Ever wondered how businesses keep their products or services consistently top-notch? It’s all about output control. This management technique ensures that what a company delivers meets its high standards, whether it’s the timely arrival of flights, the quality of electronics, or even university test scores.
In simpler terms, output control is like a behind-the-scenes superhero, quietly ensuring that everything runs smoothly and customers stay happy.
It measures and manages your business’ outcomes so that you can see tangible results. With Output Control, you’ll be able to improve performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimize processes.
This article will discuss definitions, features, powerful objectives, real-world examples, advantages, limitations, and stages of output control. It will also explore management fads and types of organizational control systems.
What is Output Control?
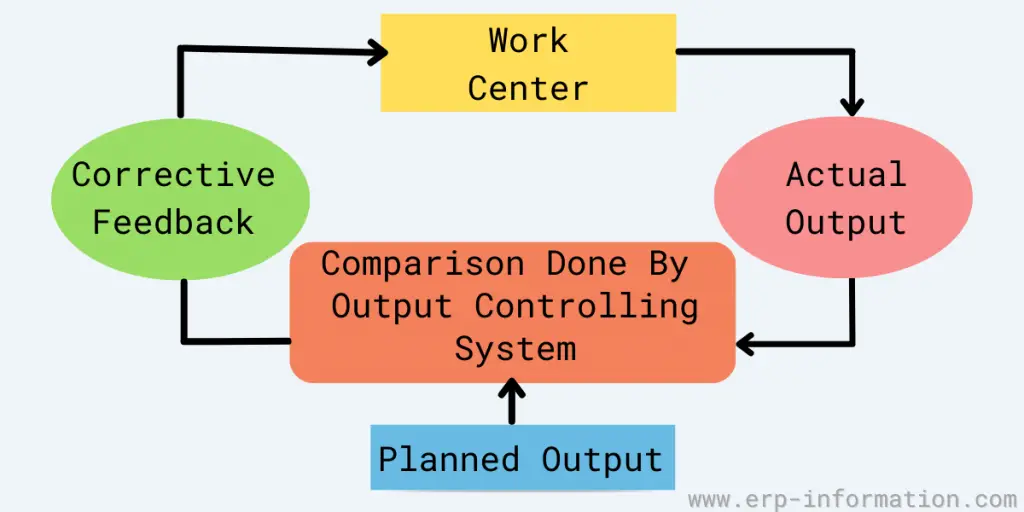
Output control is a technique for controlling output where actual output is compared to planned output to identify problems at a work center.
In detail, output control in organizational management is all about focusing on the measurable aspects of a business. It deals with things like sales numbers, the number of customers served, and work hours. This type of control is primarily concerned with the end results of actions.
Some examples of output control include setting sales targets, tracking how many potential clients you reach in a specific time, and keeping an eye on the amount of unused ingredients left at the end of the week.
Output Control in Manufacturing
Output control is a system used to ensure that products made in a factory are up to standard. This system monitors and measures different aspects of production from individual machines or work processes.
Suppose, for example, an operator’s performance is not up to standard. In that case, the output control system will note it so the operator can take corrective action before too much damage is done to the product being manufactured.
A company must know what it sells and how people will react to it. They also need to be mindful of how people accept their products when they come off the production line.
This will allow any preventive measure to overcome potential problems in future mass appeals. Doing this will make business more profitable and create long-lasting relationships between consumers/end users who receive those outputs (the end product).
Companies need to ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality. This will help them maintain customer loyalty and avoid negative feedback from other consumers who may fault your business practices!
To maintain the high quality of their products, companies need to set up a controlling system that enforces control over every aspect. This includes discrepancies and any problems with delivery or packaging before they can result in lost customers for your business!
Features of Output Control System
- Output control is an active process
- It includes continuous evaluation of the products and services
- It is a follow-up action of the functional management
- It is a forward-looking process
- Output control is a preventive action
- Reduces losses, wastage, and deviation from standards
- Takes corrective actions based on feedback
Objectives of Output Control
- Ensure that the production process follows the predetermined standards to attain the desired output.
- To know the activities of the organization.
- To find out the corrective action with minimum effort, cost, and time.
- To synchronize efforts and mixed activities.
