The need for predictive maintenance becomes more apparent as industries move increasingly toward the digital age.
It is a field of study that seeks to identify and prevent machinery failures before they happen. As a result, businesses can optimize their maintenance schedules and avoid costly downtime using data analytics and machine learning techniques.
This blog post will explore all the basic predictive maintenance concepts, like definitions, technologies, history, advantages, and disadvantages. Stay tuned!
Predictive Maintenance Definition
This methodology aims to prevent equipment failures by detecting and correcting potential problems before they cause an issue.
How does it work?
Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze data collected from machine sensors to identify patterns in how the equipment is used.
That can be used to predict when a component is likely to fail so that it can be replaced or repaired before it does. The data can also be used to schedule proactive maintenance tasks, improving the reliability of the equipment.
Work of Algorithm
Predictive maintenance solutions utilize a sophisticated algorithm to make proactive repairs and replacements, utilizing sensor data for anomaly detection, equipment diagnosis, or estimation of the machine’s lifespan.
This helps identify potential issues before they disrupt service – keeping businesses running efficiently with minimal downtime.
Algorithms need the help of engineers and too, like MATLAB and Simulink. First, they need to put information into AI or statistical algorithms.
Then, it needs to be able to be deployed on technology so it can work.
Finally, it must integrate with IT or OT systems to get predictive maintenance benefits.
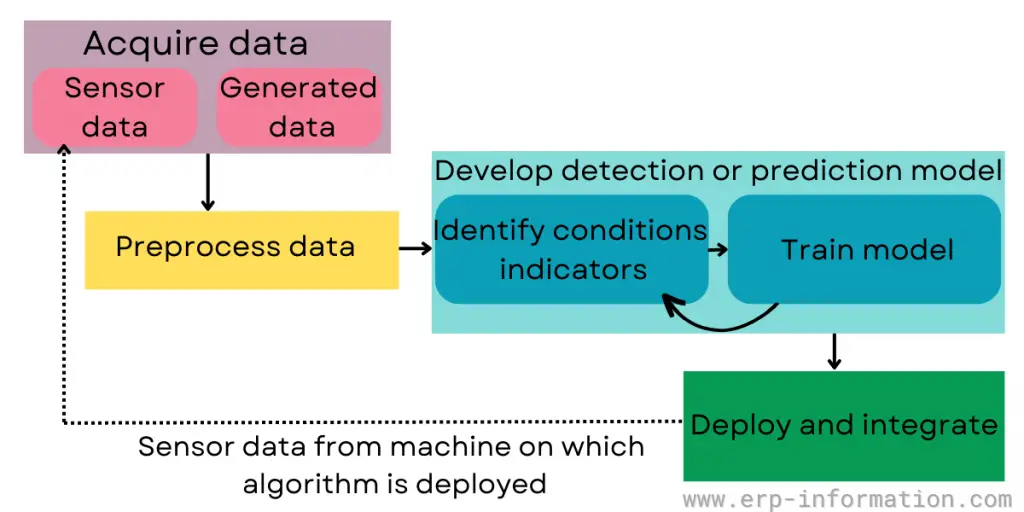
The below workflow chart will make you clear about the maintenance predictive algorithm.
- Acquiring data: To start, you need to get information. AI can help you determine if something is wrong but needs good data first. That means collecting or acquiring data that shows both when the machine works and does not.
- Condition indicators: One feature called condition indicators differentiates healthy and unhealthy operations. They are evoked using a combination of statistical, model-based techniques using tools like MATLAB.
- Train predicate algorithm: These algorithms work for Anomaly detection, Fault detection, and Remaining useful life estimation. The algorithm’s eventual goal is to detect and indicate the bad condition for maintenance.
- Deploying algorithms in operation: Businesses can experience minimized downtime and decreased maintenance expenses by deploying algorithms in operation.
Understanding this need for data security and scalability to accommodate embedded or IT/OT systems.
History
The origins of predictive maintenance can be traced back to the early days of aviation. In the 1930s, aircraft engineers began using vibration sensors to detect engine problems before they caused a failure. This early form of predictive maintenance was known as “vibration monitoring.“
In the 1960s, the industry began using vibration monitoring on a broader scale to detect machine wear and predict component failures.
C. H. Waddington introduced the predictive maintenance technique, and in and around the 1990s, industries started using this technique.
That was partly due to the development of more sophisticated software algorithms and the availability of affordable sensor technology.
Today, this technology is used in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. As a result, it has become an essential tool for improving equipment reliability and reducing downtime costs.
Technologies
Infrared thermography
Thermal imaging, also known as infrared thermography, is a technology that uses heat to create images.
This technology is used in predictive maintenance to detect and diagnose problems with equipment before they become more significant issues. Components in the equipment which are not functioning correctly generate excess heat.
