Sustainable agriculture addresses carbon emissions by promoting practices that prioritize soil health, reduce reliance on external inputs, and foster holistic farming systems that benefit both the environment and communities.
Let us explore Sustainable Agriculture and Transport, discovering the pivotal role of eco-friendly practices in revolutionizing modern agriculture and transportation in this blog post.
Overview of Sustainable Agriculture and Transport
Sustainable Agriculture and Transport form a symbiotic relationship important for environmental stewardship.
By implementing eco-conscious farming methods and optimizing transportation logistics, we reduce carbon footprints, foster food security, and preserve natural resources, paving the way toward a more sustainable future.
How does Sustainable Agriculture Work?
Crop Diversity for Soil Health

Rotating crops and practicing intercropping enhance soil health, fostering a balanced ecosystem and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
Cover Crops and Perennials
Planting cover crops and perennials protects soil year-round, preventing erosion, replenishing nutrients, and reducing reliance on fertilizers and herbicides.

Reduced Tillage Methods

Embracing no-till or reduced-till methods minimizes soil disturbance, reducing erosion and preserving soil structure, leading to improved carbon sequestration.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Systematic use of mechanical and biological controls in IPM reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides, promoting a balanced ecosystem while managing pest populations.

Livestock-Crop Integration

Integrating livestock and crops enhances farm efficiency, utilizing manure fertilizers more effectively and reducing the environmental impact of conventional separation in industrial agriculture.
Agroforestry Practices
Incorporating trees or shrubs into farming operations not only provides additional income but also contributes to carbon sequestration, shading, and the protection of water resources.

Whole Systems Management

Sustainable farms consider uncultivated areas integral to the overall system, leveraging natural vegetation to control erosion, reduce nutrient runoff, and support biodiversity, including pollinators.
Focus on Soil Health
Many sustainable practices prioritize soil health, recognizing that healthy, living soil promotes healthy crops, increases water retention, prevents pollution, and contributes to thriving farming communities.

