Achieving business success frequently depends on producing the goods that customers desire promptly and economically. Production planning plays an important role in helping companies reach these objectives.
It outlines all the necessary processes, resources, and steps involved in manufacturing, ranging from demand forecasting to identifying the required raw materials, labor, and equipment.
By doing so, production planning assists companies in creating feasible production schedules, ensuring that production operations run seamlessly and efficiently, and making adjustments when issues arise.
This blog post will explore production planning and related terms. We will discuss creating the production plan and the tools and software used.
Evaluate your overall cost of ownership by utilizing our Total Cost of Ownership Calculator
What is the Production Planning?
Production planning is a process that creates a plan for producing products. The production plan is a document that explains what will be produced and when it will be produced.
The objectives of production planning are to make sure the right products are made at the right time and in the correct quantities.
This outlines how a company’s products will be manufactured efficiently and at high quality. It specifies production targets, necessary resources, processes, and schedules. This plan details each operational step and its dependencies, aiming to streamline workflow, reduce waste, and cut costs.
Initially popular with large manufacturers, production planning has become widespread among small and midsize businesses across various industries, thanks to advancements in technology. It encompasses everything from demand forecasting to managing raw materials, workforce, equipment, and production steps.
It ensures that supply chain management, production scheduling, material requirements, lead times, and capacity planning are all optimized, contributing significantly to a business’s overall efficiency and success.
What is the Importance of Production Planning?
Production planning is vital for efficient resource management, smooth operations, and meeting customer expectations. Investing in robust production planning leads to greater operational efficiency and business success.
Boosts Profit and Revenue
A well-designed production plan minimizes errors and inefficiencies, leading to higher profit margins and revenue.
Enhances Operational Knowledge
It provides a clear framework for understanding necessary resources and production steps, helping to anticipate and mitigate potential issues.
Increases Efficiency
Streamlined planning reduces bottlenecks, optimizes resource use, and maintains high product quality within budget.
Improves Customer Satisfaction
Ensures timely delivery of products, boosting customer trust and encouraging repeat business.
Minimizes Lead Time
Reduces the time between order placement and fulfillment, crucial for industries with tight constraints or just-in-time production.
Supports Capacity Planning
Helps manage and allocate resources effectively, determining how much can be produced within a given timeframe.
Prevents Resource Waste
Ensures appropriate use of materials, labor, and equipment, preventing both shortages and excesses.
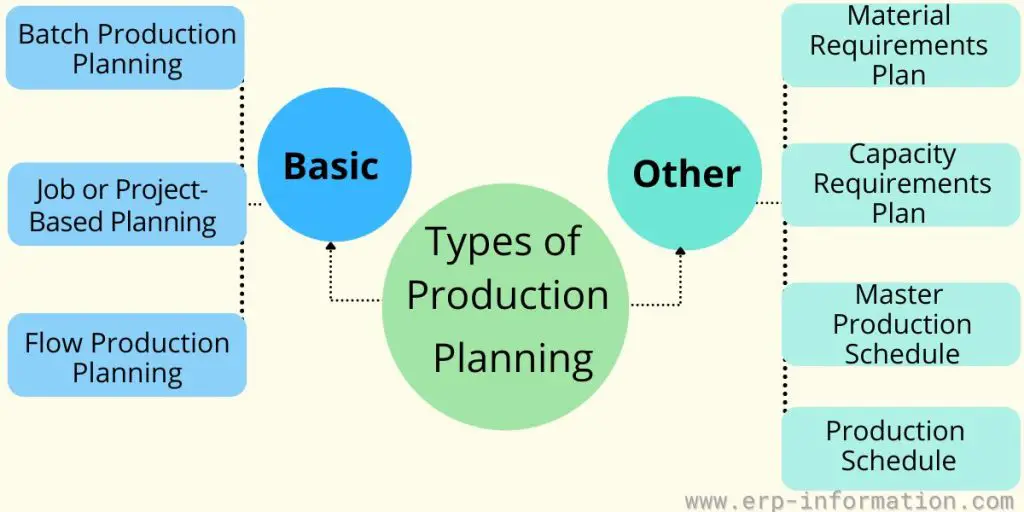
Types of Production Planning
The design of a production plan varies based on the production method, product type, equipment capabilities, and order size. Here are three main types:
Batch Production Planning
Batch production involves making identical items in groups rather than individually or continuously. This method can greatly enhance efficiency for businesses.
Effective batch production planning anticipates potential bottlenecks or delays during transitions between batches. Groups similar items for efficiency. For example, a furniture workshop may craft a batch of oak tables, chairs, and show items.
Job or Project-Based Planning
Commonly used by small and medium-sized businesses, this method focuses on creating single, customized items by an individual or a team.
