If you’re in the business of planning or forecasting for your organization, then you’ve likely heard of Rough Cut Capacity Planning (RCCP).
Do you feel like you’re always behind on your work because you can’t seem to get ahead of the demand? Are you constantly firefighting and putting out one emergency after another?
Rough Cut Capacity Planning is a planning methodology that can help your business overcome these challenges. It uses historical data to predict future demand and helps you plan for that demand by allocating the necessary resources.
This article will look at RCCP in detail and explain why it’s an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. Stay tuned!
Evaluate Rough Cut Capacity using our Online Rough Cut Capacity Planning Calculator
Definition
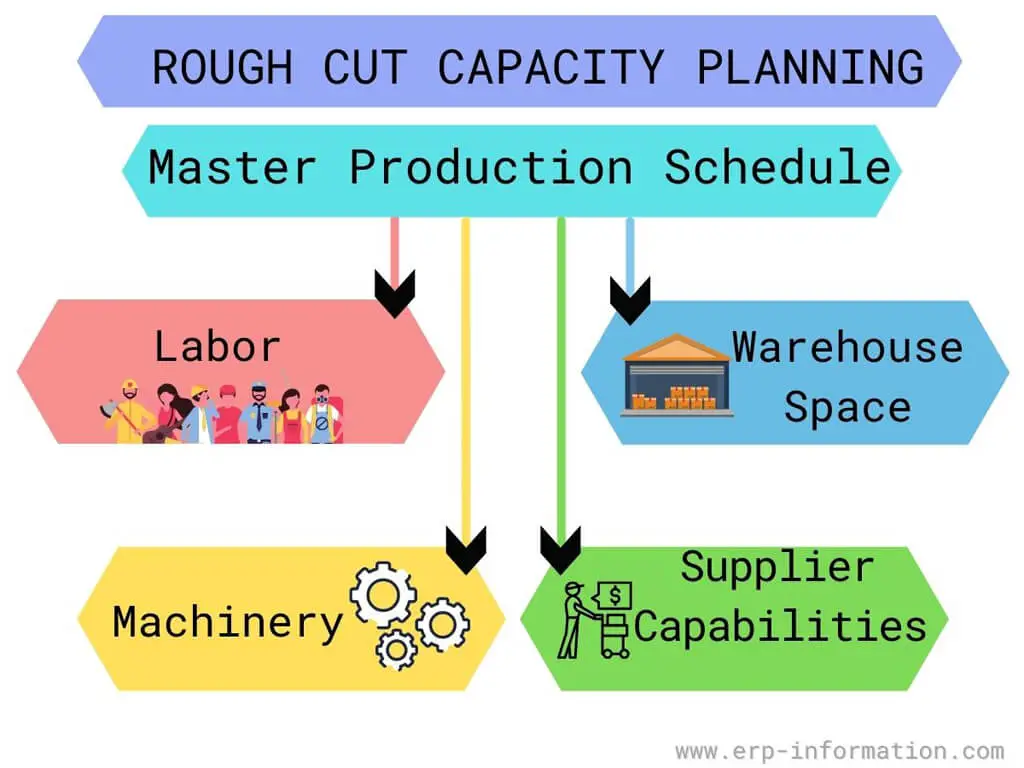
Rough Cut Capacity Planning is a long-term capacity planning that allows you to predict future capacity needs and take proactive steps to ensure your organization has the resources it needs to meet those demands. By anticipating growth and changes in your business, RCCP can help you avoid costly oversights and keep your company running smoothly.
It converts the master production schedule into requirements for critical resources, often including labor, machinery, warehouse space, and supplier capabilities.
The concept behind the term rough cut capacity is that it is the total amount of material required to fulfill the gross requirement of a company.
It does not consider scheduled receipts or the on-hand inventory; it calculates the rough cut amount needed to satisfy the gross requirement.
More on RCCP
Preparation and planning of the master schedule planner use it later, responsible for managing the resources and materials required.
Rough-cut capacity planning is an easy and simplified technique that does not involve many hidden values or inventories.
Thus, it is a streamlined capacity planning, which is more intuitive, organizational, and preliminary.
Rough cut capacity planning software
The main functionality of RCCP software usually comprises matching or balancing the assets available with the demands arising at the moment.
A firm must convert its demands into capacity, labor, materials, orders, and finished goods inventory. Therefore, it needs to balance its assets and plan accordingly.
It is a model that establishes a computational relationship between production designs, process sheets, consumption of raw materials, time available, labor availability, etc.
Types of Rough-cut Capacity Planning
In business management, capacity planning defines how much room companies will have for additional growth without incurring long-term risks or costs.
