As technologies grow in the telecommunication industry with the adoption of 5G, managing customer data become complex. The adoption of 5G created recurrent problems for telecommunications.
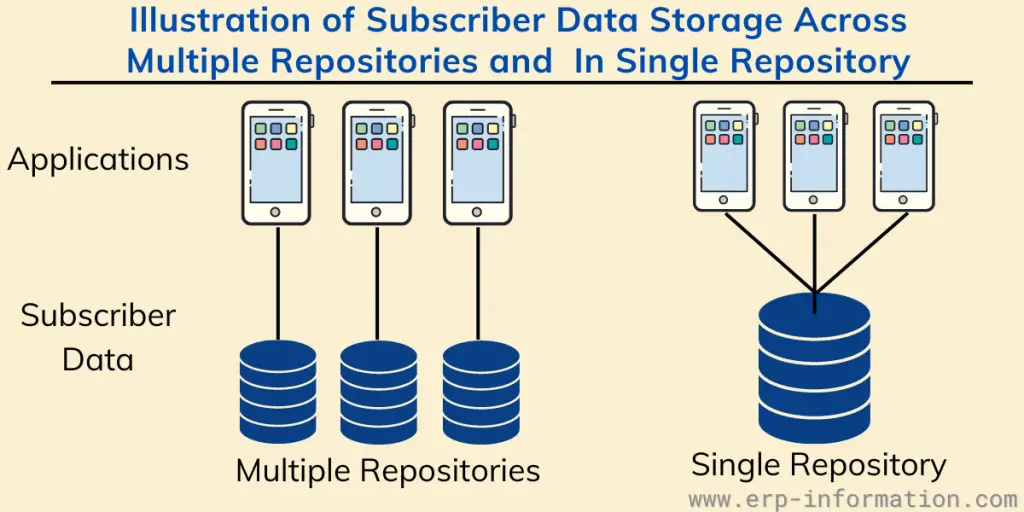
The existing practice of syncing customers’ information across multiple repositories would slow down resulting efficiencies and make it difficult to keep track of customer information in one place.
Storing and managing customer data in an organized manner allows industries to personalize offers for individual customers, respond quickly to inquiries, analyze customer behavior, and identify trends.
So, Subscriber Data Management has emerged in mobile networks as primarily a way of centralizing data for the security of users.
It stores, organizes, and accesses customer data from a central location.
This post will explain what subscriber data management is, its benefits, its role in 5G, and its components.
What is Subscriber Data Management?
It is a critical aspect of modern telecommunication networks that centralizes and consolidates subscriber data into a single, unified platform.
This system stores valuable information used by various telecom services, including user profiles, preferences, network usage, and device details.
In other words, it is a unified platform applicable to both 4G and 5G subscriptions, simplifying the network upgrade path. It’s an industry standard that helps efficiently manage users’ data.
SDM aims to provide a holistic view of subscribers, enabling telecom operators to deliver personalized services, enhance customer experience, and streamline operations.
As technology continues to evolve and the volume of data grows exponentially, effective SDM becomes imperative for telecom providers to stay competitive and ensure customer satisfaction.
Benefits of SDM
Integrated view of real-time subscriber data
Telecom providers will get a unified platform to view all real-time subscriber data across various applications. This consolidation makes accessing, analyzing, and managing data easier, leading to more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Resilience and reliability
SDM systems are built with superior robustness, offering high availability, reliability, and performance. That ensures uninterrupted access to crucial data, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Cost-effectiveness
The system centralizes subscriber data and reduces the need for multiple databases or systems, resulting in cost savings. It boosts profitability by allowing telecom operators to reduce time-to-market for new services or features.
Facilitates 5G and cloud infrastructure evolution
SDM plays a critical role in the evolution towards 5G and cloud infrastructure. It stores essential data used by diverse services, simplifying the network upgrade path and making it easier to adopt new technologies.
Subscriber-centric policy management
With SDM, service providers can adjust the distribution of network resources according to the subscriber’s payment or usage patterns. This personalized approach enhances customer satisfaction and increases loyalty and revenue.
Role of SDM in 5G Core
Subscriber Data Management plays a crucial role in 5G Core networks. It provides a converged platform for both 4G and 5G services, helping operators enable high-value next-generation use cases.