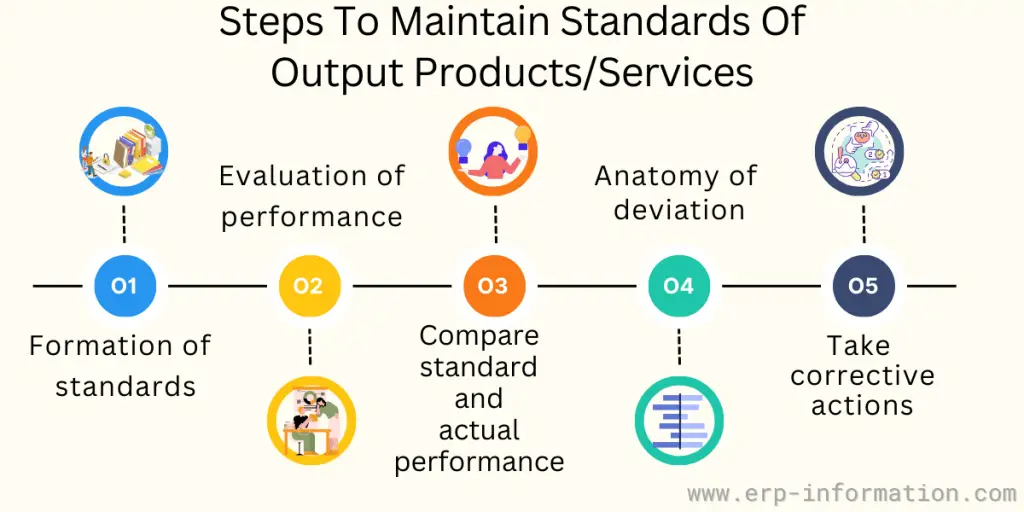
Steps to Keep Up the Standards of Output Product or Service
Here we are discussing five main steps to keep up the standards of your products or services. In short, you can call it the steps of the control process.
1. Formation of standards
This is the first step to maintaining the standards. It is the criteria against which the actual output is measured. Next, these standards review the desired result. These standards may be of two types.
- Quantitative standards: These standards are the standards that can be measured in terms of quantity, such as production and sales.
- Qualitative standards: These standards are standards that can not be measured in terms of quality, such as employee motivation and industrial relations.
2. Evaluation of performance
This step includes measuring performance concerning work in terms of control standards. Then, the evaluation becomes easy based on the established standards and goals.
If the evaluation finds any deviations, you can immediately take corrective actions.
3. Compare standard performance and actual performance
The third step is comparing actual performance with expected performance. This process gives you the deviations between standard and actual performance.
If standards are in terms of quantity, the comparison is easy. However, knee observation is necessary to determine the deviation when the bars are quality.
4. Anatomy of deviations
This fourth step is about the analysis of the deviation. You must thoroughly analyze the variation when the deviation exceeds the limit to determine the cause.
Then report to the manager or top management about the deviation’s cause and take the necessary action to correct it.
5. Take corrective actions
In this last step, the manager takes the required corrective procedures to reduce the deviation. For example, disciplinary actions will be the review of standards, employee training, and technical improvement.
Examples of Output Control
Example 1
A famous airline company once found itself losing out on shares and falling far behind its competitors on the trusted list of airlines.
The managers stepped into the matter, and soon it was discovered that not more than 77% of the flights reached their destination on time. That was a significant issue and had to be solved quickly.
The airlines started organizing elaborate periods of employee training and hired only experienced pilots for a while. Then, they introduced strict policies and penalties for breaking them.
All this had a positive effect, and soon within five years, the airlines found themselves back into the game and had also made a profit of a few million dollars.
Example 2
A company producing and selling electronics goods must ensure the standard of the products and longevity.
The finish must be high-end to attract the rich and funky and, at the same time, interest the ones after quality products.
One mobile phone company conducted a market survey after its brand value decreased.
It was found that despite starting at the top of the chart, mobile phones had fallen out of the competition.
It was found that while all its contemporaries had a massive battery capacity, this mobile phone had minimal capacity.
The company soon launched a newer version with upgraded features and huge battery capacity and took over the market.
Hence, system output control is crucial, like a preventive measure guarding an organization against imminent failure.
Example 3
We can also take university test results as an example of output control. Test results and grades are reasonable output measures of students’ academic performance.
When the students do not perform well on the test, their results will not meet their desired results. At this point, they can take corrective actions by studying harder than earlier.