In this sense, it translates into optimizing current assets by judiciously allocating available resources among priorities such as development planning, new product introduction, etc., intending to increase overall ROI through efficient resource utilization and strategic allocation.
In the case of capacity planning, it needs lots of consideration. Hence capacity planning is based on two types,
- Short-term capacity planning
- Long-term capacity planning
Short-term capacity planning
In the case of the short-term plan, the main goal is to increase the production capacity by a fewfold and handle the pressure of irregular, unexpected shifts in the face of increased demand.
Managing increased demand needs plenty of changes, but the foremost is to increase production hours, which means overtime for the employees.
Setting up extra facilities and acquiring more materials is also a way to proceed.
Many employees are happy doing overtime, which means extra bonuses and increased wages.
Overtime can go on for a few days or even a few months. Depending on the rush and also on the other aspects of production.
Long-term capacity planning
Long-term capacity planning is a cumulative effect of numerous short-term outcomes in the case of long-term capacity planning. Increasing shifts temporarily to meet immediate demands can, in the long run, add to the production capacity if continued.
Opening up a new facility or increasing hiring and investing in proper training also increases production capacity in the long run.
Adding capital equipment and modifying the production plan is another opportunity to increase production capacity.
Some manufacturing firms can efficiently delay demands by backlogging, queuing demands, or managing an anticipatory inventory that takes care of sudden rises in order during particular periods.
It allows the firm to perform at its own pace smoothly.
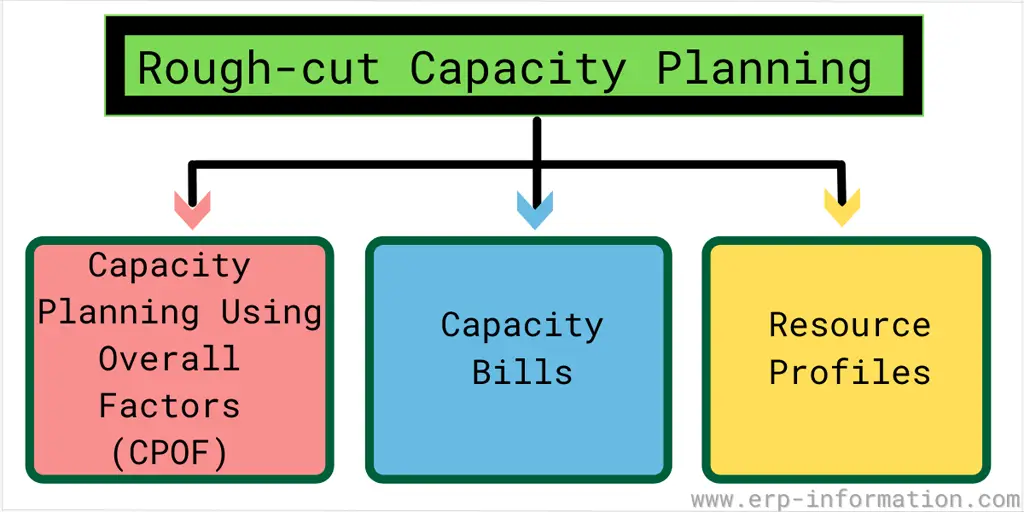
Three Methods of Rough Cut Capacity Planning
Capacity Planning Using Overall Factors (CPOF)
Capacity Planning Using Overall Factors (CPOF) is a fast and easy way to estimate your capacity needs. This method uses the overall product mix, sales volume, and lead time to calculate your needed capacity.
Capacity Bills
Capacity Bills is Capacity Planning Using Capacity Factors (CPCF) using Capacity Units, Capacity Expenses, and Capacity Releases. Capacity Bills give more detailed figures than CPOF. However, the results are highly accurate.
Resource Profiles
Resource Profiles look at your resources by product/period (e.g., monthly). Resource profiles show you how many resources you will need and when. Resource profiles provide more accurate estimates than Capacity Bills but take more time and effort.
Levels for Calculating RCCP
We can do RCCP in two levels. The first one is routing-based RCCP and Rate-based RCCP.
When you want to do a capacity plan by resource, you can use routing-based RCCP. When you want to do a capacity plan by production line, you can use rate-based RCCP.
The capacity load ratio is the output of both routing-based and rate-based RCCP. That is
Capacity load ratio = Required capacity / Available capacity
1. Routing-based RCCP
It helps you to calculate each resource’s required and available capacity in hours per week. That shows resource availability. Formula is
Resource capacity load ratio (hours per week) = Resource required capacity (hours per week) / Resource available capacity (hours per week)
2. Rate-based RCCP
It helps you to calculate the required and available capacity per week per production line. That shows production capacity. Formula is
Production line capacity load ratio (per week) = Production line required capacity (per week) / Production line available capacity (per week)
Rough Cut Capacity Planning Examples
Let us take the instance of a factory that produces two items, boots and sandals. An MPS calculation takes place before the production of the pieces begins.
