Most people know that the p2p cycle is essential in modern business operations. If you don’t manage the p2p cycle properly, it may lead to confusion and frustration when troubleshooting errors related to the p2p process.
This post will give you a crash course in the p2p cycle in Oracle apps. We’ll explain what it is, how it works, and some of the most critical tables. But, of course, it would help if you had a much better understanding of this crucial process by the end.
Let’s get started!
Our other articles on the P2P Cycle are
What is P2P Cycle in Oracle Apps, and What Does It Do?
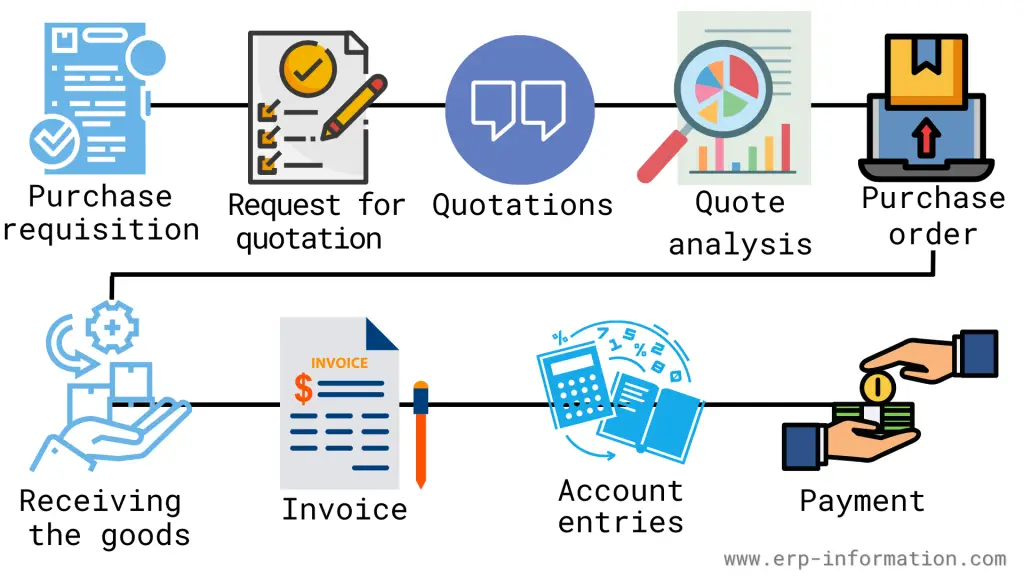
The p2p cycle in Oracle apps is a process that is responsible for the procurement and payments of goods and services. It starts with a requisition being created and ends with the supplier being paid. You must complete several steps for the cycle to be complete.
Essential Steps in the P2P Cycle in Oracle Apps
- Creating a requisition
- Request for quotation
- Quotations
- Quote analysis
- Creating a purchase order
- Receiving the goods or services
- Creating an invoice
- Creating account entries
- Making the payment to the supplier
Each step is essential in the Oracle procure-to-pay process, and we’ll take a closer look at each one now.
1. Creating a requisition
The first step in the p2p cycle in Oracle apps is creating a requisition. This is a request for goods or services sent to the supplier. You can do that by navigating to the “Requisitions” screen in Oracle Apps and clicking on the “Create Requisition” button.
You will then need to fill out the requisition form. The requisition must include all the necessary information to create a purchase order, including the item code, description, quantity, and price.
2. Request for quotation
After the requisition has been created, you can generate a request for a quotation (RFQ). It is a document sent to the supplier that outlines the goods or services needed and the buyer’s price. The RFQ will also include any other terms and conditions relevant to the purchase.
3. Quotations
Once the RFQ has been received, the supplier will send back a quotation. This document will include the price of the goods or services and any other terms relevant to the purchase.
4. Quote analysis
Once the quotation has been received, it will need to be reviewed and approved. That is known as quote analysis. Quote analysis examines the supplier’s quotation and ensures that it meets all of the buyer’s requirements.
5. Creating a purchase order
After the quotation has been approved, you can generate a purchase order (PO). The purchase order is a legal document that outlines the terms of the sale.
It will include the price, quantity, and delivery date of the goods or services. The purchase order will also include any other relevant terms and conditions.