At some universities, students will be put on probation. If their grades are below the standard rate or their performance has not improved, they may not be promoted to further studies.
Output Control Advantages
Helps to achieve the objectives of the organization
The output control system controls and monitors the organization’s activities and ensures that all the activities are planned.
If it finds any variations in activities, immediately correct them and put the activities back on the planned path. This controlled process in the organization helps to achieve the objectives.
Uses the resources effectively
This technique monitors and ensures that all the activities are going according to the planned standards. Hence there is an effective use of resources.
Determines the precision of product standards
With the help of a control system, you can quickly determine the accuracy of the product standards. It also updates the criteria as per the environmental changes.
Motivates workers and subordinates
An effective control system shares the objectives and standards of appraisal with employees and subordinates.
It also helps them to overcome their problems. In this way, it motivates them to give their best.
Reduces the errors and maintains the quality of products
The output control system continuously monitors and corrects the errors that occur.
Managers immediately find the errors and take corrective actions to reduce the mistakes in the finished product or services.
Limitations of Output Control
Hard to set quantitative standards
When the predetermined standards are not set in quantitative, it is not easy to compare actual performance and standard performance in areas such as employee behavior and job satisfaction.
Uncontrollable external parameters
You will not be able to control external factors such as changes in technology, government rules and policies, and the customer’s taste.
Workers’ resistance
You may have to face opposition from workers when you start observing them through CCTV because they do not want to lose their freedom while working.
Expensive
The control system requires a little more resources, time, and effort. Hence make sure that your expenses are giving your desired benefits.
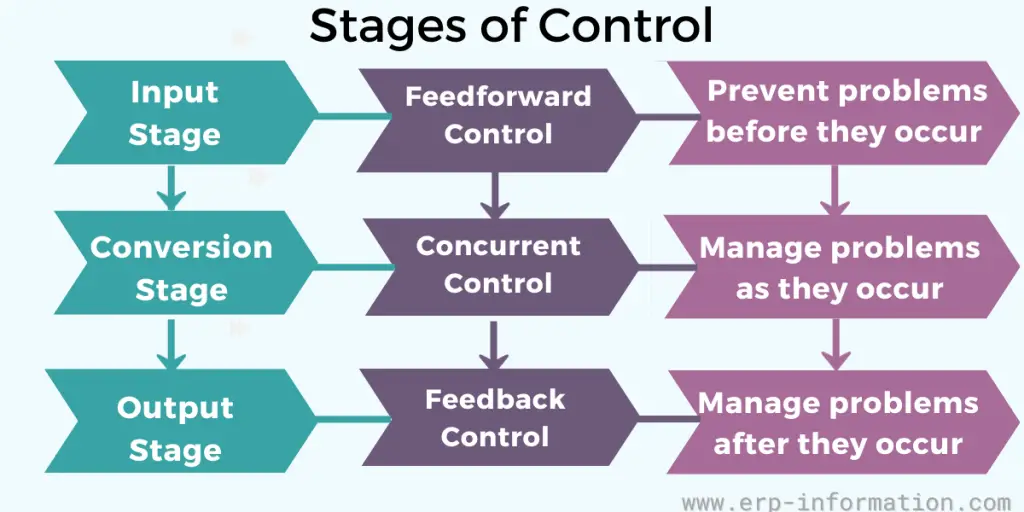
Three Stages of Control
We can divide the output control into three stages.
- Input stage – This is called feed-forward control. In this stage, the control system predicts the problem and takes preventive actions before problems occur. Hence it is a more aggressive and active method to control the output.
- Conversion stage – This is called concurrent control. In this case, the manager of the organization has to analyze the problem and take immediate action to correct the issues as they arise.
- Output stage– This stage is called feedback control and also history control. In this stage, output control evaluates results or output only after the performance. You can consider the feedback from your client about your product or services and, based on that, take corrective actions.
