In the business intelligence domain, data stands as the ultimate authority. However, raw data, in its unprocessed form, offers limited insights into the intricacies of an organization’s operations.
This is where Online Analytical Processing (OLAP in ERP) steps in. It is a transformative force converting extensive data pools into actionable intelligence and empowers businesses to make informed decisions that drive success.
It helps businesses analyze data quickly and efficiently to get a clear picture of what’s going on in their company and make the right choices for the future.
This blog post will discuss OLAP, its types, cube, analytical operations of cube, advantages, and disadvantages. It will also provide information on OLAP in ERP.
Definition
Online analytical processing is a type of database used for data analysis. It allows users to view data in different ways and analyze it differently. It is typically used for reporting and analysis; companies can track trends over time.
It helps to speed up the retrieval of complex analytical queries by organizing data in a multidimensional structure, often called a cube, and allows users to view the data in multiple dimensions. Hence it is also known as a multidimensional database.
What is OLAP in ERP?
OLAP is a process used to analyze data quickly and efficiently. It allows businesses to examine their data in multiple dimensions to understand what’s happening within their company. This can help with making informed decisions about the future of the company.
It is often used in conjunction with ERP software. ERP systems contain a lot of data that can be difficult to analyze manually. It helps to make this data more manageable and accessible.
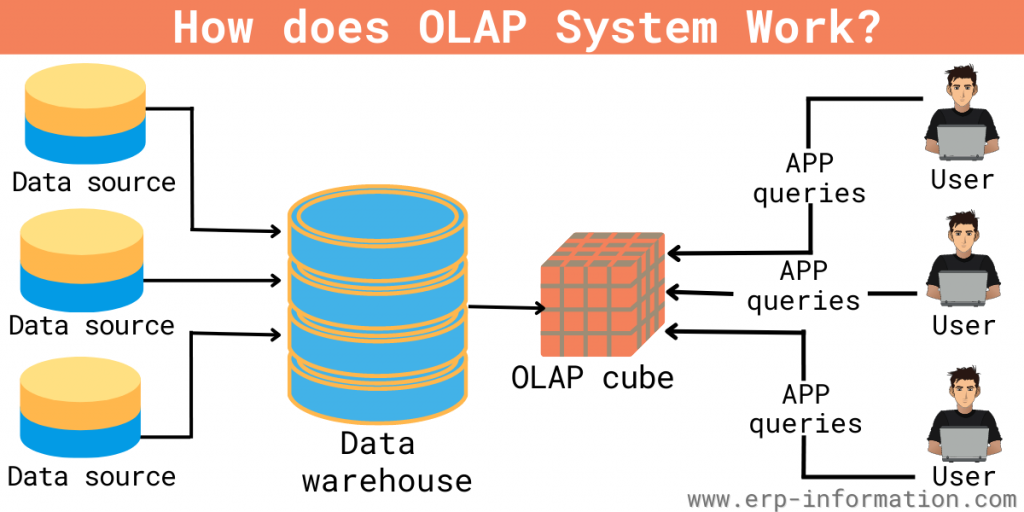
How Does It Work?
OLAP system works in the following manner.
- Data collection: Data is collected from various sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, or other data repositories.
- Data integration: The collected data is then integrated and stored in a data warehouse.
- Creation of OLAP cubes: The data from the data warehouse is organized into an OLAP cube.
- OLAP server: The chief component of online analytical processing is the OLAP server, which sits between a user and a database management system (DBMS), which understands how data is organized in the database and has special functions for analyzing the data. There are OLAP servers available for nearly all the major database systems.
- Data manipulation: Users can perform complex calculations, trend analyses, and data modeling. They can slice and dice the cube, meaning they can view data along different dimensions, drill down to see detailed data, or roll up to see summarized data.
- Data analysis and reporting: Users can then analyze the processed data and generate reports. The results can be presented in various ways, including tables, charts, or graphs.