6. Receiving the goods or services
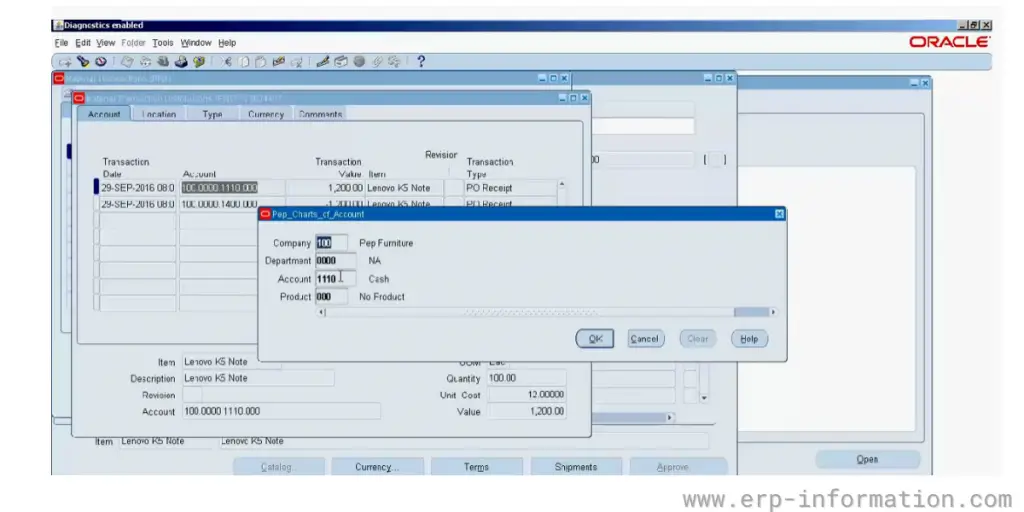
Once the goods or services have been ordered, they must be received. That is done by entering the accepted quantity into the receiving form.
The receiving form will also include fields for the supplier, ship-to address, and delivery date. This step will be completed once all of the information has been entered.
7. Creating an invoice
An invoice can be created after the goods or services have been received. The invoice is a document that outlines the price of the goods or services and any other terms that are relevant to the purchase.
The invoice will also include a due date. This step will be completed once all information has been entered.
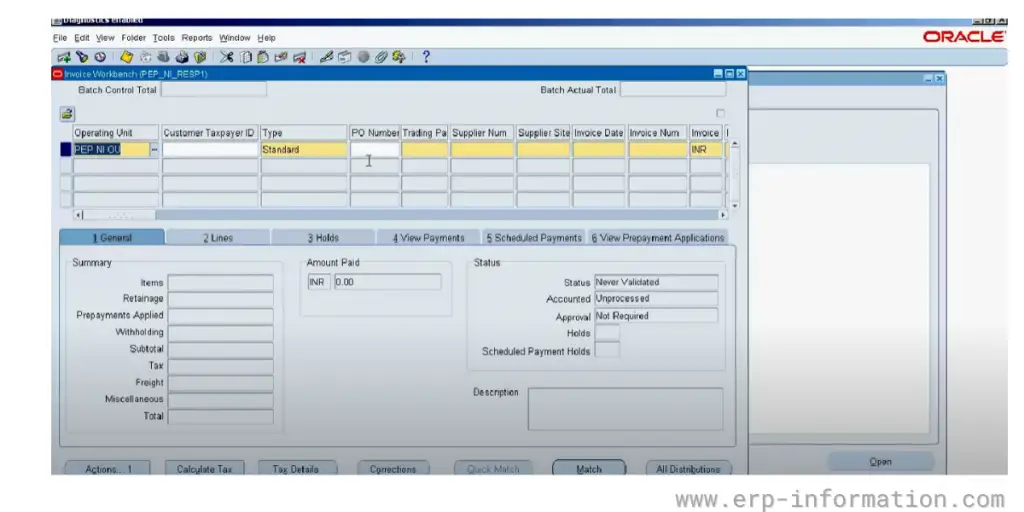
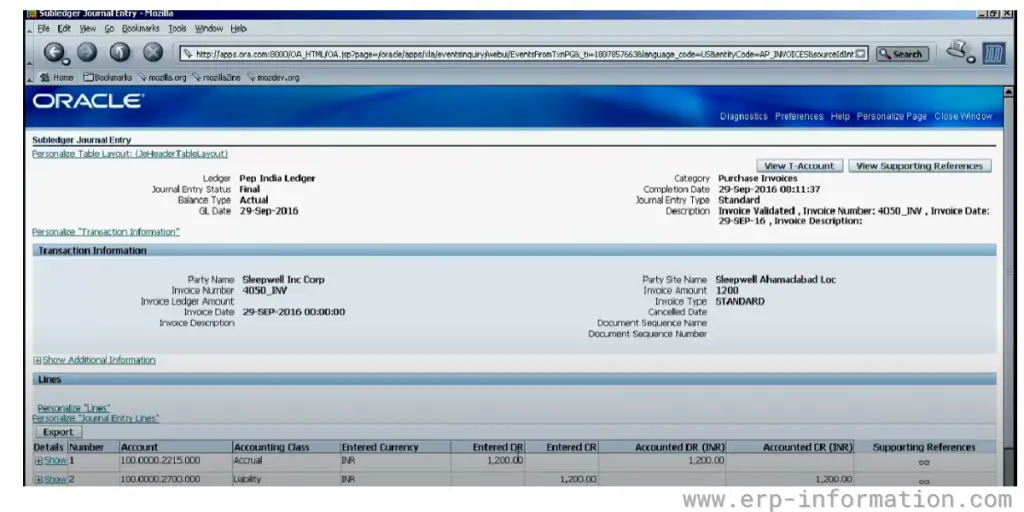
8. Create accounting entries
After the invoice has been created, it will need to be reviewed and approved. This is known as invoice validation. Invoice validation checks the supplier’s invoice and ensures it matches the purchase order.
Once the invoice has been approved, you can generate accounting entries. These entries will debit the accounts payable account and credit the cash account.
9. Making the payment to the supplier
The final step in the p2p cycle in Oracle apps is making the payment to the supplier. This is done by entering the invoice and purchase order numbers into the payment form.
The payment form will also include fields for the supplier, ship-to address, and delivery date. Once all of the information has been entered, the payment process will be completed.
P2P Cycle in Oracle Apps with Table
The following list shows the p2p cycle in Oracle apps r12 with table types.
| Type of table | What it contains |
| Purchasing Requisition Header Table | Information about requisition number, date created, and status. |
| Purchasing Requisition Lines Table | The requisition line includes the item code, description, quantity, category, and unit price. |
| Purchase Order Header Table | The purchase order includes the order number, supplier name, and ship-to address. |
| Purchase Order Lines Table | The purchase order line includes the item code, quantity, and unit price. |
| The receipt Header Table | The receipt includes the receipt number, supplier name, and date received. |