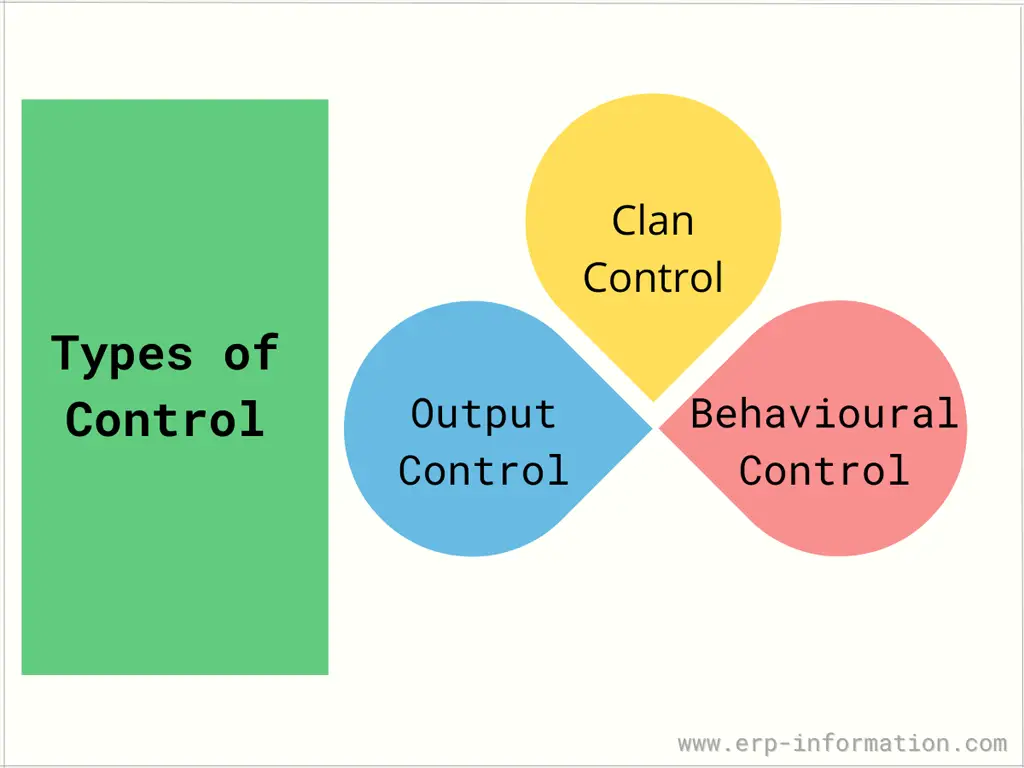
Types of Organizational Control Systems
Apart from output control, Behavioral control, and Clan control are the other two.
Behavioral control gives attention to activities carried out by people. It controls the action that leads to the desired result.
Generally, different rules and procedures are used to set standards for behavioral control.
For example,
- You can see some signboards on the road while traveling, like don’t park the vehicles here, don’t overtake, etc. These are behavioral control systems.
- When you go to a restaurant or in the washroom of a company, you can see some instructions like “don’t wastewater.”
- In some industries, you can see no-smoking areas and switch-off mobile boards.
- Attendance of the students in class
- Punctuality of the students
All these are the best examples of behavioral control.
Clan control tells about values, traditions, and expectations to give their best to the organization—for example, dress codes in a company or a college campus.
Many organizations use all three types of control to get better output of products or services.
Management Fads
You know that there are many management fads. Here we will brief the prominent three fads or trends that are firmly bound with an organizational control system.
1. Management by objectives (MBO)
It is a procedure where workers/employees and managers work together to generate their objectives.
They also put efforts together to reach those goals. These objectives help to improve the behavior of employees and enhance their performance.
2. A quality circle
It is a group that contains formal employees. They frequently meet and discuss various solutions to the organization’s problems.
Then find the solution that helps improve the quality of the output products or services.
3. Sensitivity training groups (T-groups)
It is an old practice. It was there in the 1960s. This group consists of around 8 to 15 people. These people regularly meet and discuss or share their feelings, thoughts, emotions, and beliefs about workplace issues.
Unlike MBO, these people do free-flow discussions. These conversations help them to nourish their understanding. It improves mutual understanding, and that leads to improving teamwork.
FAQs
Why is output control important?
Output control is essential because it gives you a measurable result. You can determine the level of performance and monitor whether the business’s performance meets the expectation.
What are the three types of control systems in an organization?
Three types of control systems in an organization are
1. Output control
2. Behavioral control
3. Clan control.
Conclusion
Output control is a strategy that businesses use to maintain the quality of their products or services. This can be done by setting standards for production and enforcing them.
This will help ensure that the company produces high-quality products reasonably. It may sound like an easy way to maintain high-quality goods and services; however, it’s not without drawbacks.