Carbon Sequestration

Through practices like cover cropping, reduced tillage, and agroforestry, sustainable agriculture enhances carbon sequestration, mitigating the impact of carbon emissions and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Current Trends and Future Projections in Sustainable Agriculture
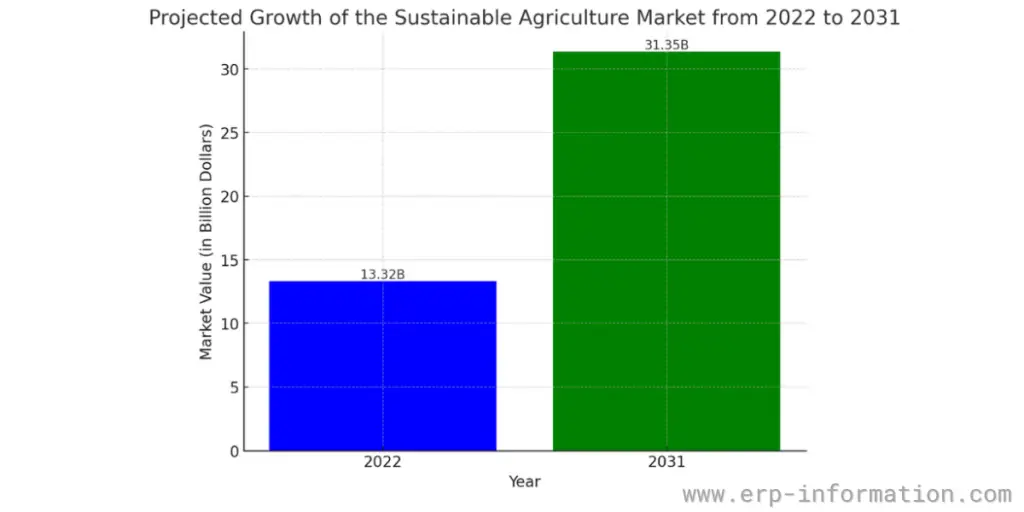
The sustainable agriculture market is experiencing significant growth worldwide. In 2022, the market was valued at $13.32 billion, and it is projected to expand to $31.35 billion by 2031, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.17% from 2023 to 2031.
Market Dynamics
The expansion of the sustainable agriculture sector is fundamentally driven by the need to conserve and optimally utilize natural resources such as soil and water.
The global market trends indicate a shifting preference towards sustainable methods that not only meet the current food demands but also ensure the conservation of environmental resources for future generations.
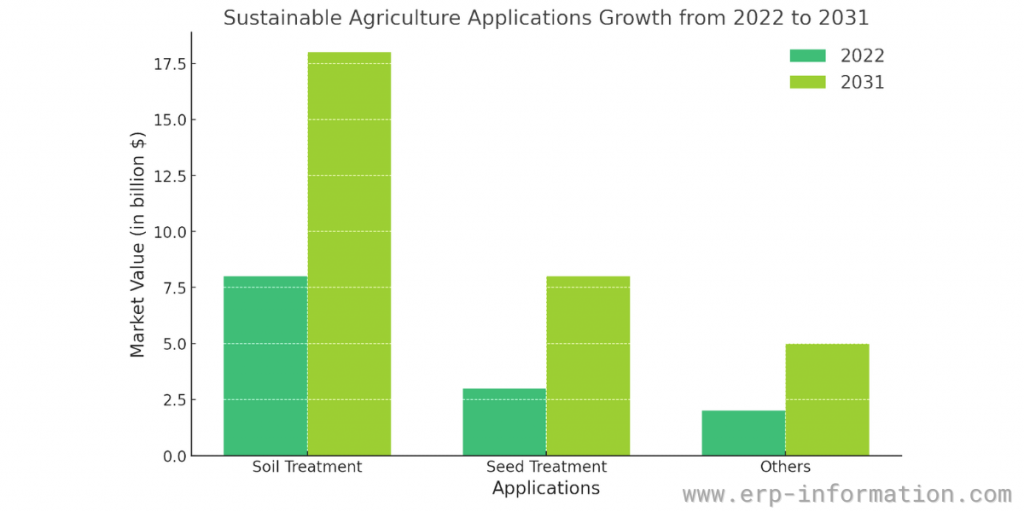
Applications
The application of sustainable products spans soil treatment, seed treatment, and other areas.
Soil treatment constitutes a major application, pointing towards the critical role of soil health in sustainable farming practices.
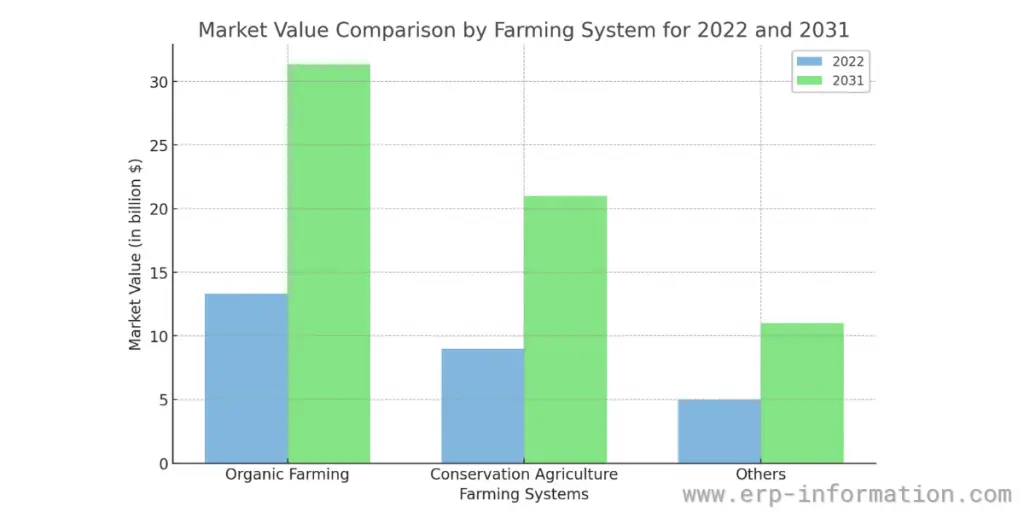
Farming Systems
When analyzed by the farming system, the data shows a substantial portion of the market is invested in organic farming and conservation agriculture.
This reflects a growing acknowledgment of the importance of crop diversity and soil conservation measures in sustainable agriculture.
Regional Insights
North America emerged as the largest region in the sustainable agriculture market, indicating robust adoption of sustainable farming practices in this area.
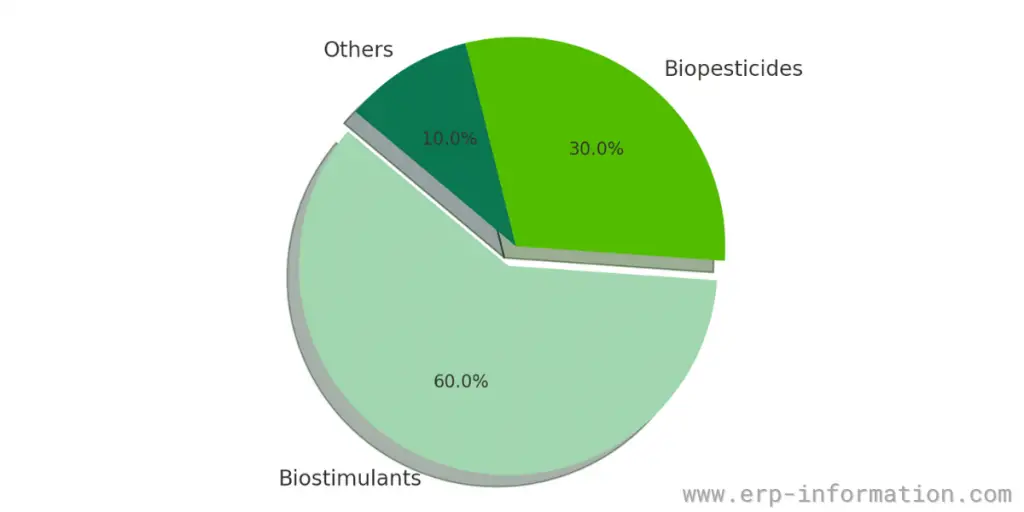
Product Types
The market is segmented into biopesticides and biostimulants, with biostimulants occupying a larger share. This suggests an increasing trend toward organic and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional pesticides.
Electric Vehicles and Sustainable Transport
Electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in sustainable transport, including high-speed rail and alternative fuels, contribute to reducing emissions from the transportation sector.