The amount of material required and the necessary working hours are calculated.
A rough-cut capacity planning includes charting out the,
- Staff hours necessary to fulfill the job
- The units required
- Days that will be needed to complete the task eventually
- The amount of material that needs to be purchased.
This chart would not consider inventory management details or scheduled late arrival receipts. Hence a rough cut capacity planning schedule is simple, intuitive, and similar to organizational planning to chart out the requirements in a rough estimation.
Some advantages and disadvantages of rough-cut capacity planning are mentioned here.
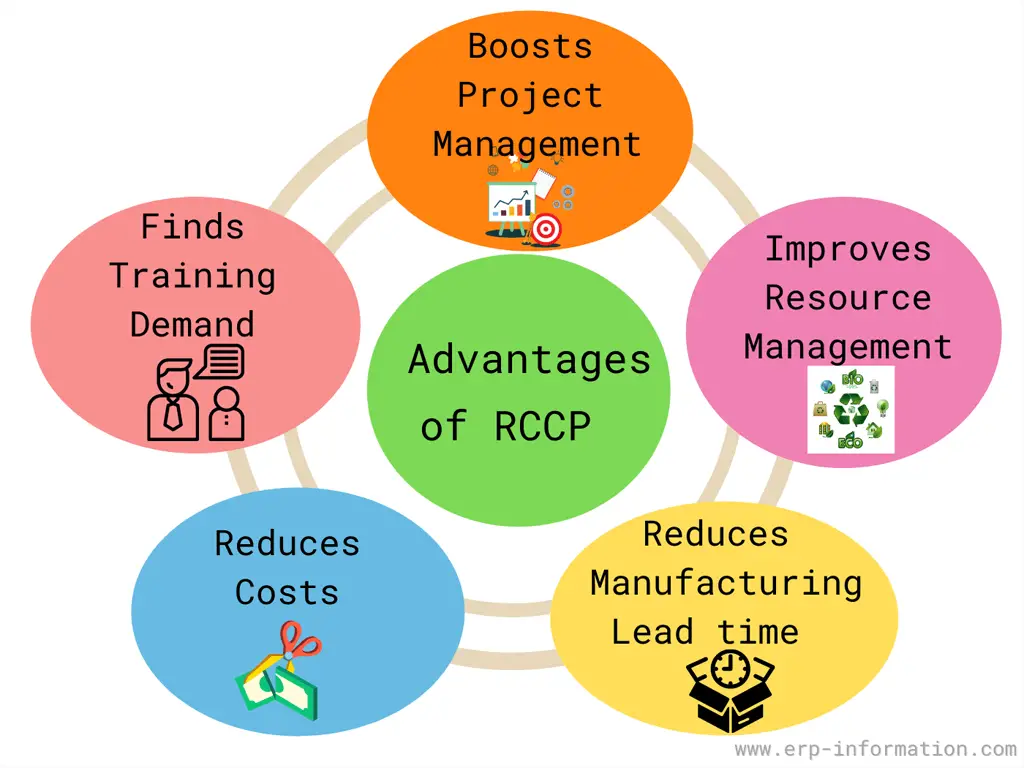
Advantages
Boosts project management
You can quickly identify which work should start first and which job you can start later because of rough cut capacity planning.
Hence you and your team make sure about your work priority. In this way, it improves your project management.
Improves resource management
You can get a clear idea of the resources available and the working hours required for each process in each workstation.
Hence you can quickly identify the more or less workload and adjust the capacity by increasing or decreasing the shifts and increasing the number of workstations.
Decreases manufacturing lead time
Rough cut capacity planning helps the manufacturer find out the issues in the manufacturing process and allows him to address the problem immediately. Hence it reduces the manufacturing lead time.
Reduces costs
Knowing your team’s capacity can forecast how you can take on many training projects in a given period. That helps to bring down costs by reducing the waste on the training team.
Helps to find training demands
It allows you to check out the training demand depending on the available resources like working hours, budget, and skills.
Challenges
Limited accuracy
RCCP relies on estimates and assumptions about future demand. It requires data accuracy about current and future demand and available resources such as labor, equipment, and materials. If this data is not readily available or reliable, RCCP plans may be inaccurate or incomplete.
So it is important to take care about gathering and reconciling information. Exporting data from trusted sources and integrating it into a single solution is the better way to overcome this problem.
Accurate calculations
RCCP depends on many calculations. Inaccurate calculation leads to inaccurate demand forecasts, which causes problems in the RCCP process.
