You’ve heard of MODAF but need to know what it is and how this framework can help your business.
It is an architecture framework that defines a standardized way of conducting enterprise architecture.
The framework was developed by the UK Ministry of Defense and is used by both the public and private sectors. It provides a way for organizations to design, plan, implement, and govern information systems.
This article will teach you all about the MODAF framework and its benefits. Once you understand how this framework works, you can start using it to streamline your business processes.
MODAF Framework
Every business is different, and as a result, each one needs a unique information system that meets its specific needs.
However, designing and building an information system from scratch can be incredibly time-consuming and expensive.
MODAF Framework provides businesses with a standardized way of conducting enterprise architecture. This framework defines a methodology for designing, planning, implementing, and governing information systems.
As a result, organizations can save time and money by using it instead of starting from scratch.
MODAF was created by the UK Ministry of Defence and is used extensively by the British MOD and other government agencies. The private sector has also adopted it for use in various industries.
MODAF Viewpoints
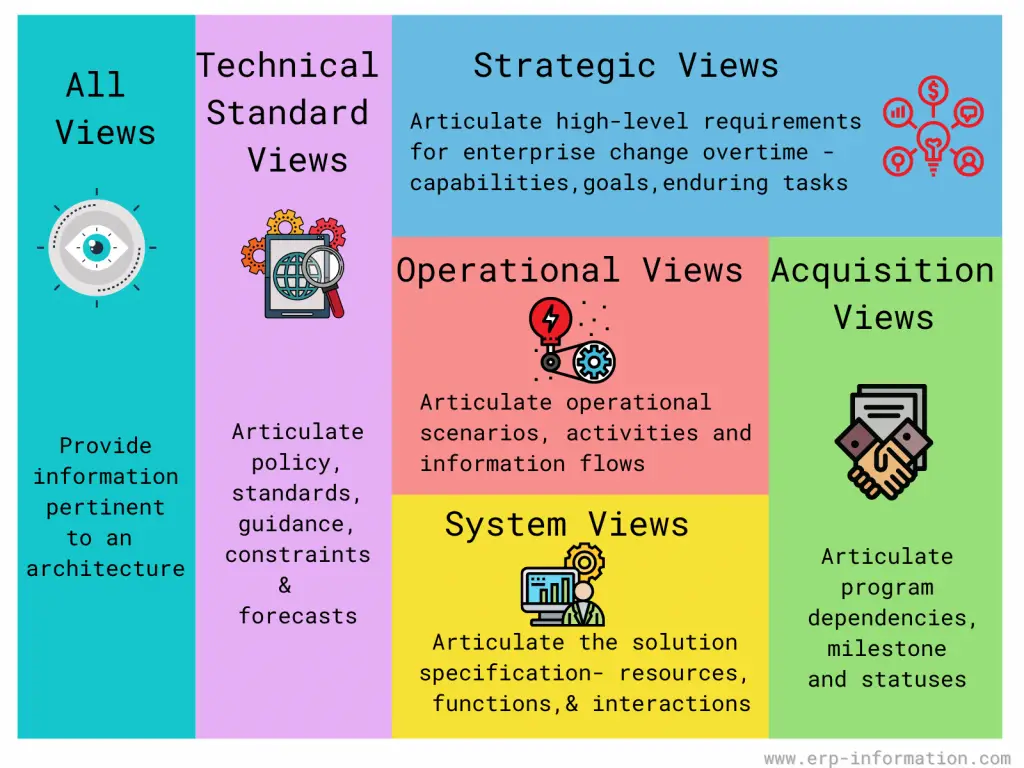
There are six categories of viewpoints.
- Strategic Views help businesses identify their goals and the skills needed to achieve those goals.
- Operational Views help to understand the steps, resources, activities, and information needed to complete business tasks.
- To define the solution, Systems Views describe what happens when Operational and service-oriented views are implemented.
- Businesses use Acquisition Views to detail the forecasted timeline and necessary elements for projects that will provide a solution.
- Technical Views encompass the standards, rules, and policies regulating different aspects of architecture.
- The All Views section contains an overview of the architecture and any related terminology, characters, or abbreviations.
MODAF Views
There are seven categories of views.
- Tabular: It consists of structured text as a subset that is primarily comprised of rows and columns.
- Structural: It contains diagrams describing the architectural components.