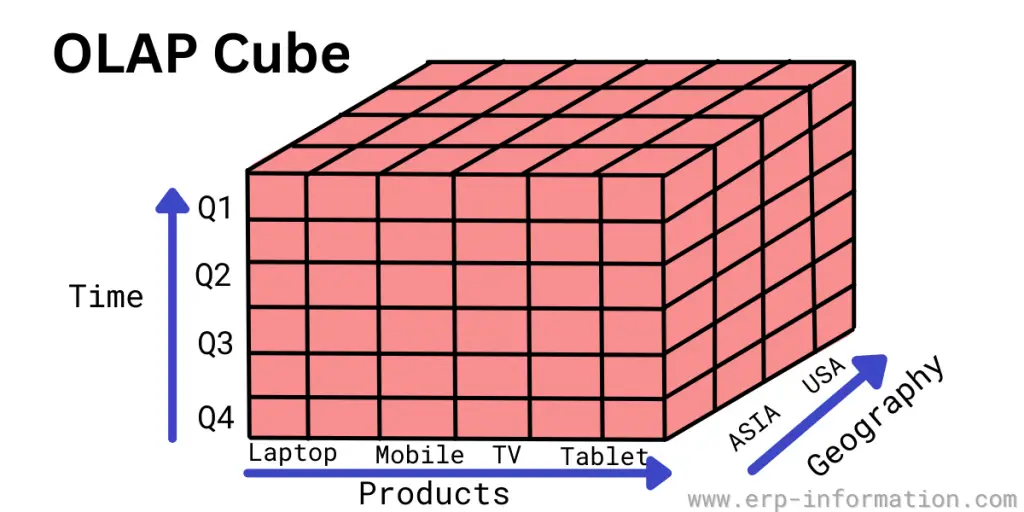
OLAP Cube
An OLAP cube is a multidimensional structure that allows users to model and view data in multiple dimensions. Each dimension represents a different category of information.
For example, dimensions in a sales analysis scenario could include product, region, time, and sales channels.
The cube classifies numerical facts (measures) by dimensions. Multidimensional data is stored and analyzed in this cube.
Analytical Operations in OLAP
Generally, it has four basic analytical operations.
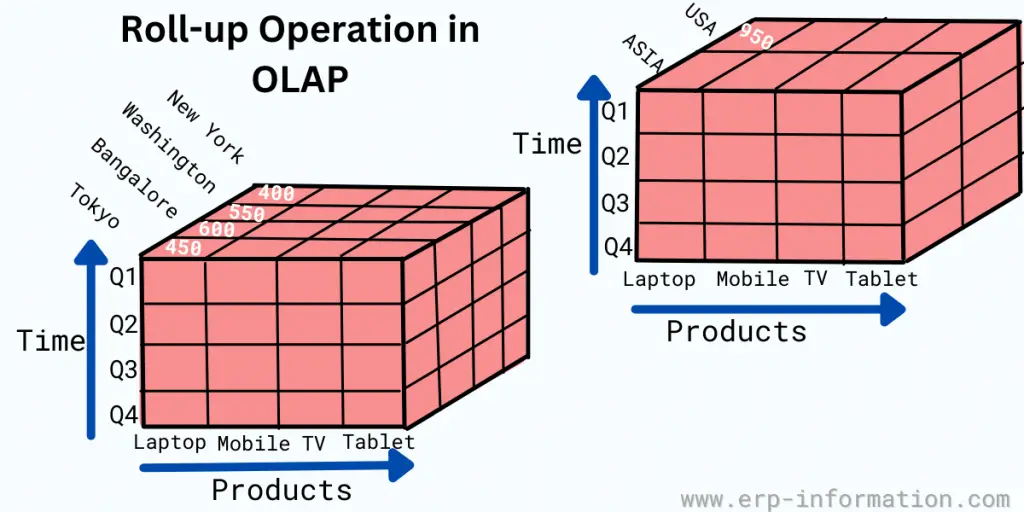
Roll-up operation
It is also called ‘aggregation.’ We can perform this operation in two ways.
- Reduction of dimension: It is the system in which the cube reduces its dimension
- Climbing up concept hierarchy: It is the system of grouping things based on their level.
The above image shows the roll-up operation.