It’s ideal when client-specific requirements make bulk production impractical. Each product is tailored to the client’s specifications For example. Tailors production to individual items, common in industries like custom electronics or artisanal crafts.
Flow Production Planning
Also known as continuous production, this method involves the mass production of standardized items on an assembly line. It’s perfect for large manufacturers seeking a constant output of finished goods. In flow production, each item moves seamlessly from one assembly stage to the next.
This method minimizes costs and delays when there’s a steady demand for products. Constantly mass-produces standardized items. For example, Think of a factory producing smartphones or packaged snacks on assembly lines.
And other production types are as follows.
Master Production Schedule (MPS)
MPS details the production timelines for specific products within a set timeframe. Typically generated by software, these schedules can be fine-tuned manually to meet precise requirements.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
MRP is a system used to plan production, schedule tasks, and manage inventory. It ensures raw materials are available, keeps inventory levels low, and coordinates manufacturing and purchasing activities. While often automated, it can also be done manually.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning evaluates an organization’s ability to meet fluctuating demands. It determines if the current resources are adequate or if adjustments are needed to handle future needs. What is Capacity Planning? (Strategies, Tools, and Process)
Click here for the Capacity Planning online calculator
Workflow Planning
Workflow planning organizes the sequence of tasks performed by employees or teams. It ensures operations are carried out efficiently and in the correct order, enhancing overall productivity.
Steps to Create a Production Plan/Process Flow
It is a comprehensive process that encompasses forecasting, process design, and monitoring. Here are five essential steps to develop a production plan:
1. Forecast Product Demand
Begin by estimating the demand for each product over a specific period. Utilize historical data and consider market trends and economic factors. Demand planning software can aid in making informed decisions about the required product quantity.
2. Map Production Steps and Options
Determine the processes, resources, and steps necessary for production. Explore various options to achieve production goals, such as outsourcing. Identify interdependent steps and those that can occur simultaneously. Ensure equipment availability and assess potential risks.
3. Choose a Plan and Schedule Production
Evaluate different production plans based on cost, time, and risks. Share the selected plan with stakeholders to ensure alignment. Develop a detailed production schedule outlining resource allocation and timing for each step.
4. Monitor and Control
Track production performance against set targets. Continuous monitoring helps detect issues promptly for swift resolution.
5. Adjust Accordingly
Anticipate unforeseen events like changes in client specifications or supply chain disruptions. Keep the production plan flexible to accommodate adjustments as needed. Regularly review and refine the plan for ongoing improvement.
Businesses employ a diverse array of tools to develop production plans and monitor progress, ranging from visualization aids to advanced software solutions. Here are some typical tools used:
Tools
Visual Timeline Tools
Gantt Charts: A Gantt chart offers a detailed visual representation of all tasks scheduled for a specific job. Originally conceived by mechanical engineer Henry Laurence Gantt over a century ago, this chart remains indispensable in manufacturing and various industries.
It visually depicts task timings and durations, facilitating coordination and scheduling in production planning.
Data Management Solutions
Spreadsheets: Initially used by small companies for basic production plan tracking, spreadsheets quickly prove insufficient for managing the complexities of production planning as businesses grow.
Advanced Software Solutions
This software encompasses a wide range of functionalities, including forecasting, supply chain management, inventory tracking, and job scheduling.
Given the multifaceted nature of production planning, businesses often rely on enterprise resource planning (ERP) suites that integrate production planning software. Such suites provide a comprehensive solution for managing various aspects of business operations, including finance.
