can include things like storage space, insurance, and depreciation.
Capacity expenditure
Businesses need to consider the costs associated with producing the product. These costs can include things like machinery, labor, and overhead.
Calculate capital expenditure using our online Capital Expenditure Calculator
Production management skills
Businesses need skilled personnel to manage the production process effectively. Poorly managed production can lead to delays, errors, and increased costs.
Evaluate stock out cost using our Online Stock Out Cost Calculator
Advantages and disadvantages of level production strategy
Advantages
Creates a consistent product
Manages workforce
Achieves economics by scale
Efficient and smooth
Disadvantages
It can lead to stockout
It can lead to overstock
It can be inflexible
Expensive
Advantages
Creates a consistent product
One of the main advantages of using the level production strategy. By producing a fixed number of products at a fixed rate, businesses can ensure that the quality of their product is consistent.
Achieves economics by scale
A level production strategy can help a business achieve economies of scale by producing a larger quantity of a product. That can lead to lower costs per unit and increased profits.
Manages workforce
A level production strategy can help a business better manage its workforce. For example, when products are produced in large quantities, the industry can schedule workers in shifts to ensure that someone is always available to make the product. That can lead to increased efficiency and productivity.
Efficient and smooth
Another advantage of the level production strategy is that it is efficient and smooth. This type of production strategy helps ensure that the production process is smooth and efficient and allows for better control over product quality.
Disadvantages
The level production strategy also has a few disadvantages, including:
It can lead to stock-out
One of the main disadvantages of the level production strategy is that it can lead to stockouts. That is because businesses must produce a fixed number of products, regardless of customer demand.
If customer demand increases, businesses could find themselves without enough products to meet demand.
It can lead to overstock
One more downside to this strategy is that it can lead to inventory buildup, as the product is produced even if there is no demand for it.
It can be inflexible
Another disadvantage of the level production strategy is that it can be severe. This is because businesses must commit to producing a certain amount of product, even if customer demand changes. This can make it difficult for companies to respond to changes in the market.
It can be expensive
The level production strategy is a pricy undertaking. This is because businesses need the necessary resources (e.g., labor, materials, etc.) to produce the product. Additionally, companies need to consider the costs associated with holding inventory.
FAQs
What are level production strategy examples?
The level production approach can be adopted in various industries. It is particularly prevalent in sectors marked by high fixed costs and predictable demand fluctuations. Here we give you a few examples of how this strategy is applied:
Food and beverage processing: The level production strategy is commonly employed by food and beverage processors to maintain a steady production of items like bread, milk, and cereal every month.
By doing so, they can reduce costs, improve overall efficiency, and guarantee a consistent supply of food and beverages to consumers.
Automotive manufacturing: In this industry, companies employ the level production strategy to produce a consistent number of vehicles each month, irrespective of changes in demand. This approach aids in cost reduction and enhances operational efficiency.
Consumer electronics: Manufacturers implement a level production strategy to generate a consistent quantity of electronic products like smartphones, TVs, and laptops every month. This helps to minimize costs, streamline operations, and ensure product availability.
Pharmaceuticals: Here the level production strategy is used to consistently manufacture drugs and vaccines every month. This approach aids in cost optimization, and operational streamlining, and ensures a reliable supply of medications for patients.
How is level production strategy helpful for fast-food industries?
Fast-food industries often adopt a level production strategy to navigate the challenges of operating in a high-demand, low-margin environment.
In this approach, production is maintained at a consistent pace, aligning with market demand.
The benefits of employing a level production strategy in the fast-food sector include ensuring a dependable supply of products, optimizing workforce and equipment utilization, minimizing wastage, and adapting efficiently to market trends.
This strategy not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to cost-effectiveness and the ability to meet customer expectations in a dynamic and competitive market consistently.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a level production strategy is an approach where the amount of output produced in each period is maintained at a constant level.
This strategy is commonly paired with chase production. In this article, we’ve delved into the advantages and disadvantages of adopting a level production strategy.
A key benefit lies in its potential to reduce costs and enhance production efficiency. Nonetheless, a notable drawback is the risk of stock shortages when demand spikes.
Despite this challenge, the overall impact of a level production strategy can prove valuable for businesses in their planning endeavors. We hope this article helped you understand level production strategy better.