Supply Chain Planning (SCP) is a process that helps businesses ensure that they have the right amount of goods and services to meet customer demand. It involves forecasting future demand and then organizing production and inventory accordingly.
In this blog post, we will discuss the definition of SCP, its types, process, examples, benefits, and processes involved in supply chain planning.
What is Supply Chain Planning?
It is part of supply chain management (SCM).
Supply chain planning can be defined as ensuring a business has the right amount of goods and services to meet the market demand.
It involves forecasting future demand and then organizing production and inventory accordingly. There are various types of SCP, each with its own set of processes.
Types of SCP
There are three types of supply chain planning:
Short term planning
This type is used to plan and manage production for weeks or months. It involves forecasting demand, organizing production, and managing inventory.
Long term planning
This type is used to plan and manage production for the next few years.
Integrated supply chain management
This type is a comprehensive approach that integrates short- and long-term planning into a single process.
Supply Chain Planning Strategies
There are a few key strategies that can help make SCP more effective.
1. Having accurate and up-to-date data is essential for making informed decisions. This means having a system to track inventory levels, sales trends, and supplier performance.
2. Planning is vital for ensuring enough stock to meet market demand while avoiding overstocking, leading to waste and lost profits.
3. Regularly reviewing and adjusting plans based on changing conditions is critical for ensuring that the supply chain runs smoothly. Factors that can impact plan adjustments include changes in customer needs, supplier reliability, and market conditions.
By following these key supply chain strategies, supply chain planners can develop more effective plans that will help improve the supply chain’s overall efficiency.
Supply Chain Planning Process
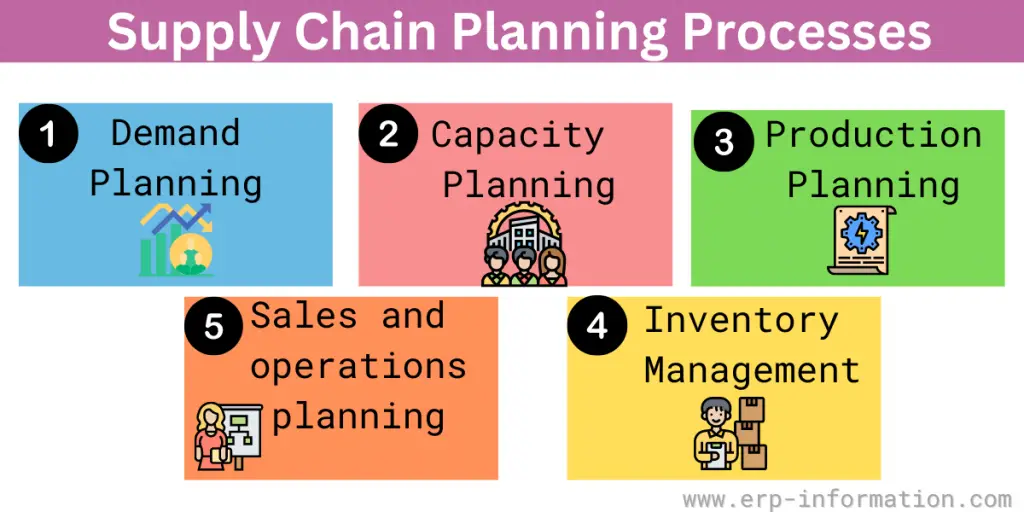
There are five main processes involved in supply chain planning:
1. Demand planning
It is part of the demand management process. The demand planning process involves predicting future demand for goods and services. This forecasting is done by analyzing past sales data and trends in market demand. The output of this process is a demand plan.
2. Capacity planning
Capacity planning determines how much supply a company has to meet forecasted demand. It includes organizing production, setting up suppliers, and managing inventory.
3. Production planning
Production planning determines what products will be made and when they will be made. This includes setting up schedules, ordering materials, and preparing production lines.
4. Inventory management
This process manages the stock level to ensure enough supply to meet consumer needs. It includes setting reorder points, ordering stock, and tracking inventory levels.
The other tool part of supply chain planning is distribution requirement planning.
5. Sales and operations planning (S&OP)
Sales and operations planning (S&OP) brings sales and operations together to make decisions affecting both departments.
The goal of S&OP is to ensure that the two departments are working together to meet consumer demand. Therefore, sales and operations planning should be done regularly, preferably monthly.