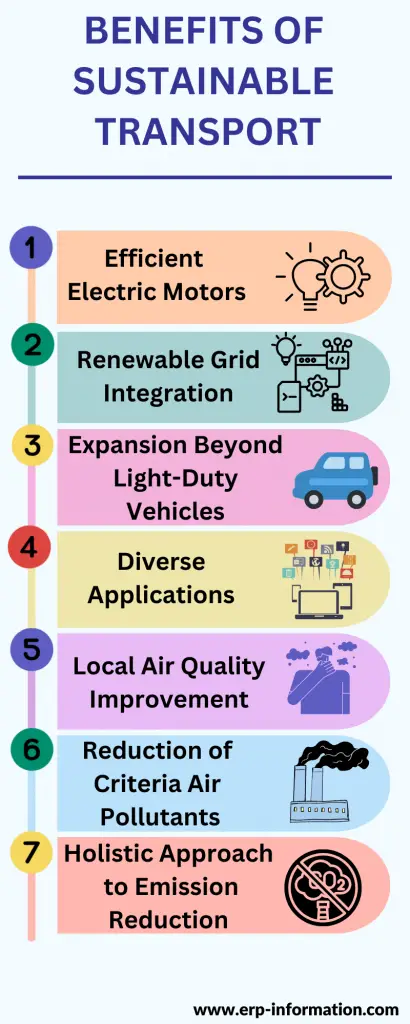
Electric vehicles contribute significantly to carbon emission reduction by leveraging efficient electric motors, integrating with renewable energy grids, and expanding into various transportation sectors, thus offering both global and local environmental benefits.
Efficient Electric Motors
PEVs utilize highly efficient electric motors, minimizing energy waste and reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional internal combustion engines.
Renewable Grid Integration
Plugging into grids with higher renewable energy sources further enhances the environmental benefits of PEVs, as the electricity used for charging comes from cleaner sources.
Expansion Beyond Light-Duty Vehicles
Electrification extends to heavy-duty vehicles, with companies like Cummins and Tesla developing electric drivetrains for tractor trucks and the deployment of thousands of battery electric transit buses globally.
Diverse Applications
Heavy-duty PEVs, ranging from school buses to port and mining equipment, are under testing and development, showcasing the versatility of electrification in various transport sectors.
Local Air Quality Improvement
Electrified transportation contributes to local air quality improvement by reducing tailpipe emissions, benefiting the health of communities near roads, particularly in urban areas where traditional vehicles contribute to air pollution.
Reduction of Criteria Air Pollutants
PEVs play an important role in reducing criteria air pollutants emitted by traditional gasoline and diesel engines, positively impacting heart and lung health, especially for those living in proximity to busy roads.
Holistic Approach to Emission Reduction
Electric vehicles work to reduce carbon emissions not only through direct emission reduction but also by promoting the adoption of cleaner energy sources and fostering a shift towards more sustainable transportation practices.
Union of Concerned Scientists Analysis According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, the average PEV produces emissions equivalent to a gasoline car achieving over 70 miles per gallon, highlighting the superior efficiency of electric vehicles.
Case studies on EV