- Here cities, New York and Washington rolled up into the USA
- The sales figures of the cities were 400 and 550 and became 950 after rolling up
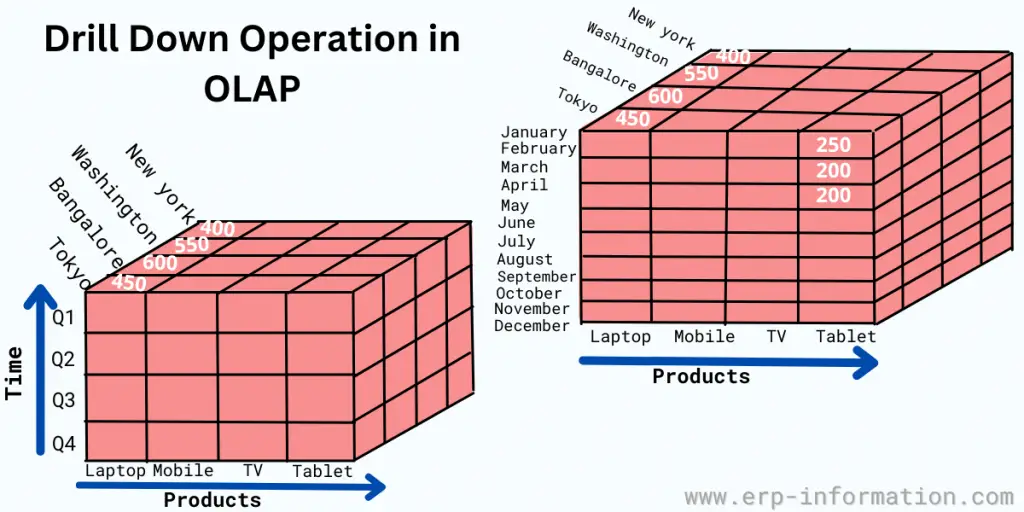
Drill-down operation
It is the opposite process of roll-up. It performs in 2 ways.
- Increasing of dimension
- Climbing down the concept hierarchy
This image shows the drill-down operation
- Quarter 1 is divided into months January, February, and March
- Months dimension is added
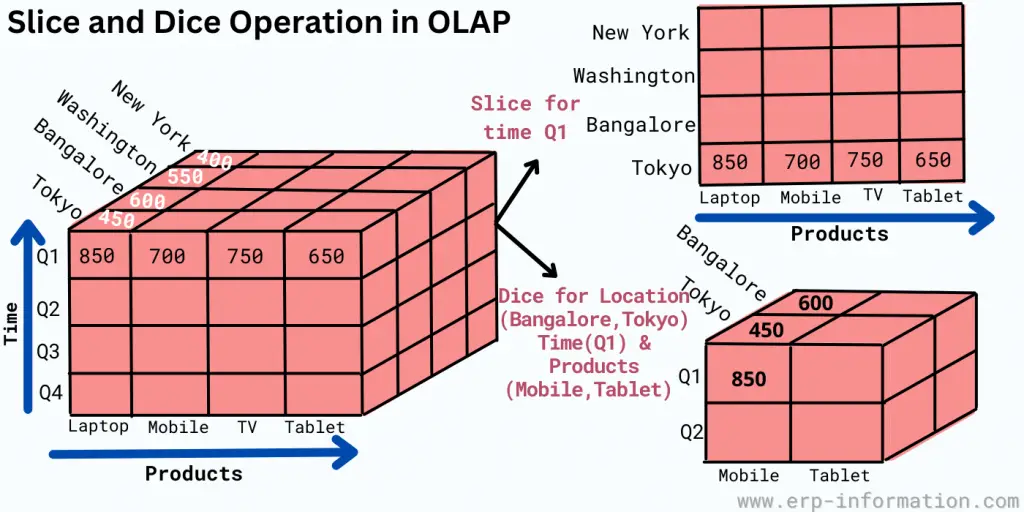
Slice and dice operation
In a slice method, one dimension is chosen, and a subcube is generated. A dice operation selects two or more dimensions, and subcubes are generated.