| Receipt Lines Table | The receipt line includes the item code of received items, quantity, and unit price. |
| Invoice Header Table | The invoice includes the invoice number, supplier name, and ship-to address. |
| Invoice Lines Table | The invoice line includes the item code, quantity, and unit price. |
| Payment Header Table | Information about the payment includes the payment number, supplier name, and ship-to address. |
| Payment Lines Table | The payment line includes item code, quantity, and unit price. |
Most Common Errors During the P2P Cycle in Oracle Apps
Some of the most common mistakes that can occur during the p2p process in Oracle apps
- Incorrect or missing account codes
- Invalid or missing vendor information
- Inaccurate or missing purchase order information
- Invalid or missing invoice information
- Incorrect or missing payment information
If any of these pieces of information are incorrect or missing, it can cause significant delays and disruptions in the p2p cycle. That’s why it’s important to double-check all of your data before initiating any part of the cycle.
Best Practices for Procure to Pay Cycle in Oracle Apps
The p2p cycle is an essential process in Oracle apps, and it’s necessary to understand the best practices for working with it. Some key things to keep in mind include the following:
- Ensure you are posted as the approver on all invoices related to the p2p cycle. This will help to ensure that all invoices are correctly processed and approved.
- Be sure to review all invoices carefully before approving them. This will help to avoid any errors or mistakes in the approval process.
- If you have questions about an invoice or the p2p cycle, please ask your supervisor or another experienced individual. Getting clarification can help to avoid any problems down the road.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that the p2p cycle in Oracle apps runs smoothly and efficiently. Understanding the process is key to being able to work with it effectively.
Conclusion
The p2p cycle is a necessary process that helps ensure the accuracy of financial data in Oracle Applications.
This blog post discussed the p2p cycle in Oracle apps, including the accounting entries and tables. We hope you found this information helpful!