Imagine walking into a bustling restaurant on a busy Friday night. The tables are full, the waiters are rushing back and forth, and the kitchen is a cacophony of pots and pans clanging. It’s all controlled chaos, but it’s somehow working.
The reason why everything is running smoothly is because of careful planning and coordination. The restaurant manager has calculated how much food and supplies will be needed for the evening, and the kitchen staff has prepared everything accordingly.
This same level of planning and coordination is essential for any business that wants to be successful.
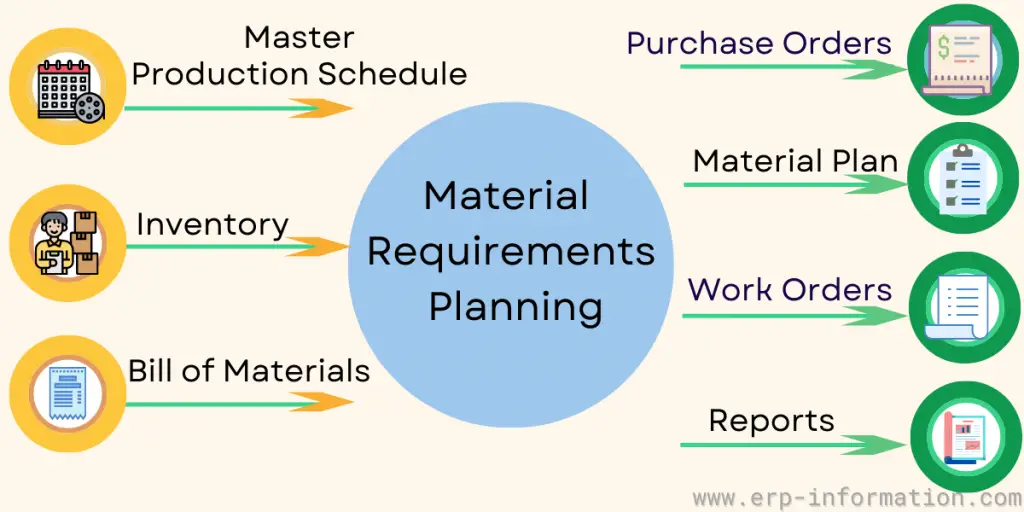
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) system helps businesses plan their material needs by predicting future demand and calculating each item’s stock levels. That ensures they have the right materials at the right time.
MRP is a complex topic, but it can be explained in simple terms. It is a software-based system that uses historical sales data, current inventory levels, and production schedules to calculate how much of each material is needed and when it is needed.
This blog post will explore what MRP is, how it works, its benefits, and its limitations. It will also give steps for implementing material requirements planning software, some essential tips, and a list of available popular MRP software systems.
Definition
Material Requirements Planning is a system for managing the production and inventory of goods. It helps businesses plan their manufacturing processes and ensure that they have suitable raw materials to meet customer demand.
It is a material management method used to ensure that the production of goods matches the demand for those goods.
Brief History
MRP emerged in the 1960s as a revolutionary approach to production and inventory control. Initially developed by Joseph Orlicky, an engineer at IBM, the MRP system aimed to address the challenges of managing complex manufacturing processes and controlling inventory effectively.
MRP gained significant traction in the 1970s, with software developers creating dedicated MRP systems. The concept spread across industries, becoming a standard in manufacturing and supply chain management.
Over time, MRP systems evolved, incorporating advanced features and integration capabilities.
Today, MRP has grown into a fundamental tool for optimizing production and materials planning, playing a crucial role in modern manufacturing and supply chain management.
How does it work?
It works by following material through the production process on a schedule. This allows companies to monitor their inventory and ensure that they have enough material on hand to meet demand.
It uses data from manufacturing operations, machines, and equipment. Materials lead time, material costs, storage cost, and inventory levels to predict what materials will be needed at specific future times.
Knowing the level of inventories available now versus what is expected will soon be required to help managers decide whether more raw materials need to be purchased directly or acquired later.