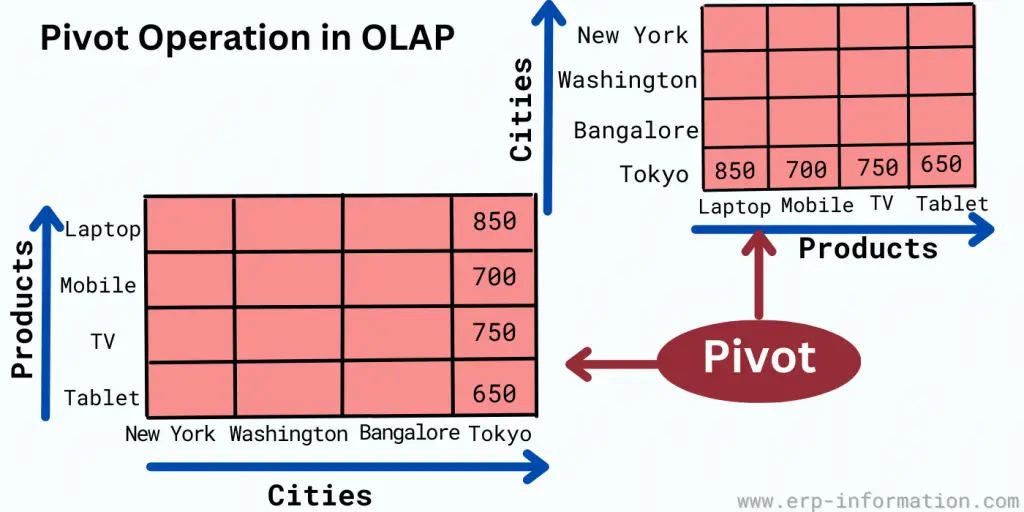
Pivot operation
To provide a substitute presentation of data, you need to rotate the data axes in this operation.
Advantages of Online Analytical Processing
- It helps to gather all the data to create accurate and quick information about the business.
- It helps to analyze the time series.
- Provides a platform for all types of business, including planning, budgeting, forecasting, financial reporting, and data warehouse reporting.
- Allows users to do compatible calculations.
- Allows users to divide a big cube into dice cube data by several dimensions, measures, and filters.
- It helps the end-users analyze data in multiple dimensions to make better decisions in business.
Disadvantages of Online Analytical Processing
- It is challenging to have many dimensions in a single OLPA cube.
- The snowflake schema required for organizing data is complex to implement.
- Modification of a cube requires a complete update of the cube that consumes more time.
When Do You Use Online Analytical Processing?
You can use it in the following situations.
- When you are required to perform complex analytical and ad hoc quickly without interrupting and affecting the OLTP system.
- When you need to issue reports using your data to business users in an easy way.
- When you want to deliver several aggregations to help the user with consistent and quick results.
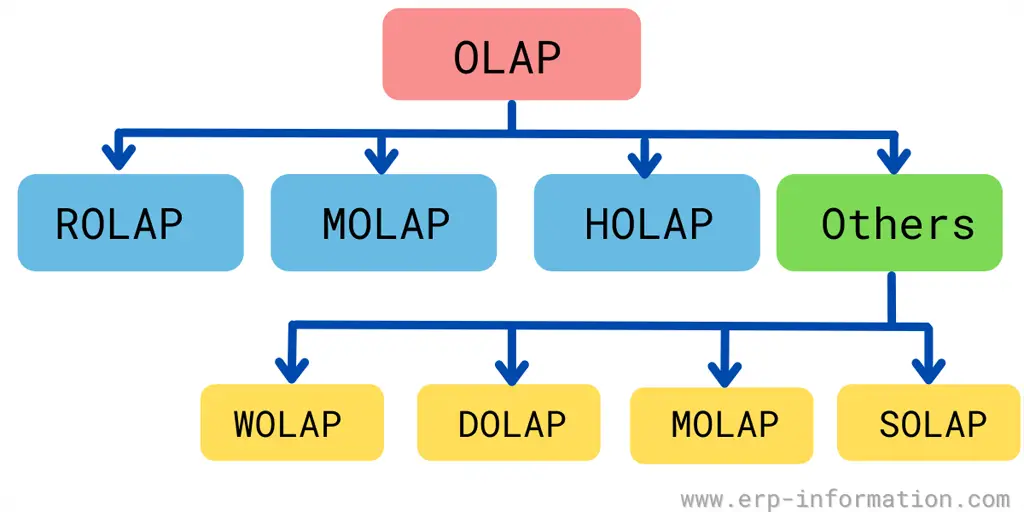
Types of Online Analytical Processing
Three main types are
- Relational OLAP (ROLAP): This type of data is stored in a relational database. It allows us to analyze multidimensional data. With this, data accuracy is very high. It offers expandability. That means it manages a large amount of data even when it is increasing. Some disadvantages are also there with this type. It requires more staffing, hardware, and software. It has the lowest query performance system.
- Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP) is a cube-based, multidimensional array of structured data storage. In this system, computation is high-speed.
- Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP): This is a combination of relational and multidimensional. Hence in this system, expandability is more, and computation is fast. It stores aggregated data in a multidimensional cube and detailed information in a relational database.
