You’ve probably seen those barcodes with all the lines and squares on them, but what are they, and what do they do?
They are Universal Product Codes. They track products through the supply chain. They’re scanned at each point of sale to ensure that the correct product is being sold.
It is a barcode symbology widely used in the United States and other countries. It consists of 12 digits that uniquely identify a product. You can find this code on most products that you buy in stores.
This blog post discusses the definition, symbology, types, advantages, and disadvantages of UPC, and how it is different from SKU. In addition, the post explains the steps to get UPC for your product.
Definition
A Universal Product Code is a unique code consisting of a series of black lines and spaces that encode numerical data. This numerical data is known as the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN).
When scanned at the point of sale, this code allows retail systems to accurately identify products and retrieve their price and other relevant information. This standardized system ensures that products are easily and efficiently tracked and managed in the supply chain, facilitating smooth transactions and inventory control.
A UPC code enables retailers and manufacturers to precisely track products within their inventory, enhancing recall accuracy and overall inventory management.
By incorporating additional details like batch or lot numbers, companies can efficiently identify and recall defective or hazardous items from retailers, distributors, or warehouses before they reach consumers.
This system is crucial for recalling contaminated food, compromised medical devices, unsafe medications, and faulty products that pose a risk of injury.
UPC-E (includes zero) and UPC-A (does not have zero) are the two main types of Universal Product Codes.
UPC Symbology
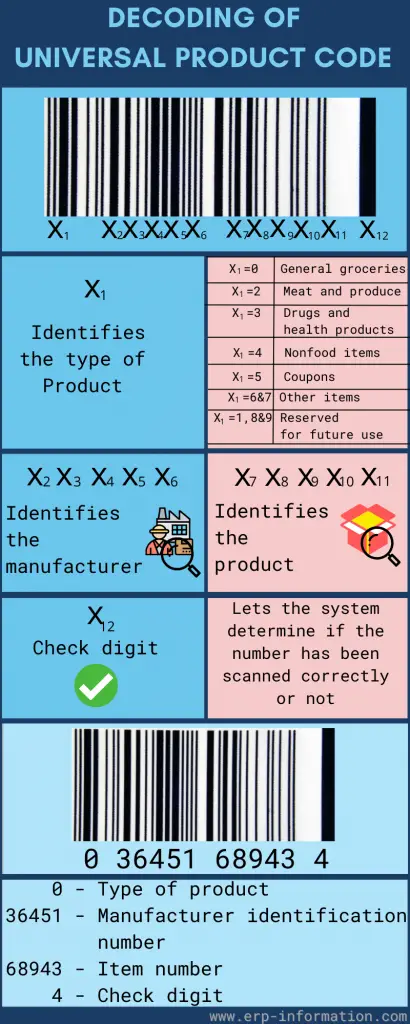
It is made up of four parts:
- The number system identifies the type of product;
- The manufacturer code, which UCC Council assigns to a specific company;
- A unique item identifier or SKU, which is posted by the manufacturer for each product they make; and,
- A check digit is calculated using a special algorithm to ensure a valid code.
The first digit indicates the product type, and the following five digits are a unique code provided to the vendor. Thus, the vendor will have the same code even if the store differs.
The following five digits act as the unique reference specified for the product, and the last digit will be the check digit which is generally used to cross-check if it is correct.
It is scanned against a scanner that reads the bar code and lets the system know if everything is okay or not.
Steps to Get UPC Code for a Product
Application filling
The first step is to get the GS1(Global Standard Organization), also known as the Unifor Code Council company prefix. For that, you have to fill out the online application form and sign up for a prefix capacity plan to get it. It shows the number of universal product codes under your company prefix.
Paying fee
You have to pay the fee for the code. A prefix capacity plan can be expensive. So make sure that the plan you have chosen will accommodate the long-term use of your business.
Once you pay the fee, GS1 allocates a 6-digit number with the manufacturer identification number. This number becomes the first six digits of the universal product code on your company’s products.
Internal product number generation
After getting your company prefix, you can give your product internal product numbers (5 digits). You have the freedom to choose your digits, but each product should have a unique UPC. Ensure that the exact number is not used for more than one product. This 5-digit number represents the product itself.
Check digit generation
After generating your company prefix and internal product code, generate your check digit.
It is generated after several calculations by adding and multiplying digits in the code based on an algorithm monitored by the Global Standard Organization (GS1). Manually also, you can calculate the check digit.
Confirm check digit is correct or not. If the check digit is incorrect, the UPC code will not scan properly.
Registration of final barcode
Once all three sets of digits, company prefix, internal product code, and check code are generated, register this number with GS1 so that you will tie your product information to the number you have created.
The below infographic provides summarized information on UPC barcode generation steps.
