MRP II stands for Manufacturing Resource Planning, a system designed to help companies plan their manufacturing process more efficiently and accurately.
Manufacturers use MRP II systems to forecast demand, schedule production processes such as assembly lines, and maintain inventory levels across various channels like warehouses or stores.
This post will discuss the basics of MRP II, including its importance, benefits, and how to create it. The post also discusses the difference between MRP 1 and MRP 2.
Key insights
- MRP II is a comprehensive system that integrates and manages various resources, including materials, human capital, and machinery, to optimize manufacturing processes.
- MRP I (Material Requirements Planning I) is a system focused on managing and planning materials needed in manufacturing processes.
- MRP II extends beyond materials to manage and integrate the entire manufacturing process, including human resources and production capacity, while MRP I focuses primarily on material requirements planning.
What is Manufacturing Resource Planning?
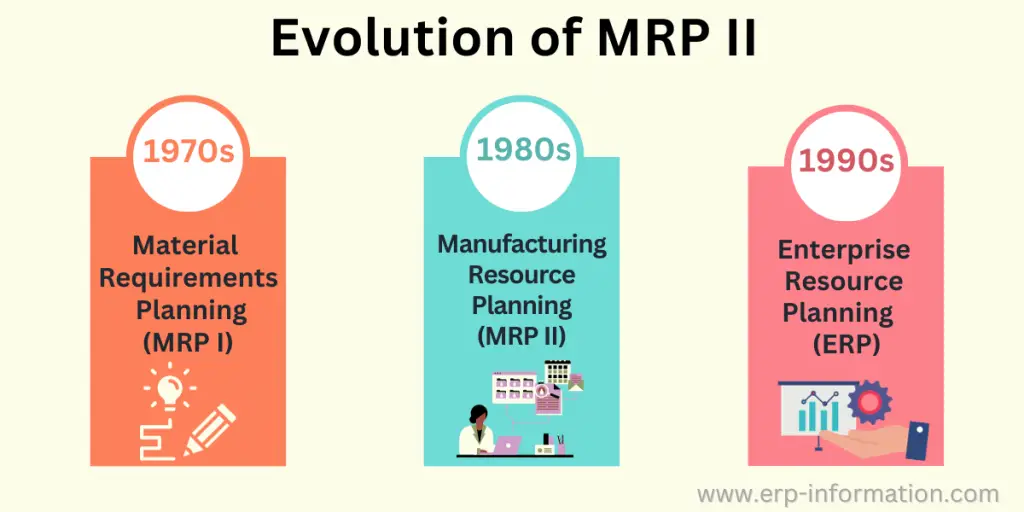
Manufacturing Resource Planning is an integral part of an information system used by businesses. It has evolved from the initial Materials Requirements Planning (MRP I) systems by incorporating additional data, including employee and financial requirements.
The integrated information system of MRP II concentrates, accumulates, and processes the information so that the third party can leverage this information for scheduling, design engineering, inventory management, and cost control in manufacturing.
Material Requirements Planning and Manufacturing Resource Planning are the predecessors of Enterprise Resource Planning(ERP), a procedure-oriented methodology in which manufacturers smartly manage all the critical aspects of their business.
An ERP management information system unifies various areas like planning, purchasing, inventory, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources. ERP is commonly associated with software, and numerous extensive applications have been developed to assist companies in properly implementing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).
Overview
Manufacturing Resource Planning is a computer-based integrated information system that devises precise and accurate production schedules. It leverages real-time data to synchronize the arrival of raw materials with machine and labor availability.
Its advent aim is to fix the shortcomings or constraints of Material Requirements Planning (MRP I). To maintain backward compatibility, it contains all the critical features of MRP I. It is often a helpful and relevant tool to enhance the core functionality of the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system.
By the end of the 1980s, manufacturers and business owners realized that they needed a specific kind of software that could easily incorporate into their accounting system and prophesy the amount of inventory required to accomplish a particular task.
Manufacturing resource planning is a leading software-based integrated information system that boosts the overall performance of the organization. It relies on a sales forecast-based helpful system in scheduling raw material deliveries and quantities.
Aside from all these managerial uses, it has been extensively used to precisely predict the amount of human capital, machinery, and IT Infrastructure required to achieve a sales target.
How to Create an MRP II System?
