Storage costs can be a significant expense for businesses, and it becomes very necessary to find ways to keep these costs as low as possible.
Businesses frequently incur significant costs in storing their inventory, which can accumulate substantially over time.
Employing effective storage practices remains the optimal strategy for minimizing storage expenses. Multiple storage methods exist, each accompanied by its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
This blog post will discuss storage costs, its formula, and tips for reducing those expenses. It’ll also give an example of how the formula works in practice. Read on to learn more!
We will provide some online calculators to make your work easy
- Evaluate your storage cost using our Storage Cost of Inventory Calculator Online
- Calculate your Buffer Stock using our Buffer Stock Calculator Online
- Evaluate your warehouse storage cost using our Warehouse Storage Costs Calculator Online
- Do ABC analysis using our online ABC Classification Calculator
Key Insights
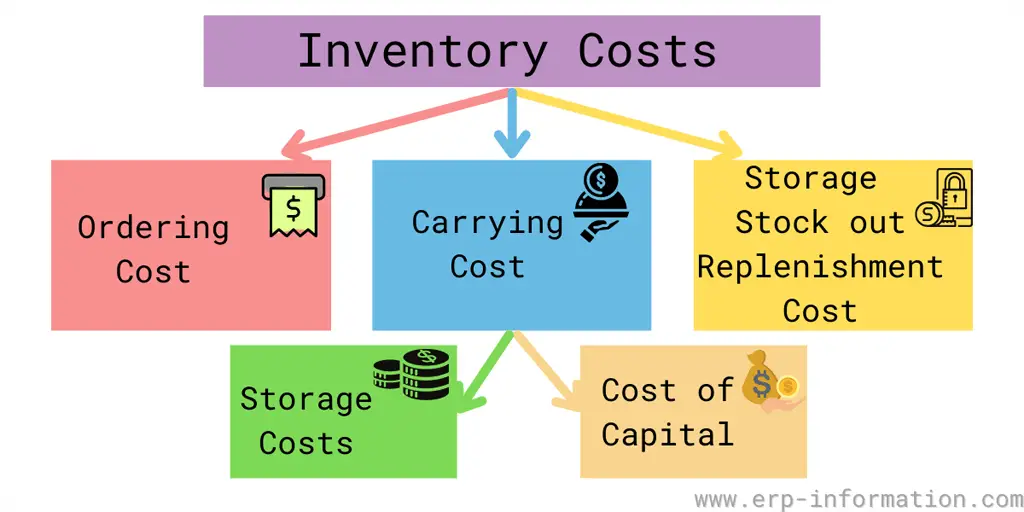
- Storage expenses encompass warehouse costs, labor, and materials involved in preserving inventory.
- Key considerations in inventory storage costs include Facility Expenses, Capital Costs, Risk Management, Taxation, and Obsolescence.
- Some strategies that help effectively manage inventory storage costs are essential for maximizing your financial performance, like demand forecasting, ABC analysis, Just-in-time inventory, etc.
- Storage expenses fluctuate based on several factors, ranging from the facility’s location and square footage to the duration of rental, quality standards, climate control, and the level of required security measures.
- Reducing inventory costs is more important. Accelerate marketing efforts, maintain on-hand inventory, and explore other strategic avenues for savings.
What are the storage costs?
The cost of storage is the amount spent on storing inventory. This includes the cost of warehouse space, labor, and materials.
The goal of inventory management is to minimize the cost of storage while still maintaining enough inventory to meet customer demand.
There are many ways to reduce storage costs, including reducing inventory size, automating order fulfillment, and using just-in-time inventory management. By carefully managing storage costs, businesses can improve their bottom line.
Why is it important?
One of the main factors in determining how much an organization spends on inventory is the cost of storage. Businesses that produce goods with closely linked components don’t need to store any items since there aren’t many fluctuations in production from one day to the next.
However, most businesses have various items that need to be kept safe and secure. This requires people who need to be paid. Utilities also cost money, so companies need to decide if it is more beneficial to incur these costs or make money from selling their products.
The storage costs of inventory are usually deductible. While most companies do not add their storage and transportation costs to the price of the finished product, some products with very high storage costs have hidden or indirect storage costs added to their price.