Difference Between Production Planning and Production Scheduling
| Aspect | Production Planning | Production Scheduling |
| Definition | Provides an overview of what the company plans to produce. | Creates a detailed view of how the company will execute the production plan. |
| Focus | Outlines production targets, required resources, processes, and overall schedule. | Specifies when each step will occur and assigns workers, machinery, and other resources to specific tasks. |
| Complexity | Generally broader and less detailed. | Can be extremely complex, especially with many interdependent steps and simultaneous production of multiple products. |
| Details | Maps out operational steps and their dependencies. | Details the specific timing and resources for each production step. |
| Tools | Often involves planning software and forecasting tools. | Utilizes scheduling software to create, monitor, and adjust detailed schedules in real time. |
| Goal | To design an efficient, cost-effective production process that meets quality standards. | To ensure that the production plan is executed smoothly and efficiently on a detailed, day-to-day basis. |
| Adjustments | Provides a framework for adjustments when problems occur. | Allows for real-time monitoring and quick adjustments to address issues as they arise. |
| Scope | Covers long-term production strategy and overall workflow. | Focuses on the short-term execution of the production plan, including daily and weekly schedules. |
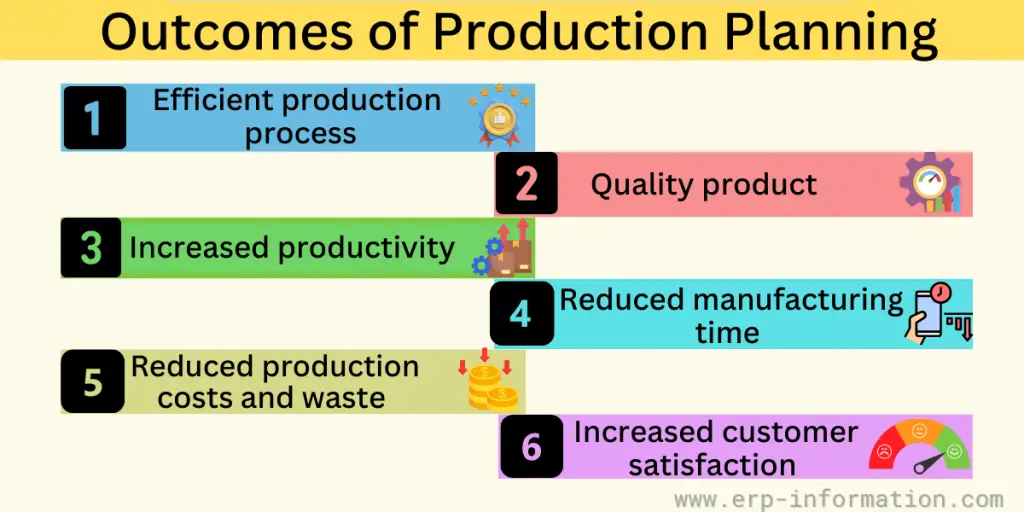
Outcomes
The outcomes of a better production planning process are:
- A well-organized and efficient production process
- Improved quality of the final product
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Reduced manufacturing time
- Reduced waste and scrap
- Reduced production costs
- Increased customer satisfaction and reduced lead time.
List of production planning software
- Microsoft Excel – Microsoft Excel is one of the most common and popular software for production planning. Small and medium businesses widely use it because it is easy to use and versatile.
- Oracle Primavera – Primavera is a production planning software used by larger businesses. It offers more features than Microsoft Excel, such as creating Gantt charts.
- SureTrak Project Manager – SureTrak is another production planning software used by larger businesses. It has more features than Primavera, such as tracking inventory and costs.
- Microsoft Project – Microsoft Project is a project management software used for production planning. It has more features than Microsoft Excel, such as creating timelines and tracking costs.
- Workfront production planning software – Workfront is a cloud-based software that helps businesses manage their production planning. It has features such as the ability to track tasks and costs and to create reports.
Most modern ERP solutions include a production planning module in them.
FAQs
Why is production planning important in supply chain management?
Production planning is essential in supply chain management because it allows for the smooth and efficient flow of goods from the supplier to the customer. Production planning also helps ensure that the correct quantities of goods are produced and produced on time. Production planning also helps to keep costs down and minimizes waste.
How do you plan human resources in production?
When planning human resources as part of manufacturing production planning, it is vital to consider its needs and the available workforce. Some factors to consider when planning human resources include:
– The number of employees needed
– The types of positions needed
– The skills and experience required for the positions
– The geographical location of the employees
– The availability of qualified employees
What is Production Planning and Inventory Control?
Production planning and inventory control (PPIC) is a process that determines the number of products to produce when to make, and what resources are needed.
PPIC also determines the types and quantities of materials from suppliers and the need for finished goods inventory. As a result, PPIC helps companies ensure they have the right products on hand to meet production orders while minimizing costs.
What are some common mistakes in production planning?
Common mistakes in production planning include inadequate forecasting, insufficient consideration of resource availability, underestimating setup times, and overlooking potential bottlenecks in the production process.
What is the history of production planning?
Production planning originated during the Industrial Revolution to manage mass production more effectively. Key figures like Frederick Taylor and Henry Gantt pioneered early techniques, with Gantt’s chart revolutionizing task scheduling. The demands of World War II advanced systematic planning approaches. The mid-20th century saw computers enhance precision and data analysis, leading to the development of complex planning software. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems emerged later, integrating various business processes. In the 21st century, advancements in AI, machine learning, and IoT have further evolved production planning, making it more adaptive and efficient.
Conclusion
Effective production planning is important for any business aiming to meet customer demands efficiently and cost-effectively. By understanding and implementing the various types of production planning, utilizing the right tools, and monitoring key performance indicators, companies can streamline their operations and improve productivity.
A well-constructed production plan not only optimizes resource use but also minimizes downtime and enhances overall product quality.