You might be familiar with the importance of having a validation plan prior to launching your product.
This plan outlines the specific steps you’ll follow to assess if your product is feasible. Establishing a validation plan beforehand is vital as it can prevent expensive errors in the process of launching your product. Read on to know more.
This post tells you about the validation master plan in detail and its essential elements, examples, and templates.
What is validation master plan (VMP)?
It is a document that describes the overall strategy for validating a process or system. Organizations use it to ensure that their processes and systems comply with quality, safety, and regulatory standards.
It outlines the validation activities’ objectives, scope, approach, and responsibilities. It also includes details on the validation process, tests and assessments, the validation team, documentation requirements, and the acceptance criteria for each stage of the validation.
Why do we need it?
We need this plan to ensure that all validation activities are controlled and organized and to explain why certain validation activities were carried out.
A VMP is a document that outlines the goals, objectives, processes, and methods for validating a product or system. In addition, it is used to define the timeline for validation activities and their planned and expected outcomes.
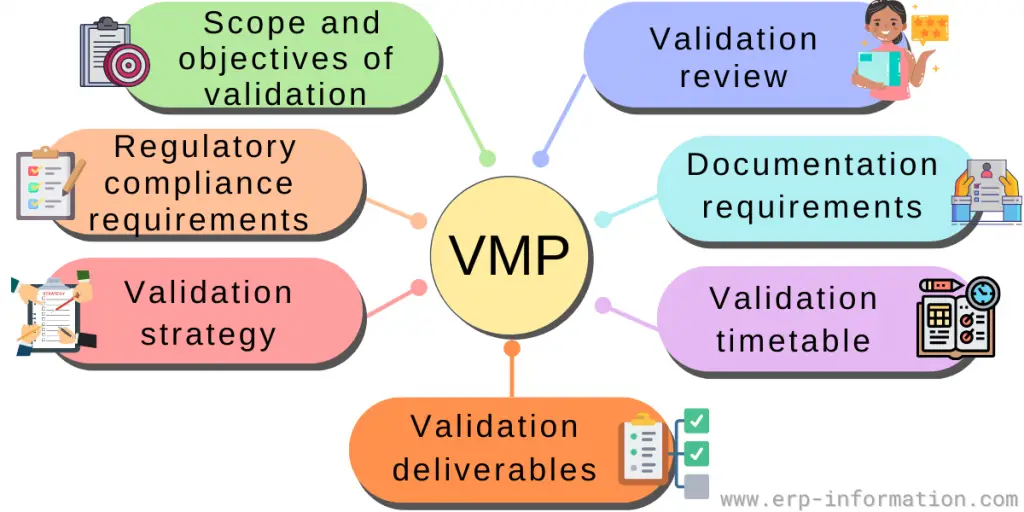
Essential elements of VMP
This document should include the overall process, any necessary risk assessments, management strategies, and details on validation deliverables, timelines, and milestones.
Some essential parts of a VMP include:
Scope and objectives of the validation: This should outline the system or product to be validated, any applicable regulatory requirements, and the desired outcome.
Regulatory compliance requirements: These are the rules and laws that need to be followed locally to make sure everything is done right.
Validation strategy: This outlines the approach that will be taken to validate the system or product, such as whether it will include a software validation or performance qualification. It should also detail any risk management strategies and how they will be implemented.
Validation deliverables: This should detail any documentation required for system or product validation, such as user manuals and training materials.
Validation timetable: This should set out the timeline for each validation activity, such as when protocols must be written, tests conducted, and reports generated.
Documentation requirements: The necessary documents and papers required are covered here. Such as guides and training material, to indicate that the system or product is working well.
Validation review: This should outline the process for verifying and approving validation activities and any other quality assurance checks that need to be performed.
Validation master plan examples
Example 1: Risk-based validation master plan
For a risk-based plan, the primary focus is on identifying and mitigating risks. The validation plan aims to identify potential risk areas and develop strategies to reduce or eliminate them.
A typical approach to risk management is to identify the sources of risk, assess the likelihood and impact of each threat, prioritize the risks based on their potential severity, develop plans for mitigating them, and monitor their effectiveness.