Storage cost formula
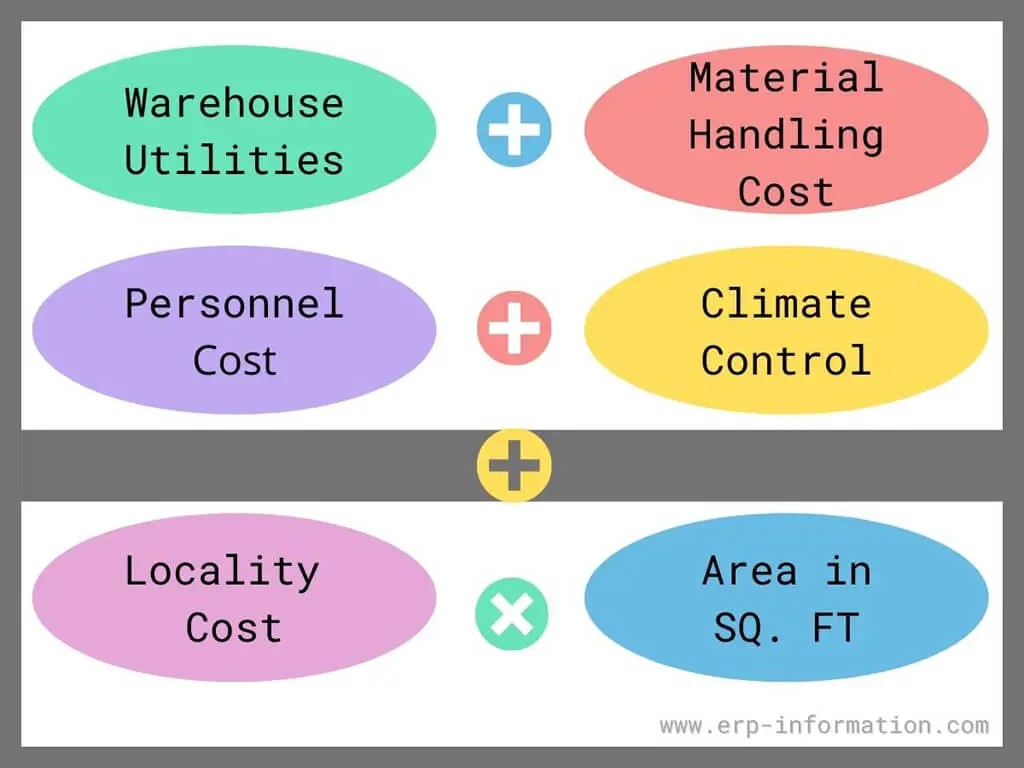
Storage cost includes the cost of warehouse utilities, material handling cost, personnel costs, and climate control costs. Hence the formula will be as follows.
Storage cost = warehouse utilities cost + material handling cost + personnel cost + climate control cost + (locality cost x area in square feet).
Example of storage cost
First, we need to measure the storehouse by square feet and calculate the total rent cost, along with charges like electricity and water supply.
Next, the finished items to be stored, like furniture, are considered inventory.
Finally, raw materials like wood, nuts, bolts, and metal plates can be a part of the inventory.
Components such as wood-cutting machine parts, gallium for adhesive purposes, and even wood fillings or sawdust utilized in manufacturing may necessitate inventory storage.
When safeguarding your furniture, all these items contribute to incurring a specific expense referred to as storage costs.
What is an inventory, and how does it incur storage costs?
An inventory is a stock or store of goods maintained by the firm. For example, it might be near the retail store or the production site.
The number of finished products in the storage is known as the on-hand inventory at any given moment.
Various other types of inventories are not related directly to the independent demand of the finished product but consist of goods involved in maintaining the production line.
Inventories of raw materials, machine parts involved in the production, assemblies, and sub-assemblies processed or waiting to be processed in the next step are known as work-in-progress inventory.
These are dependent demands and do not directly connect to the finished item’s market demand.
The cost of keeping inventory skyrockets for many reasons, but you can keep it under control with intelligent thinking.
Some major inventory storage costs
Cost of facility
The warehouse running cost is no small strain on the pocketbook. This includes covering depreciation for buildings and interior racks, insurance payments to keep your goods safe, and utility costs like electricity and fuel.