By using infrared cameras, the maintenance person can determine the temperature above average in equipment and appears in the thermal image.
By identifying problems early, maintenance teams can fix them before they cause any severe damage.
Vibration analysis
This technology is used most commonly for high-speed rotating equipment. With the help of sensors in the kit, a person can analyze the machine.
When the machine runs, it generates a particular vibration rhythm. The vibration rhythm pattern will change if the machine is not in good condition.
An experienced technician observes the vibration rhythm pattern constantly and fixes problems before they cause a breakdown.
This technology is often used on large industrial machines, such as turbines and motors, but it can also be used on smaller machines.
This technique can also identify misalignment, out-of-shape shafts, unbalanced elements, loose mechanical components, and motor issues.
Acoustic monitoring
Acoustic monitoring technology uses sound waves to create images of the equipment inside, which can then be analyzed for abnormalities.
Acoustic Monitoring uses sonic and ultrasonic technologies to detect sounds of gas emissions and liquid leaks in the equipment.
Ultrasonic technology is expensive compared to sonic technology. But it is reliable.
Oil analysis
Oil analysis technology is used to predict when a machine will need maintenance. In addition, this technology helps to detect contaminants while checking oil conditions that can indicate a problem with the machine.
The machine can be repaired before it fails by detecting these problems early.
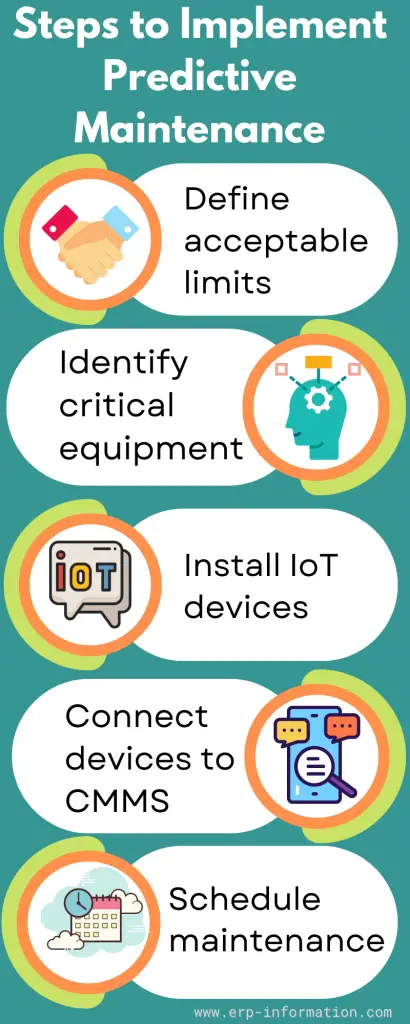
Steps of implementation
1. Define acceptable limits
First, the maintenance team needs to define the acceptable limits for machinery and equipment
2. Identify critical equipment
The team needs to identify the equipment which is expensive and requires a high cost of repair
3. Install IoT devices
Then fix the relevant IoT devices to equipment. For example, fix the sensor for the mechanical instrument, vibration meter for equipment with gears, and temperature sensor for the boiler.
4. Connect devices to CMMS
Connect all IoT devices to a computerized maintenance management system(CMMS) that collects and analyzes data.
5. Schedule maintenance
CMMS helps to identify the problem when equipment condition crosses the acceptable limits and schedules maintenance.
Examples
Example 1
Assume that a company has a machine that needs a new part every six months. That time maintenance team may receive a signal or notification when the machine was starting to wear down so that they could order the new part and have it installed before the machine broke.
Example 2
Another example is keeping an eye on the wear of a car’s brake pads. A mechanic can predict when the brake pads will need to be replaced based on how much they have been used and how much wear they have taken.
Advantages
- Decreases equipment downtime
- Increases equipment life
- Enhances cost savings by reducing labor time and repair cost
- Increases safety
Disadvantages
- Some of the monitoring technologies are expensive
- Needs specialized and experienced personnel to monitor and maintain the equipment
- Needs to do effective data analysis
Predictive maintenance vs. Preventive maintenance
| It is a proactive form of maintenance. | It is a scheduled form of maintenance. |
| It uses data-driven analysis to identify potential issues before they occur. | It relies on regularly scheduled interventions regardless of equipment condition. |
| This type of maintenance is typically used for systems with a predictable failure pattern. | This type of maintenance typically uses a checklist of tasks to be completed and is often performed on a set schedule. |
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance is a preventative measure that can save your business time and money. By identifying potential issues before they occur, you can fix them before they cause a problem.
While it may seem daunting initially, our outlined techniques are easy to implement and can be used by businesses of all sizes.
Reference