The process of sales and operations planning usually involves the following steps:
- Collecting data
- Analyzing data
- Developing plans
- Communicating plans
- Tracking results
Five Steps to Supply Planning and S&OP Success
1. A supply plan is created by forecasting future demand and organizing production and inventory to meet that demand.
2. Forecasting future demand – Forecasting future requests is made by analyzing past sales data and trends in customer demand. Various forecasting methods can be used, including trend analysis, regression analysis, and causal models.
3. Determining inventory levels – The inventory levels are determined by calculating how much supply is needed to meet forecasted demand. This process includes setting reorder points, ordering stock, and tracking inventory levels.
4. Planning production – Planning production by setting up schedules, ordering materials, and preparing production lines. S&OP integrates short-term and long-term supply chain planning into a single process.
5. Adjusting plans as needed – The supply plan and inventory levels are adjusted to meet changes in demand. This can involve modifying production schedules, ordering more or less stock, and adjusting inventory levels.
These five steps work together to help a company keep its supply chain running smoothly and meet customer demands.
Flows in the supply chain
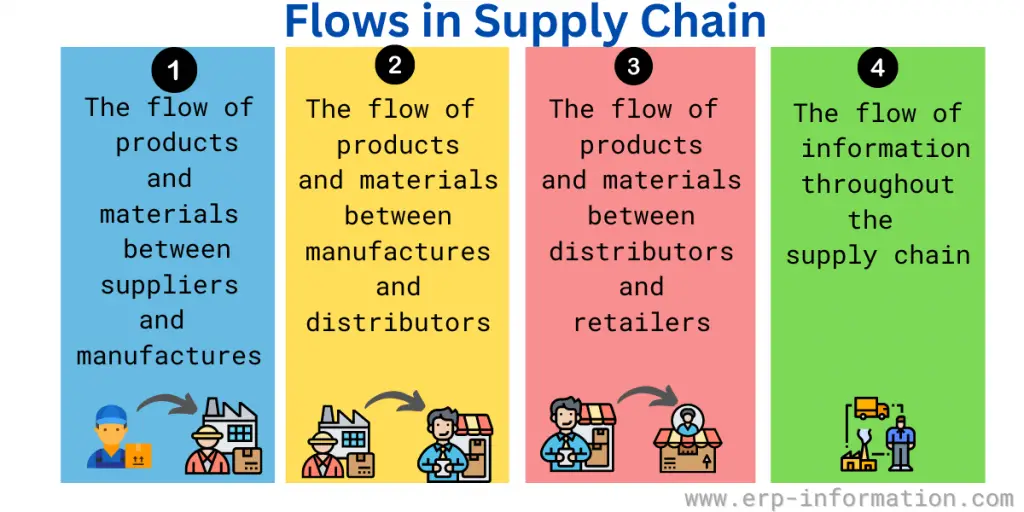
- The flow of products and materials between suppliers and manufacturers
- The flow of products and materials between manufacturers and distributors
- The flow of products and materials between distributors and retailers
- The flow of information throughout the supply chain
Supply Chain Planning Examples
One standard supply chain planning example is for a company that sells products online. In this case, the SCP process would involve forecasting how the company will sell many products in the next month.
Then you need to figure out how many resources (such as employees, products, and shipping supplies) you need to meet that demand. And then arrange for the production and delivery of those resources.
Another example would be a company that needs to replenish its stock of products. The company would need to forecast how much product it will need and then order that amount from its suppliers.
The company needs to plan for changes, like increasing demand for a product. This could require the company to place a larger order from its suppliers, or it could mean that it would need to find a new supplier if its current supplier can’t meet the increased demand.
Benefits of Supply Chain Planning
Mainly they benefit production operations substantially. The following are other benefits of supply chain planning:
Increased profitability
Planning helps companies produce the right products in the right quantities, increasing profits.
Improved customer service
Supply chain planning helps businesses meet customer orders quickly and efficiently by forecasting demand and organizing production.
Reduced inventory costs
Properly managed inventory can help reduce stock outages and excess inventory costs.
Improved supply chain coordination
When all parts of the supply chain work together, it leads to a more efficient and coordinated supply chain. This can lead to increased profits and improved customer service.