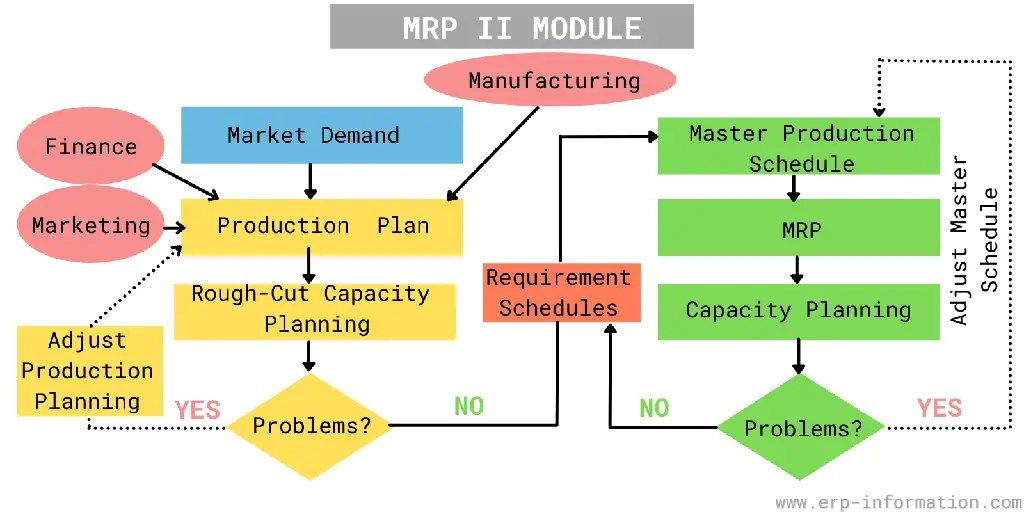
To create an MRP system, consider the following main resource management and manufacturing processes.
The Master Production Schedule (MPS)
Master Production Schedule (MPS) is a planning tool used to help manufacturing businesses manage production schedules, inventory levels, and customer demand. The MPS outlines the quantity of each product that needs to be manufactured within a certain time frame based on the forecasted demand.
The MPS considers many factors, such as sales forecasts, inventory levels, lead times, and capacity constraints, to ensure that production schedules are optimized and meet customer demands.
The Inventory Status File (ISF)
An Inventory Status File (ISF) is a document that provides up-to-date information on a company’s inventory levels. It contains information such as the quantity of each product on hand, the location of each item in the warehouse or storage facility, and any outstanding orders or backorders.
ISF is used by businesses to help them manage their inventory levels and ensure that they have enough stock to meet customer demand.
By regularly updating the ISF, companies can quickly identify any potential shortages or overstocks and take action to adjust their production or reorder levels accordingly.
The Bill of Materials (BOM)
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a comprehensive list of all the materials, parts, components, and sub-assemblies needed to manufacture a product. It outlines the quantity of each item required to produce the final product.
The BOM is an essential tool for manufacturers, providing a detailed breakdown of all the raw materials and other inputs needed to create a specific product.
Shop Floor Management
This feature tracks manufacturing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and monitors all activities on the production floor, ensuring real-time oversight and efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Order Management
This functionality enables companies to efficiently handle customer purchase orders, issue sales orders, and monitor the entire production, shipping, and delivery cycle, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational transparency.
Cost Management & Accounting
When selecting MRP II software, organizations must ensure it includes robust capabilities for tracking the costs of direct materials and labor involved in the production process, aiding in precise cost control and financial planning.
Production Capacity Planning
Effective workforce and asset management functionalities are crucial for determining resource availability, facilitating accurate production capacity planning, and optimizing resource utilization.
Use our online Production Capacity Calculator for production capacity planning.
Real-World Examples of MRP II Software
It is a tool that helps manufacturing businesses and supply chain managers stay in today’s competitive business world.
Currently, the following are the vendors, and they are well-known providers of MRP II software.
- Acumatica
- Infor
- Epicor
- Oracle Netsuite Manufacturing Edition
- Microsoft Dynamics
- IQMS
- Fishbowl
- FactoryEdge
- Prodsmart
- Abas
- S2K Enterprise
Importance of MRP II software
- Helps you to acquire valuable details about the right time for ordering.
- Helps you to determine the amount of raw materials needed to order from the suppliers
- Generates orders for raw material input.
- Makes the periodic arrangement of all the orders.
These are crucial to address the ever-growing demands of customers and the whole manufacturing process. The software regularly calculates raw materials requirements, and all the calculations are based on order forecasts.
Additionally, this software also changes to offset the potential issues that may arise in the future. This attribute is way more effective and accurate than the traditional management system.
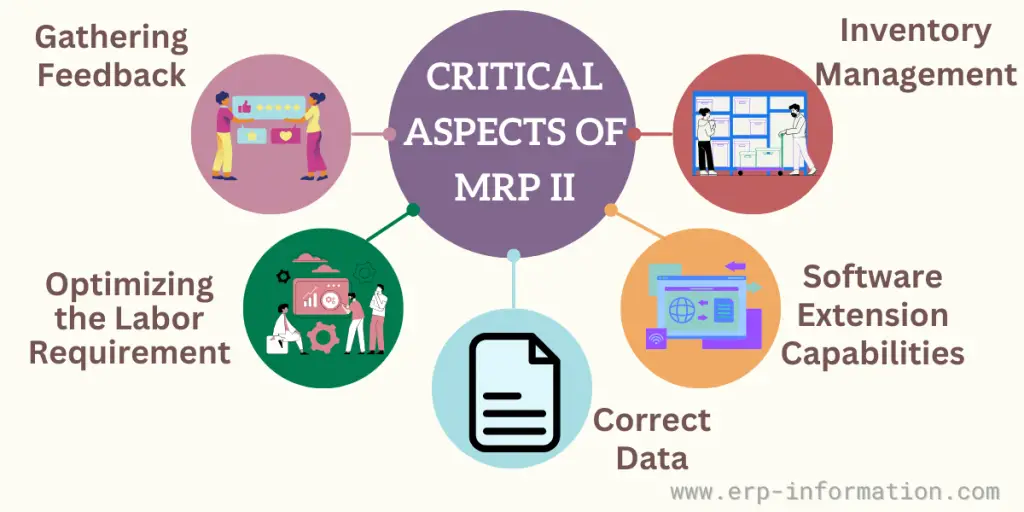
Few Critical Aspects
Following are the critical aspects of it categorically.