A fixed cost with each item stored in this space– regardless of size – facility costs are essential investments in protecting one’s inventory against unforeseen events down the road.
Cost of funds
Companies invest borrowed funds to purchase inventory, trading interest costs for potential future earnings. As the market rate fluctuates, so do their costs of investing in stock – a fact that can directly affect how profitable each unit is.
Understanding and managing fund costs are essential to maximizing returns on invested capital.
Risk mitigation cost
Securing and protecting valuable inventory can be costly, from installing fire suppression systems to planning flood mitigation or hiring security guards.
These measures help safeguard cherished possessions while accruing sizable expenses that are largely fixed depending on the value of those items being safeguarded.
Taxes
The business owner knows that staying ahead of property taxes on inventory requires a strategy.
Costs can be reduced significantly without sacrificing value by carefully controlling stock levels and selling off excess items before tax measurement dates.
Disuse cost
Even when thoughtfully managed, inventory can be costly; over time, it may lose its value or become obsolete due to changing technology.
This especially holds for items with slower sales turnover and impacts the overall worth of your stock – sometimes requiring steep discounts to get rid of merchandise that’s no longer wanted.
10 strategies to optimize the reduction of inventory storage costs
Effectively managing inventory storage costs is essential for maximizing your financial performance. Here are 10 strategies to help you manage or fine-tune storage costs without compromising on inventory levels:
1. Demand Forecasting: Accurately predict demand to avoid overstocking and minimize storage expenses.
2. ABC Analysis: Categorize inventory based on importance and turnover rate to allocate storage space efficiently.
3. Just-in-Time Inventory: Adopt JIT practices to order inventory only when needed, reducing holding costs.
4. Supplier Collaboration: Work closely with suppliers to establish efficient ordering and delivery processes, minimizing safety stock levels.
5. Optimize Storage Layout: Organize your warehouse for maximum space utilization with vertical storage solutions.
6. Inventory Rotation: Implement FIFO or LIFO systems to minimize obsolescence risk.
7. Reduce Safety Stock: Keep safety stock at a minimum while still handling demand fluctuations.
8. Regular Audits: Conduct inventory audits to identify slow-moving or obsolete items for discounted disposal.
9. Economical Packaging: Choose packaging that maximizes storage capacity and lowers costs.
10. Advanced Inventory Management Software: Invest in real-time tracking and demand forecasting software for better decision-making.
By following these strategies and continuously refining your storage cost management, you can reduce expenses while maintaining optimal inventory levels and satisfying customer needs.
How is the cost of storage distributed?
Distribution of storage costs:
- Total area in terms of square feet
- Total time of renting
- Quality maintenance
- Climate control storage
- Security charges
Storage costs can vary on a lot of issues. They start from the location of the facility, the total area in terms of square feet, the total time of renting, quality, and climate control to the security needed to be provided.
A top-tier storage facility amplifies the on-hand inventory costs. Opting for a customized self-storage space aligned with specific needs proves a superior alternative.
Yet, this option tends to cater primarily to well-established companies boasting substantial inventory at all levels. Generally, a conveniently situated facility emerges as the most astute choice.
Climate-controlled storage units come at a premium of around 15% compared to non-climate-controlled ones. However, in regions with high humidity or extreme heat, these units become indispensable for ensuring the appropriate preservation of stored goods.
Security stands as a vital aspect of this arrangement. Insufficient security measures jeopardize the safety of stored items, rendering the entire undertaking ineffective.
Though developing an ideal storage facility and managing associated costs may seem demanding, it serves as a shield for your company against unforeseen losses and potential raw material shortages.
What are the reasons to store inventory by the company?
The reasons to keep inventory in the company are
1. To have safety stock
2. To fulfill seasonal demands
3. To avoid a lack of raw materials because of mid-way inventory
4. Rotational inventory
5. Sleepy inventory
The company stores inventories even though it has to bear storage costs for these reasons.
Safety stock
The company has to hold some extra inventory to fulfill the unexpected increase in demand for its product. So it is necessary to have the additional supply for the most desired products.