Historically, it has been used to manage the material flow in manufacturing companies. It uses a mathematical model of material flows through an organization and production facilities (e.g., factories).
This is done by linking work centers together using bill-of-materials data from each affected work center. The result is that organizations can track material.
Benefits
Its benefits are vast and can significantly impact any business. The system allows businesses to optimize their production process by forecasting material needs and managing inventory levels.
As a result, it can help companies minimize waste, ensure timely production, and reduce costs.
It has several benefits for manufacturers and suppliers. First, material requirements are known as forecasted demand, which estimates material needed during the time frame for production or deliveries to customers.
Some of the benefits of MRP include the following:
- Efficient Inventory Management: MRP helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing excess stock, and minimizing carrying costs.
- Enhanced Production Planning: It aids in creating production schedules based on actual demand, leading to better resource allocation and production efficiency.
- Improved Customer Service: MRP ensures timely deliveries and minimizes stockouts, resulting in better customer satisfaction.
- Reduction in Lead Times: By planning material procurement in advance, lead times can be reduced, leading to faster production cycles.
- Cost Reduction: MRP optimizes resource utilization, reduces waste, and lowers production and inventory costs.
Limitations
However, it also has some limitations.
- Complex Implementation: Setting up an MRP system can be complicated and requires extensive data input and training.
- Data Accuracy: It heavily relies on accurate data, and any inaccuracies can lead to incorrect planning and costly errors.
- Inflexibility: This system may struggle to adapt to sudden changes in demand, making it less suitable for dynamic markets.
- Costly Software: The software can be expensive to purchase and maintain, especially for small businesses.
- Overemphasis on Quantities: It tends to focus on quantity and may not consider other factors like supplier reliability or quality.
- Time-Consuming: Running MRP calculations and maintaining the system can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Risk of Overstocking: If not properly managed, it can lead to overstocking, tying up capital in excess inventory.
Steps for MRP Implementation
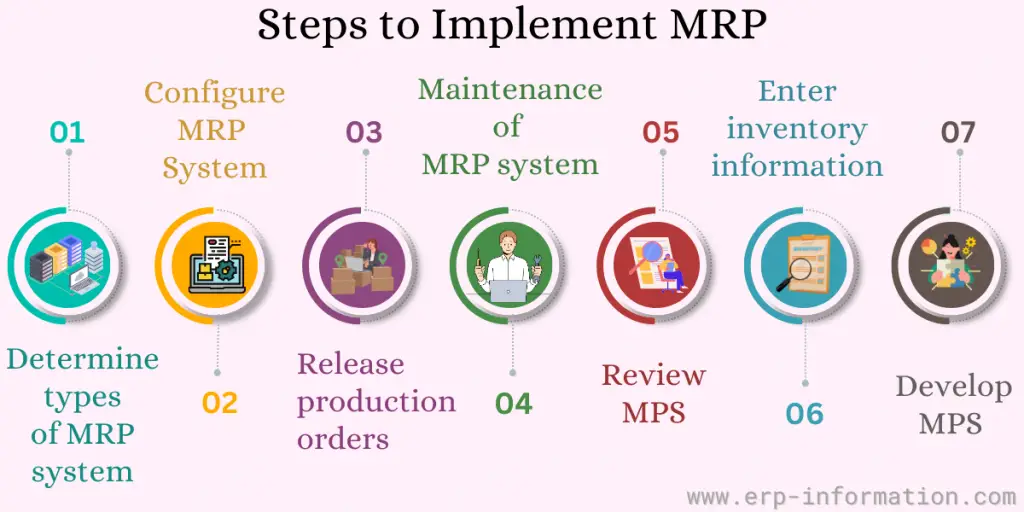
If you’re looking to implement this system in your business, there are a few key steps. You can ensure that your business has a smooth and efficient production process by following these steps.
The implementation steps are as follows:
- First, determine the type of system that is best for your business.
- Next, develop a master production schedule.
- Configure the system.
- Enter inventory information into the system.
- Review and revise the master production schedule.