The varying conclusions drawn from different case studies on electric vehicles (EVs) and their impact on carbon emissions highlight the complexity of this subject.
Here’s a nuanced exploration of how case studies contribute to the broader understanding of carbon emissions in the context of EVs:
| Some EV Studies | Highlights the contrast in findings, with some studies asserting that EVs have emissions up to 43% lower than diesel vehicles. Indicates that discrepancies arise from varying assumptions made by researchers, such as specific vehicle comparisons, electricity grid mix, use of marginal or average electricity emissions, driving patterns, and environmental conditions |
| Media Response | The Wall Street Journal editorial characterizes the situation as “Germany’s dirty green cars,” reflecting a critical perspective on the environmental impact of EVs. Points out that these findings have sparked debates and pushback from electric vehicle advocates and other researchers. |
| Factors Influencing Study Outcomes | Prof Jeremy Michalek underscores that the technology comparison outcome depends on multiple factors, including the specific vehicles studied, the assumed electricity grid mix, the consideration of marginal or average electricity emissions, driving patterns, and even weather conditions. |
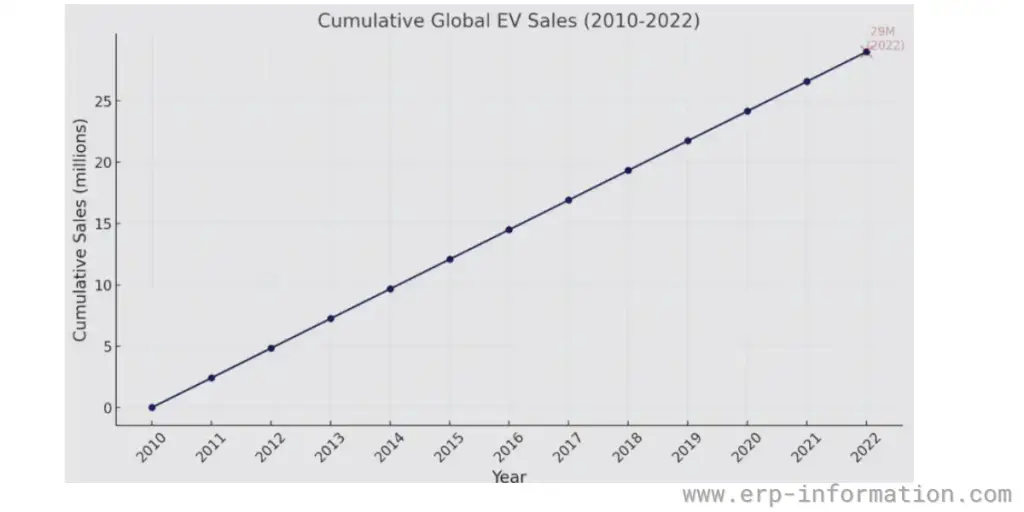
Cumulative EV sales 2010 to 2022
This “milestone” graph depicts the growth in cumulative EV sales from 2010 to 2022, with the significant achievement of 29 million sales by the end of 2022 highlighted.
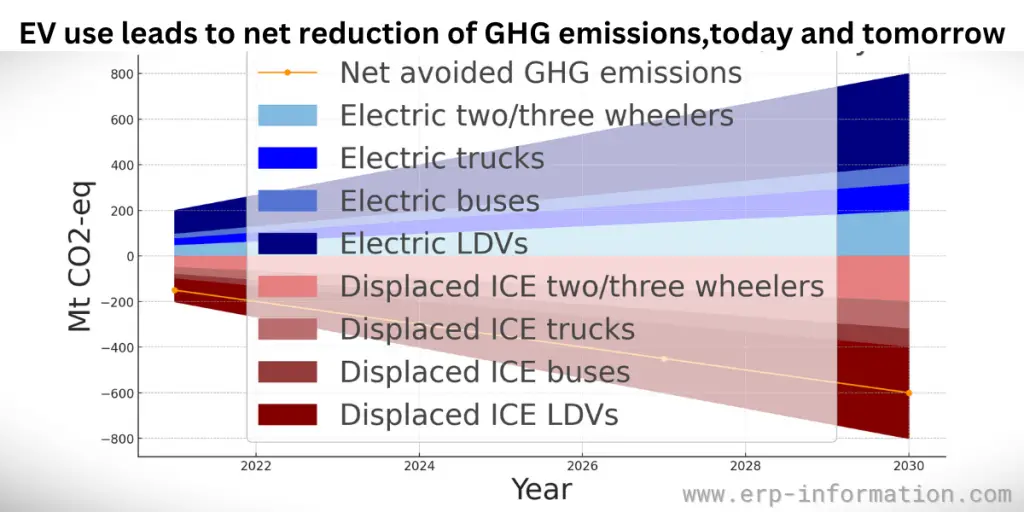
Scenario comparison of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions impacted by the use of electric vehicles (EVs)
The area graph illustrates two scenarios: the Stated Policies Scenario and the Announced Pledges Scenario, showing the expected net reduction in GHG emissions from the global EV fleet between 2021 and 2030
Conclusion
The symbiotic relationship between sustainable agriculture and transportation is crucial for building a resilient and environmentally conscious future.
As we navigate the challenges of a growing global population and the imperative to mitigate climate change, adopting innovative and eco-friendly practices in both agriculture and transportation becomes paramount.