Less waste and fewer delays
By forecasting demand, companies can plan production, which helps avoid wasted time and resources due to last-minute changes in the market. This also helps eliminate or reduce delays when different parts of the supply chain are not coordinated.
How to Get Started with Supply Chain Planning?
If you’re interested in getting started with SCP, here are a few tips:
Talk to your suppliers
Your suppliers can be a valuable resource when it comes to capacity planning. First, ask them about their current production capabilities and plans.
Use historical data
Historical data can help forecast future demand. Use past sales, surveys, and market research data to help you plan demand.
Use software tools
Software tools can automate the supply chain planning process and make it easier to manage. Various supply chain management software options are available, so find one that fits your needs. SCP is critical for any business to meet customer demand while maximizing profitability.
What are the Tools Used for SCP?
Companies can use various management tools and techniques for effective supply chain planning. However, some of the critical supply chain drivers are:
- Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) – S&OP is a process that helps companies to align supply and demand. It involves forecasting future sales, organizing production, and managing inventory.
- Master Production Schedule (MPS) – An MPS is a schedule showing each product’s planned production. It can plan production, track inventory levels, and set supply chain deadlines.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP) – MRP is a process that helps companies order the correct amount of materials to meet production demands. It uses past sales data and current inventory levels to calculate how much material needs to be ordered.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) – JIT is a supply chain strategy that aims to reduce inventory levels and improve delivery times. It relies on suppliers to deliver materials just in time for production.
- Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP) – CRP is a process that helps companies to plan for future production needs. It uses historical data and current capacity levels to forecast future production demands.
- Inventory Management – Inventory management is tracking and managing inventory levels. This can include tasks such as ordering, stocking, and shipping inventory.
- Transportation Management – Transportation management is organizing and coordinating transportation resources. This can include selecting carriers, arranging shipments, and tracking freight.
Who does the supply chain planning in an enterprise?
In most organizations, supply chain planning is a centralized function carried out by supply chain planners.
The supply chain planners are responsible for developing and executing the supply chain strategy, ensuring that the supply chain can meet the demands of the business.
Supply chain professionals use various tools and processes to carry out their work. Some of the most common tools include supply chain modeling, inventory management, and forecasting.
The New Trend in Supply Chain Planning
The new trend in supply chain planning is moving away from traditional, siloed planning processes and towards collaborative, end-to-end supply chains.
This involves breaking down the barriers between different parts of the supply chain and working together to plan and execute supply chain operations.
Another trend is the use of big data and analytics. With so much data available, businesses can use analytics to develop predictive models that help them forecast demand more accurately.
This allows them to better plan their production and inventory levels, which leads to increased profitability and improved customer service.
The Future of Supply Chain Planning
The future of supply chain planning will likely include more automation and artificial intelligence (AI). AI can help planners optimize their supply chains by predicting demand, identifying bottlenecks, and recommending solutions.
Artificial intelligence
There are several ways that businesses can use AI in SCP, including the following:
Forecasting
Companies can use AI to predict future demand based on past data. Demand planning can help companies to plan their production and inventory levels better.
Supply network design
AI can help companies optimize their supply networks, ensuring they have the right suppliers and inventory at suitable locations.
Order management
AI can help companies optimize their order processing, reducing time and money spent on processing orders.
Overall, AI can play a vital role in improving supply chain execution and ensuring that companies meet customer satisfaction. In addition, companies can improve their efficiency and competitiveness in the market by using AI.
Blockchain technology
Another potential trend in supply chain planning is the use of blockchain technology. For example, companies could use blockchain to create a distributed ledger of transactions they can share between supply chain partners.
This would help to ensure transparency and trust among supply chain partners.
It is still early for blockchain in supply chain planning, but it holds great potential for the future. As businesses become more familiar with the technology and its benefits, we expect to see more blockchain implementations in supply chain processes.
Big data and analytics
The use of big data and analytics is a trend that is likely to continue in supply chain planning. With so much data available, businesses can use analytics to develop predictive models that help them forecast demand more accurately.
This allows them to achieve integrated business planning, increase profitability, and improve customer service.
Conclusion
In supply chain planning, you should consider three key things: minimizing stock-outs and other supply disruptions, ensuring your suppliers are reliable and cost-effective, and meeting customer demand.
This article details supply chain planning and the tools that can help you do it more effectively.