A smart factory is a facility that uses information and communication technologies to monitor and control the production process.
It aims to make the manufacturing process more efficient and productive.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into what a smart factory is, the technologies used, how to create it, levels of this type of manufacturing, benefits, and examples of the intelligent factory.
What is Smart Factory?
The smart factory is a term used to describe the use of several different combinations of current technologies to create a hyperflexible, self-adjusting production.
All machines and a central computer system are connected to a smart factory. That allows for real-time production process monitoring and makes it possible to make changes on the fly if necessary.
Initiatives toward smart factories may also be called “Digital Factories” or “Intelligent Factories.”
Its purpose is to make the manufacturing process as efficient and productive as possible.
Industry 4.0 Technologies Used by the Smart Factory
Industry 4.0 is characterized by integrating physical and digital technologies, which led to smart factory’s creation. Here we listed some Industry 4.0 technologies, including big data and analytics, cloud computing, cognitive computing, IoT, digital twins, 3D printing, Etc.
Big Data and Analysis
Data must be collected and analyzed to make decisions about improving the production process. In a smart factory, this data is collected in real time and is often processed using big data analytics tools.
Cloud Computing
It stores, manages, and processes data via internet-based remote servers. As a result, it allows businesses to have a single source of truth.
Cognitive Computing
A computer program that simulates a person’s thought processes is known as cognitive computing. It’s part of AI and focuses on imitating human thought processes. As a result, it can improve decision-making, optimize operations, and create new products and services.
Artificial Intelligence(AI)
It enables machines to learn and make judgments independently. Thus they can do tasks that would otherwise require human intelligence, which may help optimize procedures and efficiency.
Machine learning, pattern analysis, natural language processing, and decision-making are just a few of the AI techniques available.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The application of IIoT technologies in industrial settings is called Industrial IoT. The IIoT, or the industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), is a framework for integrating physical items and devices with digital systems.
This integration allows businesses to remotely control and monitor industrial equipment, providing real-time data that may be used to optimize operations and efficiency.
Digital Twin
It is a replica of a physical object or system. It can be used to simulate the behavior of the physical object or design and test different scenarios before they are implemented in the real world.
Know more about industry 4.0 technologies.
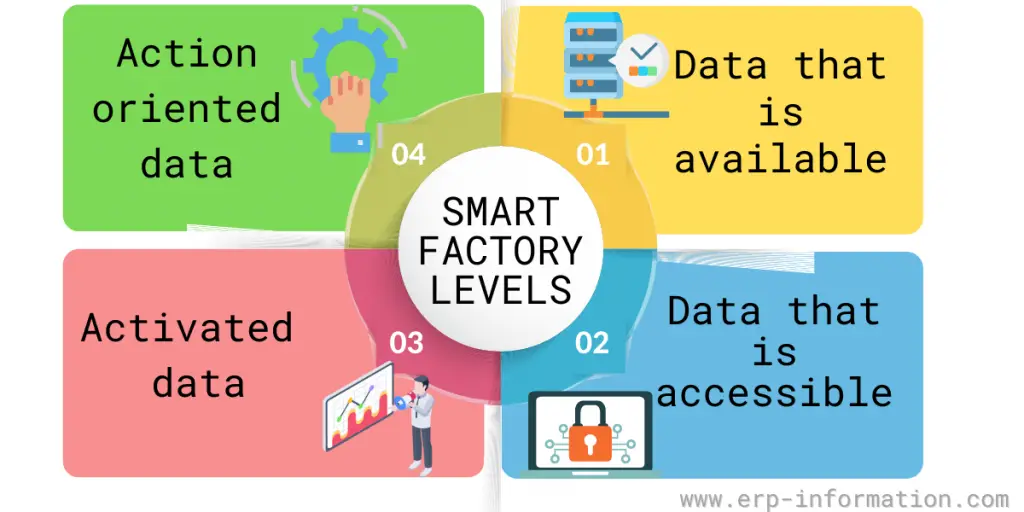
Smart Factory Levels
1. Data that is available
The first stage of data structure in a smart factory is available data. Here data is available but not accessible. Sorting and analyzing data requires manual work and can be time-consuming, adding inefficiencies to product improvement.
2. Data that is accessible
The second stage of data structure is data that is accessible. That implies that information is given in a more consumable form.
Data is structurally organized and sorted in one location, with additional systems to visualize data that help visualize data and display dashboards. In addition, the factory is capable of proactive analysis, though this may still take some time and effort.