- Behavioral: It includes diagrams that illustrate the behavioral aspects of Architecture.
- Mapping: It offers a way to compare two different types of information side by side.
- Ontology: This View builds upon the MODAF ontology for a specific Architecture.
- Pictorial: The only category with a view is OV-1a, which shows a free-form picture.
- Timeline: It contains diagrams explaining the programmatic side of Architecture.
The MODAF framework is based on five core principles,
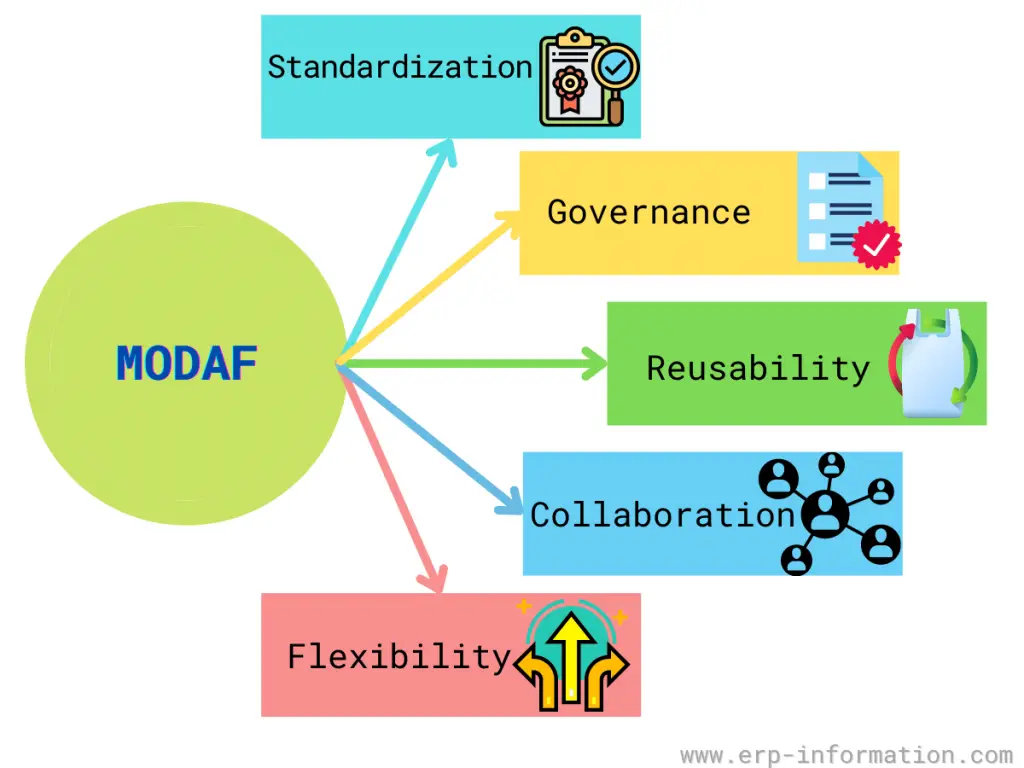
Flexibility
It is a flexible framework that can be applied to any organization and scaled up or down. As a result, it provides an adaptable approach for defining, designing, implementing, and governing information systems.
It offers four levels of granularity: strategic, operational, tactical, and technical; each class has its own set of models and views to support decision-making at that level.
Standardization
It provides a standardized way of conducting enterprise architecture, enabling organizations to share information and best practices. It is based on a standard set of principles, methodologies, and tools used across all MOD projects.
It also provides a standardized approach to enterprise architecture, enabling organizations to share information and best practices. Finally, it is based on a standard set of principles, methodologies, and tools used across MOD projects and other government organizations.
Collaboration
It enables collaboration between business and IT teams, which is essential for successful enterprise architecture projects. The framework provides a common language and approach that helps firms and IT teams work together more effectively.
Governance
It provides a governance model that ensures the quality and integrity of the architecture. In addition, the framework defines a set of processes and procedures for managing MODAF projects, which helps ensure that the architecture meets the organization’s business needs.
It also provides a governance model that ensures the quality and integrity of MOD architectures.
Reusability
It promotes reuse by ensuring that MOD architecture is based on reusable components. That helps to reduce costs and boost efficiency in MOD projects.
The framework encourages reuse by using common principles, methodologies, and tools; these can be applied to any organization, regardless of size or sector.