New requirements for storing and managing data emerged because of 5G. SDM sits at the center of the core network and stores valuable data used by diverse telecom services. It ensures that stored data is available in real time with all security measures.
5G doubles the complexity in the control plane because of varying requirements in different services across multiple domains and devices. SDM reduces this complexity by providing a unified repository.
SDM is a cloud-native architecture and supports different deployment options to serve multiple use cases for edge computing and network slicing with CAPEX, OPEX, and the low total cost of ownership (TCO).
SDM offers a flexible solution in 5G Core network architecture, where unified data storage and centralized subscription management services are split. That helps to handle the subscriber data more efficiently and enhances the network responses.
Additionally, the SDM is integral to the Service-Based Architecture (SBA) of the 5G core network. The service-based interfaces in this architecture use HTTP/2 over TCP, enabling efficient communication between network functions.
Types of data held by the subscriber repository
- SIM identities
- Subscription profiles (data, IMS, V2X, and more)
- Contexts, sessions, and policies
- Application states for 4G and 5G subscriptions
- User identities (SUPI/SUCI/IMSI/GPSI for each subscriber in 4G+5G)
- AMF/MME and SMF contexts for UEs
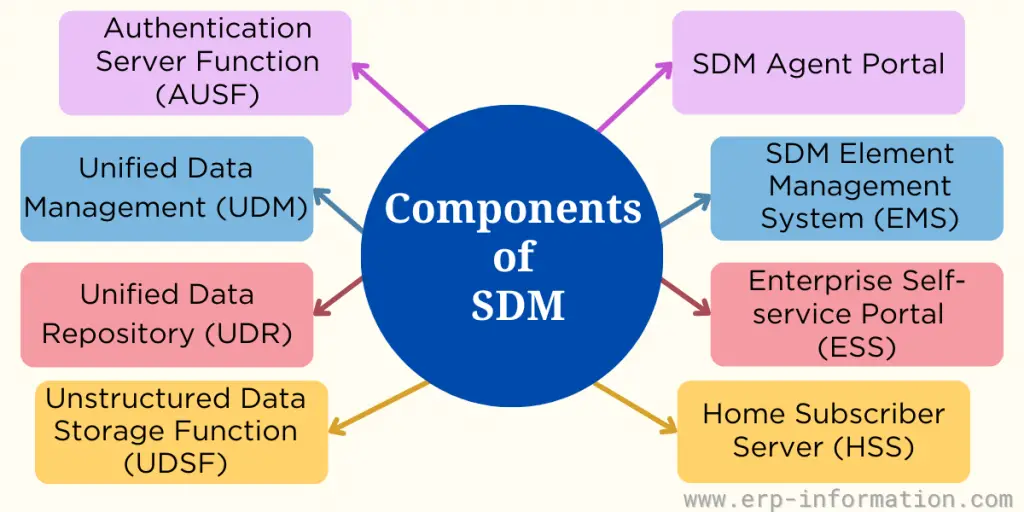
Components of SDM
Authentication Server Function (AUSF)
This component is responsible for verifying a subscriber’s identity (authentication) in a 5G network.
Unified Data Management (UDM)
It provides authentication and authorization access services in 4G and 5G networks.
Unified Data Repository (UDR)
This component is a subscriber database that stores SIM identities and subscription profiles for 5G and 4G services.
Unstructured Data Storage Function (UDSF)
It stores, manages, and retrieves network function sessions in an unstructured format.
SDM Agent Portal
It is a web portal that manages subscriptions, SIM cards, service parameters, and troubleshooting.
SDM Element Management System (EMS)
This component is for managing network element configuration and monitoring system performance and health.
Enterprise Self-Service Portal (ESS)
It is a web portal in private 5G deployments that manages SIM/subscription profiles, device lifecycle, and real-time connection status and monitors usage.
Home Subscriber Server (HSS)
This is the main database that contains all the subscription-related data required for the system to work. It includes information like user profiles, credentials, and network access configurations.
Conclusion
Subscriber Data Management is essential in the telecommunications sector, offering a centralized platform for consolidating and efficiently managing user data.
As networks evolve to accommodate the surge in data volumes and the transition towards 5G and cloud infrastructure, SDM provides a critical solution.
It enhances policy management, facilitates software updates, and offers a comprehensive view of real-time subscriber information. By effectively leveraging SDM, telecom service providers can get more benefits.