- Release production orders to the shop floor.
- Perform system maintenance.
Tips to Use Successfully
Following are a few tips that can help while using systems. The following list is not specific to any particular system. However, general guidelines are applicable to most of them.
- Multiple requirements cannot be scheduled for the same material, material group, lot size, or change date.
- You will not create requirements if no lead time is specified under material or item properties.
- It does not generate nodes with inventories below the “minimum safety level.”
- When you change the material or the item, the requirements are not recalculated automatically.
- You must calculate the material required for each dependent demand node with the same lead time and sequence used on the master production schedule.
- Maintain correct storage locations to avoid calculating incorrect requirements. For example, if a material is received in storage, store all its parts there.
- It does not recalculate requirements if a vendor change or stock transfer occurs after the production order has been released but before it releases to production. Therefore, make sure to update material requirements when this happens manually.
- The company will not automatically send you more when you run out of material and need more.
- When material groups, lot sizes, or change dates below the minimum safety stock level have been entered for requirements and a negative quantity of controlled items results, no further material requirement is calculated. Therefore, it must be deleted from production to avoid triggering this error message again.
- If material groups are defined for material, then a material requirement will be calculated when the node has released quantities. It does not depend on other nodes with different lot sizes or change dates.
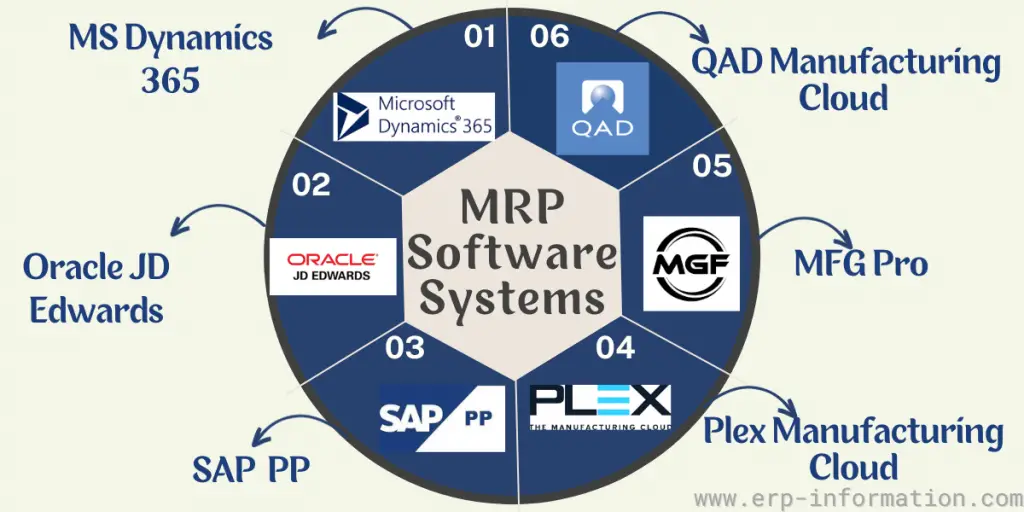
List of Popular Systems
Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Manufacturing
Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Manufacturing is a comprehensive system that can handle all aspects of your manufacturing process, from material requisition to finished product shipping.
Oracle JD Edwards
It is a widely used system for medium to large businesses. It offers robust features and functionality for managing material requirements and Production operations.
SAP Production Planning (PP)
PP is part of SAP enterprise resource planning. With PP, companies can create detailed production plans that consider the availability of resources, the requirements of customers, and the capacities of manufacturing facilities.
PP also helps companies optimize their production processes by predicting how changes in one area affect other production areas. For example, suppose a company adds a new product to its lineup.
PP can help show how much more production capacity you will need. Of course, it would be best if you had this in a place close to the people who want it.
Plex Manufacturing Cloud
It is a comprehensive system that helps you plan and control the flow of materials through your production process. It gives you the ability to optimize inventory levels and improve production efficiency. It is a cloud-based system, so you can access it from any device with an internet connection.