UPC Code’s Location
They can be found in most products that you buy in stores. The code is usually located somewhere on the product packaging, and you may also print it on the product. They are also found in product manuals, promotional materials, and shipping boxes.
How to Find a Manufacturer’s UPC?
Suppose you want to find the Universal Product Code for a specific product. There are several ways to do so. You can visit the manufacturer’s website or contact them directly to ask for the code. You can also use a UPC lookup tool to find the code. These tools are widely available online, and they are free to use.
When using a lookup tool, you need the product’s name or SKU number. You can usually find the SKU number on the product packaging or manual. Once you have entered the information into the lookup tool, it will return the Universal Product Code for that product.
UPC Lookup Tools
These tools allow you to search for product codes by keyword or browse by category. They also provide information about the product, such as the manufacturer’s name, address, photos, and descriptions. Some tools even let you add products to your inventory.
One example is the GSOne Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) Database.
Types of UPCs
There are a few different types of Universal Product Codes. The most common type is the 12-digit code used to track store products.
Codes can also be 6 or 9 digits long. The 6-digit code is used to track products sold in vending machines, and the 9-digit code is used to track online products.
Universal Product Code Generator
A Universal Product Code Generator is a tool that allows you to create Universal Product Codes for your products. This tool is helpful if you want to make your barcodes for tracking purposes or if you want to include them on your product packaging.
There are several generators available online. Most of these tools are free to use and easy to use. You need to enter the information about your product, such as the name and SKU number, and the generator will create a valid code for you.
UPC Barcode Specifications
The Barcode Specifications are guidelines that describe how they should be formatted and used. These specifications are maintained by the Uniform Code Council (UCC), a nonprofit organization that oversees the system.
The specifications define the following:
- The structure and format
- The type of information that can be encoded
- How it should be scanned and read
- They use it in retail environments
- They use it in other industries
The UPC barcode specifications are essential for businesses to create or use barcodes. By following the guidelines in these specifications, companies can ensure that their barcodes will be compatible with scanning equipment and that they will be readable in retail stores.
Advantages
- It is easy to use and can be scanned by retail scanners.
- It speeds up the checkout process in stores.
- It helps businesses track their inventory and sales.
- It can be used to create marketing materials such as flyers and product labels.
Disadvantages
- Barcodes can be expensive to create and print.
- They are not always accepted in all countries.
- They can be challenging to create without using a barcode generator tool.
- They may not be suitable for all products or businesses.
- They require special scanning equipment to read them correctly.
SKU vs UPC
| SKU | UPC |
| Stock keeping unit is an internal tracking number used by retailers to manage inventory and sales data. | It is a globally accepted barcode that identifies a product. |
| Specific to a particular retailer or brand, customized for their inventory management. | Standardized and recognized worldwide, used across different retailers and locations. |
| Created and assigned by the retailer, can vary between different stores for the same product. | Assigned by the manufacturer and remains consistent for the product regardless of where it is sold. |
| It can be used by a retailer to track different variations (like color or size) of a product by grouping them under a single product type. For example, a retailer might assign one SKU to a shoe style and use that SKU to manage inventory for all colors and sizes of that shoe. | Each variation of a product (such as different colors or sizes) will have its own unique UPC. For instance, white shoes and black shoes of the same style would have different UPCs to distinguish them individually. |
FAQs
How many types of bar codes are there?
There are three types of bar codes. They are
1. Universal Product Code (UPC)
2. International Article Number (IAN)
3. International Standard Book Number (ISBN).
What is EAN
EAN stands for European Article Number, also known as International Article Number. It is an international standard for identifying products and services within the EU and elsewhere.
In 2009, 13-digits Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) replaced EAN. EAN-13 is the most commonly used 13-digit EAN standard.
What are the differences between UPC and EAN?
The differences are as follows.
EAN is used mainly in Europe, while UPC is primarily used in the United States.
EAN codes have 13 digits, while UPCs have only 12 digits.
Furthermore, EANs are encoded to contain information about the product’s country or region of origin. In contrast, UPCs do not include this information because they are only used in the US and Canada.
What is the difference between GTIN and UPC?
GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) is the numerical identifier encoded in the barcode. It provides a unique identification number for products, ensuring they can be tracked and managed globally.
UPC is the scannable barcode that appears on product packaging. It visually represents the GTIN in a series of black lines and spaces that can be read by scanners at checkout points. GTIN and UPC together make a barcode.
Conclusion
Understanding the Universal Product Code is essential for modern retail and inventory management.
This unique 12-digit code, represented by black lines and spaces, simplifies product identification and ensures smooth operations throughout the supply chain.
By enabling precise tracking, facilitating recalls, and speeding up checkout processes, UPCs are indispensable for businesses worldwide.
In this post, you learned what Universal Product Codes are and how businesses can use them. You also learned about advantages and disadvantages of them. We hope the article provided quality information.