Apart from these three main types, some other types are below.
Web (WOLAP): This is based on a web browser. In this, the application is available through the web browser. It is a three-tier architecture that includes a database server, client, and interface.
This application does not require deployment in the client’s system. It requires only a web browser and a network connection.
Desktop (DOLAP): This is installed on the user’s desktop. It includes a client application and server.
The advantage of this type is that it offers better performance because the data is located near the user. The disadvantage is that it needs more storage space on the user’s computer.
Mobile (MOLAP): It is used to process data on a mobile device. The engine resides on a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet.
Spatial (SOLAP): This is used to process spatial data. In this, the engine resides on a server.
Some of its features are mapping, proximity searches, and routing.
Challenges
While Online Analytical Processing systems offer numerous benefits, they also have challenges.
Complex implementation
Setting up an OLAP system can be quite complex. It requires a thorough understanding of the business processes, data sources, and the relationships between different data elements. The process of building cubes can be time-consuming and technically challenging.
Cost
OLAP systems can be expensive to implement and maintain. The costs include the software and hardware, licensing fees, staff training, and ongoing maintenance.
Complex data integration
Data used in OLAP cubes often comes from various sources, each with its structure and format. Integrating this data into a single, consistent model that accurately represents the business can be challenging.
Cube design
Designing the cube requires a deep understanding of business processes and data. Deciding which data to include, how to structure and hierarchize the dimensions, and determining the level of granularity can be complex and time-consuming.
Performance issues
Depending on the volume of data and the complexity of queries, OLAP systems can sometimes face performance issues. Large data sets can slow the processing speed, particularly when performing complex calculations or multidimensional analyses.
Security concerns
As with any system dealing with potentially sensitive data, security is a concern. It is important to ensure only authorized users have access to the appropriate level of data. If not properly managed, there could be a risk of data breaches or misuse of information.
Training and adoption
Users must understand how to use and interpret the OLAP cube effectively. Providing adequate training and support can be challenging, particularly for users unfamiliar with OLAP technology.
What are OLAP Tools?
These tools are the software that helps perform the slicing and dicing of data.
Following are the key features of the tools.
- Ability to support parallelism
- Front end flexibility
- Powerful metadata layer
- Good performance
- Security
Best OLAP software
- Microstrategy
- Microsoft Power BI
- Google cloud platform
- Apache Kylin
- SAP AG
- Operations Hub
- Pentaho BI
- icCube
Difference Between OLAP and OLTP
| OLAP | OLTP |
| It is the system used for data analysis. | It is the system used for data transactions. |
| A large amount of data identifies it. | A large number of small amounts of data identify it. |
| Its reply time is longer, and it usually takes seconds to minutes to respond. | It is small in size ranging from 1 MB to 10 GB. |
| It operates with a data warehouse. | It operates with a traditional database management system. |
| Its processing speed is less. | It has a faster processing speed. |
| Its reply time is more, and it usually takes seconds to minutes to respond. | It responds quickly and takes only milliseconds. |
| It needs only read operations. | It needs both read and write operations. |
| Its objective is to make decisions with the help of significant data sources. | Its objective is day-to-day operations. |
| Queries are complex. | Queries are simple. |
| User strength is low (Its database allows only hundreds of users). | User strength is high (Its database allows thousands of users). |
| It helps to improve the productivity of business analysts. | It helps to improve the productivity and self-service of users. |
| It is created for business analysis. | It is created for real-time business operations. |
FAQs
What is OLTP?
OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) systems are designed to meet this demand, providing companies with a fast and effective way to conduct online transactions.
Whether ordering products or making payments, OLTP systems are designed to complete the job quickly and efficiently. In many cases, OLTP is the primary function of an ERP system.
However, businesses can also include OLAP capabilities to help them analyze their data. It allows enterprises to examine their data in various ways, providing valuable insights that can be used to improve operations and make better business decisions.
When it comes to online transaction processing, OLTP and OLAP provide a powerful one-two punch that can help any business take its operations to the next level.
Conclusion
OLAP is a process used to analyze data quickly and efficiently. It allows businesses to examine their data in multiple dimensions to understand what’s happening within their company.
This can help with making informed decisions about the future of the company. It is often used with ERP software, making data management more accessible and efficient. As a result, it can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes.
If you’re looking to grow your business, it’s essential to have accurate data at your fingertips. It can help you do just that!