3. Activated data
The activated data stage is the third stage of data organization. That implies that data can utilize machine learning and artificial intelligence to offer insights without requiring many humans.
4. Action-oriented data
The fourth and final stage of data structure is action-oriented data. Machine learning can generate actionable solutions to issues identified in the earlier stages. Collecting data, identifying problems, and developing solutions happen in sequence with little human input.
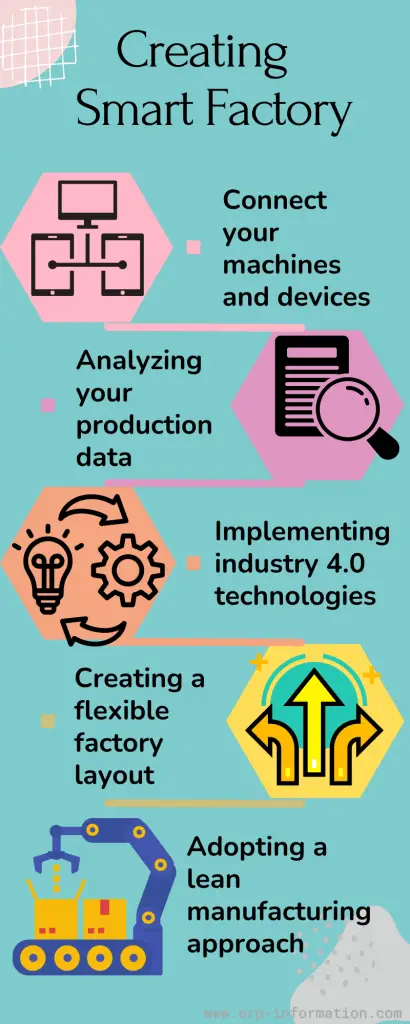
How to Create a Smart Factory?
It is essential to keep a few things in mind when creating a smart factory:
Connecting your machines and devices
A big part of making a factory “smart” is collecting data from all your machines and devices, aggregating it, and analyzing it to improve your production process. That requires connecting your machinery via sensors and other data-gathering methods.
Analyzing your production data
Once you have collected all of your production data, you need to start analyzing it to see where there are bottlenecks or inefficiencies in your process. That can be done with specialized software that helps you model and simulate your approach to make changes and improve production efficiency.
Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies
One of the critical aspects is the use of Industry 4.0 technologies like big data and analytics, cloud computing, cognitive computing, IoT, digital twins, and 3D printing. These technologies can help you optimize your process and improve your product quality.
Creating a flexible factory layout
In a smart factory, the structure of the production line is more flexible and can be reconfigured to meet changes in demand. That helps you avoid interruptions in your production process and keeps your operation running smoothly.
Adopting a lean manufacturing approach
Lean manufacturing is a philosophy that aims to reduce waste and increase efficiency in the production process.
That can be achieved by eliminating steps that don’t add value, streamlining processes, and using data to drive decision-making. Lean manufacturing is a vital element of the smart factory and can help you achieve your goal of increased efficiency.
Solutions Provided by the Smart Factory
It can provide many benefits, such as:
- Improved decision-making: The ability to collect and analyze data in real time can help businesses make better decisions about the production process.
- Optimized processes: IoT and digital twin technology can help businesses optimize their processes and increase efficiency.
- New products and services: 3D printing and other advanced manufacturing techniques can help businesses create new products and services.
- Increased capability: The ability to deliver an agile, iterative production process can expand both equipment and people’s capabilities, resulting in lower expenses, less downtime, and less waste in the production process.
- Reduced costs: Big data and analytics, cloud computing, and cognitive computing can help businesses reduce costs.
FAQs
What are examples of a Smart Factory?
Tesla factory: It is an example of a smart factory. The factory uses big data and analytics to optimize the manufacturing process.
Deloitte Smart Factory is a manufacturing facility that uses advanced digital technologies to enhance productivity, quality, and agility while reducing costs.
Is there a difference between Smart Factories and Smart Manufacturing?
Yes, there is a difference between smart factories and smart manufacturing. Smart factories are physical places where goods are produced using advanced digital technologies. Smart manufacturing, on the other hand, is the application of these technologies to the manufacturing process.
Conclusion
The smart factory is the next step in the evolution of manufacturing. Technological advances allow smart factories to monitor and control production using information and communication technologies.
This automation and integration enable a more efficient and productive manufacturing process. As a result, the intelligent factory can provide several benefits, such as improved decision-making, optimized processes, increased productivity, and reduced costs.
It is the future of manufacturing.