Evaluate Safety stock using our Online Safety stock calculator
Seasonal demands
Some companies get more revenue in some seasons, like the cloth industry. So to fulfill that demand, they should have some extra stock in their warehouse
Mid-way inventory
It means material that is ordered but not yet delivered. The type of material and the vendor’s location may take several weeks or months to reach your warehouse. So the company has to have stock.
Rotational inventory
Product-based industries must have rotational or cycle inventory to create sales and satisfy customer demand.
Sleepy inventory
The company should hold some “not sold” products. These are called dead or drowsy inventory.
How do we reduce the storage cost of inventory?
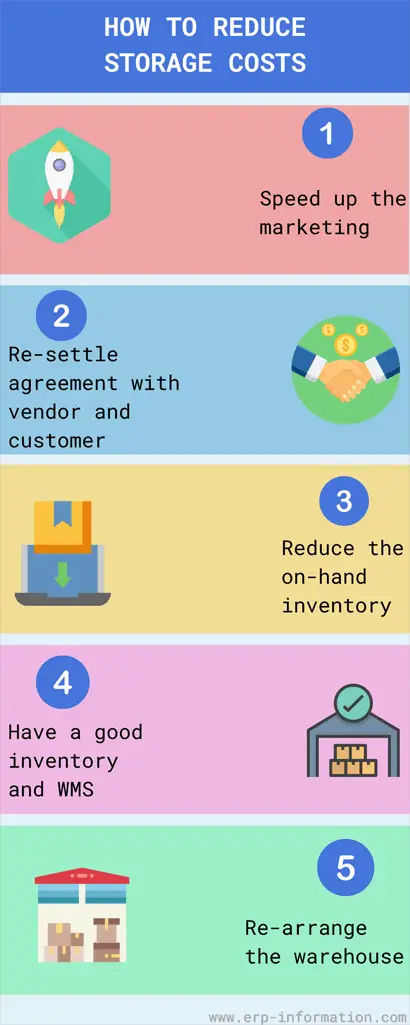
Here are a few ways to reduce inventory storage costs.
1. Reduce the on-hand inventory
Unnecessary storage of inventories leads to an increase in storage costs. Hence keep a minimum on-hand inventory sufficient to fulfill the order requirement.
2. Speed up the marketing
Take necessary actions to speed up your sell-through ratio so that products in the warehouse move fast, which helps reduce storage costs.
3. Rearrange the warehouse
Rearrange the design of your warehouse by adding extra shelves in the limited space. Use containers for efficient storage.
Once again, re-evaluate the arrangement of products in the warehouse so you can move some unwanted, unnoticed products from the warehouse.
4. Have a good inventory and warehouse management system
It is important to adopt good warehouse management and inventory management technology.
These management systems give real-time visibility of inventory levels and help do effective shipping.
5. Re-settle the agreement with the vendor and customer
Re-settle the agreement with your customer by specifying the maximum holding time for inventory so that you can avoid the holding cost of finished goods.
Since the inventory cost is included in their price, it’s important to note that you will be charged for any extra held over. You can also arrange an agreement with your vendor so they are responsible when shipping damaged goods, even if there was no fault on either end!
FAQs
What kind of items need climate-controlled storage?
The need varies based on the composition of the item. For instance, wooden items require a climate-controlled setting to avert cracking and warping induced by hot or cold conditions.
Similarly, leather furniture demands such an environment as extreme temperatures can lead to cracking and brittleness in the leather.
Also, other items like books and artwork often benefit from climate control. Books stored in high humidity settings might develop mold, while artwork can suffer damage if not stored in an environment with regulated humidity levels.
Some of the other items that need to be stored in the climate-controlled storage area
– Clothing and fabric
– Computers
– Electronic items
– Household appliances
– Musical instruments
Conclusion
Reducing inventory storage costs is crucial for maintaining a healthy bottom line. By implementing effective strategies such as demand forecasting, ABC analysis, and just-in-time inventory management, businesses can significantly cut down on these expenses.
Optimizing storage layout, maintaining efficient supplier collaborations, and utilizing advanced inventory management software also play pivotal roles. While storage costs encompass facility expenses, labor, and risk management, they can be mitigated through smart practices.
Embracing these techniques not only enhances financial performance but also ensures that inventory levels are kept optimal, safeguarding against obsolescence and ensuring customer satisfaction.