MFG Pro
MFG Pro is a system that helps you manage your inventory and production. It is a comprehensive solution integrating manufacturing, distribution, and accounting operations into a single system. MFG Pro enables you to plan production, schedule jobs, track material usage, etc.
QAD Manufacturing Cloud
It is a comprehensive system that helps you plan and control the flow of materials through your production process. It gives you the ability to optimize inventory levels and improve production efficiency.
MRP in manufacturing
When a company begins manufacturing a product, it first determines the necessary materials and components for the product. This process is known as material requirements planning (MRP). MRP involves creating a parts list for the product and then ordering the necessary materials to produce the product.
To create an accurate parts list, the company must first determine the bill of materials (BOM) for the product. The BOM lists all of the individual components that make up the product. The company then creates a schedule for producing the product, which includes ordering times and quantities for each component.
The company uses this schedule to order the necessary materials and components for the product. Once the components arrive, the company can begin manufacturing the product.
Input and outputs
Inputs for material requirements planning can include forecasted demand, past sales data, inventory levels, and supplier lead times.
The output of MRP is a production schedule and a materials requirement list.
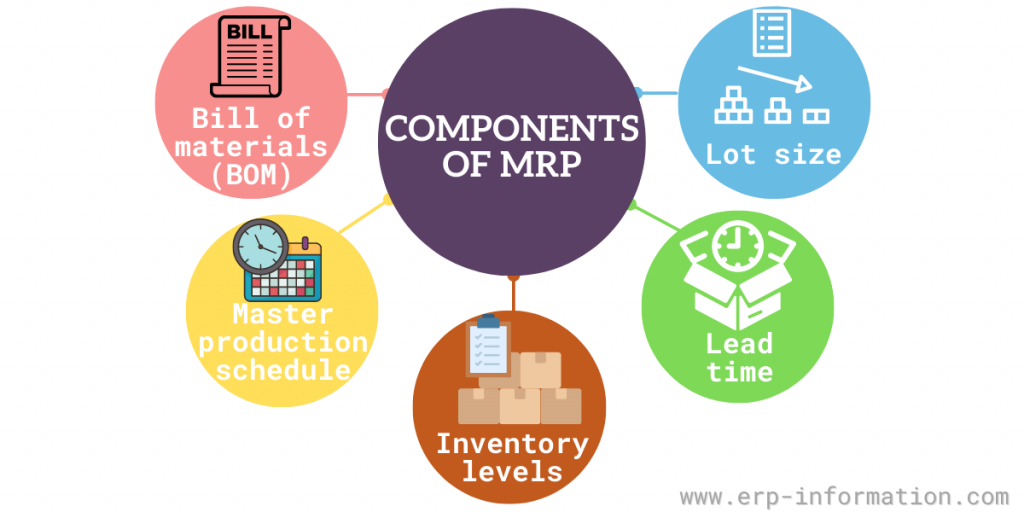
Components
The components of material requirements planning (MRP) are:
- Bill of materials (BOM): A list of the components that make up a product, along with the quantity of each component needed to produce one unit of the product
- Master production schedule (MPS): A schedule that shows how much product needs to be produced and when it needs to be produced
- Inventory levels: The amount of each component on hand and how much is needed to meet the demand from the MPS
- Lead time: The time it takes to produce a component or finish a product
- Lot size: The number of components or products that are produced at one time
Relationship and Difference Between MRP and ERP
There are several interconnections between Materials resource planning and ERP in the domain of manufacturing and supply chain management. MRP often functions as a subset within ERP, with seamless integration.
Both systems rely on common data, encompassing bills of materials, inventory levels, production schedules, and demand forecasts, ensuring consistent and accurate decision-making.
However, they differ significantly in scope and functionality
MRP
(Material Requirement Planning)
- It specializes in material planning and inventory management, generating purchase orders and production schedules to meet demand.
- It is operationally focused and primarily used by production and inventory management teams.
- It is typically employed by manufacturers with a primary focus on production planning and inventory control.