These principles are embodied in the MODAF meta-model, which provides a standard structure for describing IT systems.
The meta-model is composed of six core elements,
Systems
MODAF defines a system as an entity that provides a set of services to meet the needs of its stakeholders. A MOD system comprises software, hardware, and people, including data and documentation.
Processes
It defines a process as a set of activities performed to produce an outcome. People, software, or hardware may carry out MOD processes.
Products
A MOD product is something that is made using a process. It can be physical or intangible and can be used to support a system’s operation or meet stakeholders’ needs.
Data
It defines data as information collected and processed to provide insights and support decision-making.
MOD data may be structured or unstructured, and it may be used to support the operation of a system or meet the needs of stakeholders.
Organizations
It defines an organization as a collection of systems managed by one or more processes. An organization represents the highest level of abstraction in MODAF; it provides a way to group methods and procedures.
People
It defines a person as an entity responsible for operating a system or delivering a service. For example, a MOD person may be an employee, contractor, or stakeholder.
Benefits
Some of its benefits of it include:
- A common language for all stakeholders involved in defense
- Focuses on business needs rather than technology
- Helps with collaborative planning and execution
- Efficient and effective communication
- Reduced complexity and improved decision making
- Accelerated knowledge transfer and reuse
- Enables the business model to be shared across the organization
- Flexibility and agility
MODAF’s Process
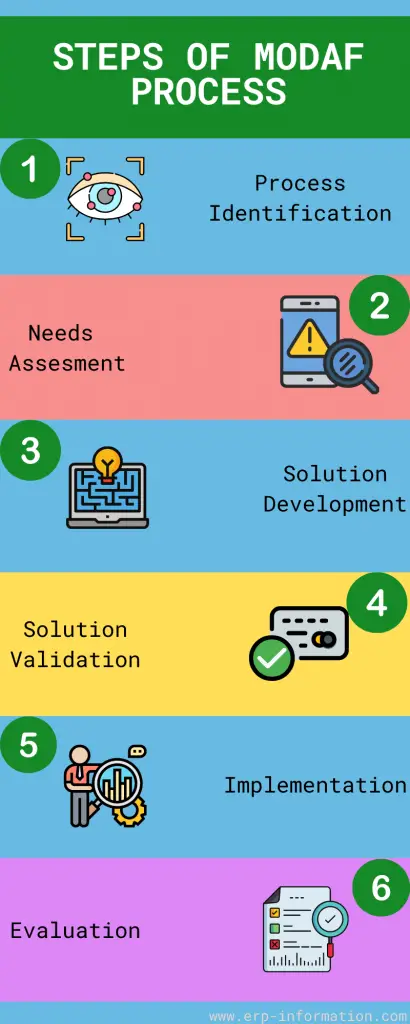
Following are the steps involved in the process,
Process identification
The first step in this process is to identify a small set of techniques that can be used to create a proof of concept. Once this has been achieved, the organization can model its business processes using MODAF.
Needs assessment
Each project begins with a needs assessment that identifies the business requirements for modeling processes.
The MOD Architecture is used to model all MOD processes, so there must be a clear requirement for this architecture before any work begins.
Solution development
MODAF’s process modeling and design tools can develop a solution that meets the business requirements and complies with MODAF architecture standards.
Solution validation
In this step, the solution is validated against MODAF’s process and product models. That ensures it meets all requirements and is consistent with MODAF’s standards.
Implementation
In the MODAF implementation phase, the MOD processes and MOD products are implemented. The MOD architecture is used to model all processes and products. That means there must be a clear requirement for this type of architecture before any work begins.
Evaluation
After implementing MOD products and processes, you must evaluate whether they meet the business requirements. MODAF provides many tools for evaluation, including process performance measurement and product conformity assessment.
MODAF’s Advantages over other frameworks
One of the key advantages over other architecture frameworks is its focus on business needs rather than technology.
It is also known for its flexibility and agility, enabling it to adapt to changing business requirements. The framework also provides a common language for all stakeholders involved in defense, which helps with collaborative planning and execution.
Additionally, it is known for its efficiency and effectiveness in communication, which leads to reduced complexity and improved decision-making.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have explored the MODAF Framework and discussed its benefits for business owners.
We have also looked at its process and advantages over other frameworks. Hoping this information was helpful and you will consider using it for your enterprise architecture needs.