Inflexibility
Once an RCCP plan has been developed, adjusting for unexpected changes in demand or resource availability can be difficult. That can lead to over- or under-utilization of resources and increased costs.
Resource constraints
Even with accurate data and robust planning processes, there may be situations where resource constraints limit an organization’s ability to meet production demands.
For example, a shortage of skilled labor or raw materials could prevent an organization from fully utilizing its capacity.
Communication
During the RCCP process, all departments of an organization participate. That may lead to a communication gap. To avoid this gap, have a single location for planning that improves communication between departments.
Time
The process can consume more time. Because data collection, analysis, and making decisions takes more time. When you repeat this process, you need to commit more time. To avoid this, you can use capacity planning software solutions to automate data collection and analysis.
Difference Between RCCP and Capacity Planning
Capacity planning and rough cut capacity planning (RCCP) are both planning processes that help organizations ensure they have the resources to meet their production requirements. Let us have a look into some key differences between these two approaches.
| RCCP | Capacity planning |
| It estimates whether an organization can meet its production plans. It is typically done before capacity planning. | It analyzes current & future demand, assesses available resources (such as labor, equipment, and materials), and develops a plan to optimize resource utilization. |
| It does not consider the specific details of individual machines or processes. Instead, it focuses on identifying potential capacity constraints at a high level and determining whether additional resources may be needed. | It considers specific details about individual machines or processes, allowing for more accurate resource allocation. |
Difference Between RCCP and CRP
| RCCP | Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP) |
| It is used in the beginning planning stage for the master production schedule. | It is usable for the final capacity check for the master production schedule. |
| It gives rapid feedback. | It gives feedback slowly. |
| It is less precise comparatively. | It is more precise. |
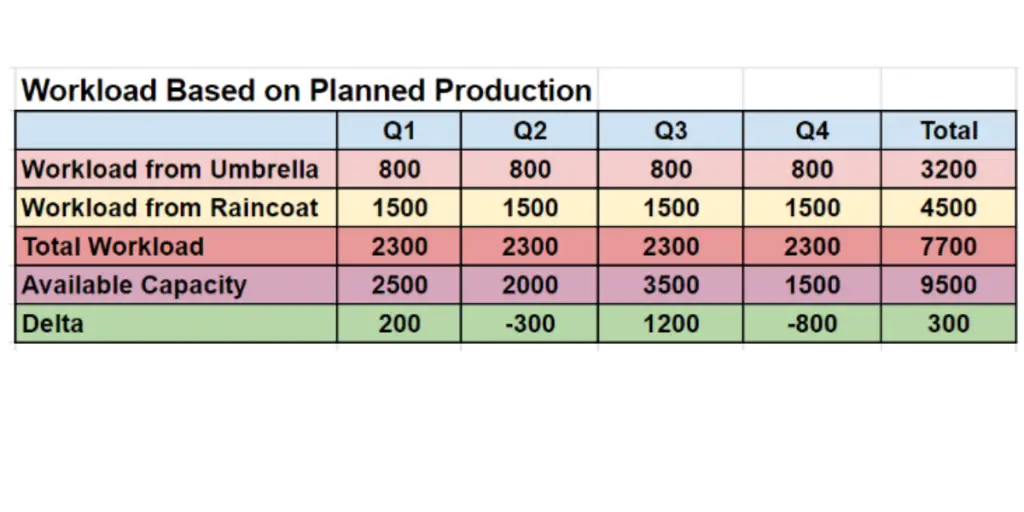
RCCP Calculation
To calculate RCCP, download the below sheet.
FAQs
What is rough cut capacity planning in SAP?
Rough cut capacity in SAP is a collection of outlooks on the organization’s resources. That means the organization considers one whole working day instead of hours and minutes and considers work center groups instead of a single work center.
SAP capacity planning predicts future needs based on available resources and anticipated demands. This type of planning is a wide-ranging activity that involves decisions related to people, processes, products, equipment, and finances.
Conclusion
RCCP stands for rough-cut capacity planning. RCCP is a process that helps manufacturers estimate the number of units they can produce in a given period, and it’s an integral part of manufacturing.
With the proliferation of data and information, it has become increasingly difficult for organizations to anticipate demand. As a result, many businesses have turned to rough-cut capacity planning as an effective way to ensure they can fulfill customer orders on time without sacrificing quality or exceeding their budget.
The goal is not just about meeting immediate needs but also being proactive with future growth by ensuring that there are no bottlenecks in production before they occur.
RCCP in manufacturing provides a methodology that combines these two aspects with cost-effective tools for optimizing productivity levels across your organization’s operations.
The rough-cut capacity planning technique has various advantages and disadvantages but is considered a safe starting point.