Gathering Feedback
MRP II gleaned valuable feedback from the production floor and stored this information more robustly and systematically.
It integrates the stored information to all schedule levels to ensure the regular up-gradation of the next run.
Inventory Management
Inventory management control includes a scheduling capability that strongly emphasizes the significant resources, such as plant, machinery, and raw materials, which are crucial in producing finishing goods.
It generates the most precise and accurate data that can assist an individual in gaining firm control over the manufacturing process.
Software Extension Capabilities
Aside from inventory control and recovery, other programs are incorporated into the MRP II. Some of these programs are specifically designed to make the scheduling process more helpful.
It also comes with an in-built option for sale ordering processing. In addition, stock recording and cost management accounting lie in their realm.
The above attributes are embedded in the company’s primary database system. MRP has in-built advanced planning capabilities that include:
- Minimize the panning activities
- Automated computerized ordering of raw materials for the production of finishing goods
- Hard and soft allocation
Optimizing the Labor Requirement
For example, the software calculates the labor required to meet daily, weekly, or monthly labor schedules. MRP II smartly manages the labor based on qualifications and relevant skill sets.
Correct Data
This system is useful when the initial data must be correct and accurate. It is evident from the past track record that the companies that develop and deploy software strongly recommend their users to enter only the correct and accurate data. That helps in utilizing the full potential of MRP II.
Benefits of Manufacturing Resource Planning
These are the potential benefits,
- Undoubtedly, MRP II is an innovative and highly competitive tool that has completely revolutionized the traditional stock control and management method.
- Software framed an effective and consistent production schedule, allowing any company to manage its operating expenses smartly by reducing money, time, and human capital.
- Planning with the aid of automated software MRP II makes a company way more efficient than ever before. Thus, in simple words, we can say that MRP II acts as a helpful tool for profit optimization as it reduces unnecessary expenses.
- Data gleaned through MRP allows the companies to frame an effective strategy for the future and prophesy how their strategy can affect the business’s profitability.
- The automated system of MRP provides a piece of more robust and detailed information that any company can easily leverage to accomplish its core functions, such as planning, effective decision-making, and production.
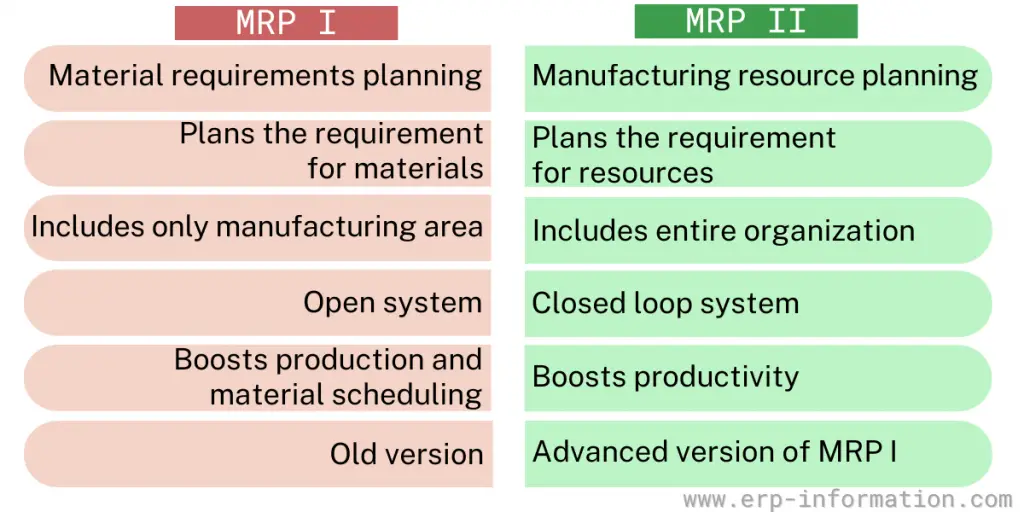
MRP I vs MRP II
MRP II is an advanced version of MRP I. MRP II is much ultra-modern software providing the best vision into all production areas.
MRP II includes the functionalities of MRP I along with some additional functionalities. MRP I is the plan for the materials requirements, and MRP II is the plan for resource requirements.
Conclusion
Manufacturing Resource Planning has revolutionized the way manufacturers manage their resources and processes. By integrating various elements such as materials, human resources, and machinery, it provides a comprehensive and precise system for optimizing production.
Its advanced capabilities surpass those of MRP I, offering a more holistic approach to resource management. As businesses continue to seek competitive advantages, adopting MRP II can be a game-changer, driving better decision-making, cost control, and overall operational excellence.