ERP
(Enterprise Resource Planning)
- It is a comprehensive system that extends beyond MRP.
- It manages various business functions, including finance, HR, sales, manufacturing, and supply chain, serving as a central system for decision-makers across the organization.
- It can accommodate a wide range of industries and business sizes, from small enterprises to large corporations. It is designed to support complex business processes and integrated management, allowing for a holistic view of organizational operations and facilitating cross-functional decision-making.
Relationship and Difference Between MRP and DRP
In the domain of supply chain management, both (MRP) and Distribution Resource Planning (DRP) have unique roles contributing significantly to its efficient operation.
MRP
(Material Requirement Planning)
- It is to prioritize the planning and supervision of essential raw materials and commodities, ensuring streamlined production and inventory operations.
- It relies on data related to production requirements, inventory levels, and bills of materials.
- It concentrates primarily on production and material management, ensuring the availability of necessary materials for manufacturing processes.
DRP
(Distribution Resource Planning)
- It focuses primarily on supply chain logistics, aiming to efficiently manage the transportation of finished goods from production or storage sites to distribution centers, retailers, or end customers.
- It works with data such as sales forecasts, order information, distribution center inventory, and transportation logistics.
- It is dedicated to optimizing the distribution network, ensuring the timely and cost-effective delivery of finished products to customers.
While MRP and DRP often operate in conjunction, integrated within an overarching Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) framework, they serve distinct purposes.
This integration ensures seamless collaboration between material planning and distribution planning, streamlining the overall supply chain.
FAQs
What are MRP systems?
These systems are automated inventory management solutions that use material requirement data to determine how much material you need. In addition, MRP II introduced the idea that materials are required with production schedules.
What is the Material Requirements Planning system in SAP?
In SAP, it calculates the need for materials and components to meet planned production demands. The MRP run in SAP produces a material requirements plan, a schedule for each manufacturing order, and a planned delivery date.
What is the difference between material requirements planning and manufacturing resource planning (MRP II)?
Manufacturing resource planning is a complete version of material requirements planning that considers dependent demand. Manufacturing resources planning includes capacity planning, production scheduling, and purchasing features. MRP II is used in larger organizations that have complex manufacturing processes.
Can I still use material requirements planning if my business is small?
Yes, it can be used by businesses of all sizes. However, smaller companies may find it more challenging to implement due to its comprehensive nature.
Is material requirements planning the same as inventory management?
No, MRP is a computerized production and inventory management solution that determines material needs based on a master production schedule. On the other hand, more administrative inventory management includes material storage and recordkeeping activities.
What is the difference between material requirements planning and production planning?
Material requirements planning is an automated inventory management solution that determines material needs based on a master production schedule. On the other hand, production planning organizes the work needed to produce a product.
What is the inventory status file?
The inventory status file is a report that shows the current stock levels of materials and components. This report determines whether materials or components are available to meet production needs.
How often should I run material requirements planning?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. However, it should be run as frequently as your material needs change, typically every few days or weeks.
What is a material master?
A material master describes materials used in production and includes item description, purchase information, and cost. In SAP terminology, the material master is known as a “material.”
How to calculate dependent demand in MRP?
Calculating it in material requirements planning can be done in simple steps. To calculate it, you first need to identify the independent demand and the material requirements. You then need to calculate the material required in the finished good. Once you have done that, you need to subtract the independent demand from the material requirement in the finished good. This will give you the dependent demand.
What is the Master Production Schedule in MRP?
A production plan shows how much of a product is needed and when. It tells when to make the product. The MPS is created by considering the forecast demand for products and the lead times for producing those products.
The MPS is used to create the production schedule, which tells workers when to produce each product. The production schedule tells you how much each product needs to be made and what resources are required. This information helps ensure that the correct number of products is made and that the right resources are available when they are needed.
Conclusion
If you have to deal with material requirements planning in your job, this post is for you.
We’ve detailed Material Requirement Planning systems and how they can help improve production schedules, material management, inventory control systems, demand calculations, and more! Learn about the fundamentals here today!
Reference