Example 2: Quality-based validation master plan
The primary focus of a quality-based validation plan is on ensuring product quality. In addition, this validation plan aims to ensure that all products meet their required specifications and adhere to regulatory guidelines.
This approach typically includes activities such as developing quality control procedures, identifying potential areas of nonconformity, implementing corrective actions, conducting internal audits, and evaluating the effectiveness of the quality management system.
Example 3: Prototype-based validation master plan
The primary focus of a prototype-based validation plan is on creating and testing prototypes.
This validation plan typically includes developing specification requirements, designing a prototype, creating a test plan, and conducting tests to evaluate performance and reliability. Following this process helps ensure that the final product meets its intended purpose.
Example 4: System-based validation master plan
This validation plan’s primary focus is ensuring that all systems working properly. In addition, this validation plan typically includes verifying system requirements, developing test plans, and conducting tests to evaluate the system’s performance and reliability.
After testing, the results can be used to ensure that all systems are functioning correctly.
No matter what type of validation master plan you use, it is important to have a template outlining the activities and tasks involved. A quality template should cover key areas such as purpose, process flow, roles, required resources, deliverables, timelines, and steps for review and approval.
What is a validation master plan template?
This template is a tool for creating a customized plan for validating a product, system, or process. It can include information such as the scope of work, timeline, resources needed, risk assessment criteria, quality control procedures, and acceptance criteria.
It can also outline the roles and responsibilities of each team member involved in validation activities.
Here we are providing the outline of the template. That includes
1. Purpose
To document the overall validation strategy and to determine the necessary tasks to validate facilities, utilities, equipment, processes, and products.
2. Scope
To define the scope of validation activities, including company, buildings, and products.
3. Responsibility
To define the roles and responsibilities of the validation team members or departments.
4. Standard operating procedures (SOPs)
To guide and support validation activities. The list of SOPs are
- Validation SOPs
- Metrology, facilities, and engineering SOPs
- Quality control SOPs
- Quality assurance SOPs
5. Validation overview
To provide overall product quality assurance. The validation process defines how the entire manufacturing system is consistent and reliable.
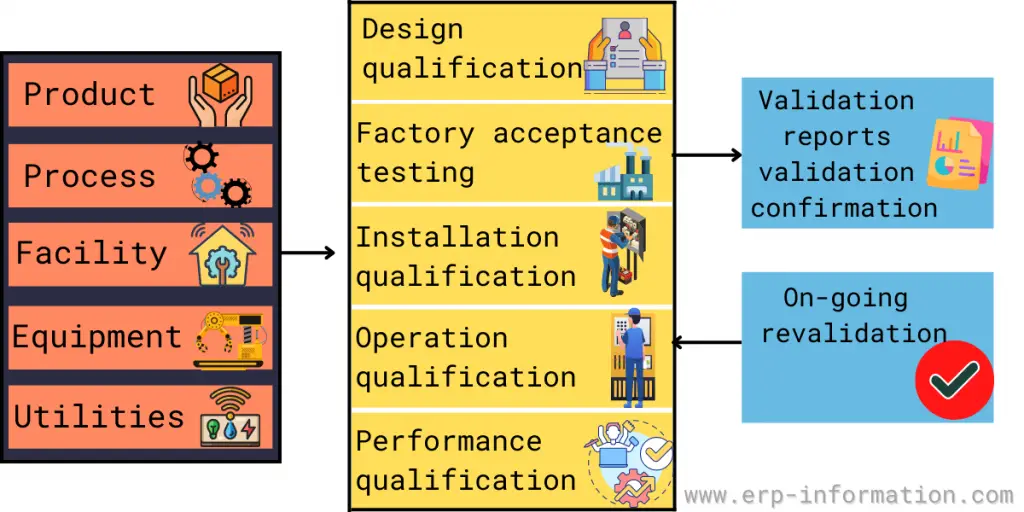
The types of validation to reach the manufacturing process validated state are Equipment, Utilities, Facilities, Computer systems, Cleaning, Sterilization, Methods, and Process.
- 5.1 Installation qualification
- 5.2 Operation qualification
- 5.3 Computerized system validation
- 5.4 Performance qualification
- 5.5 Method validation
6. Product validation
To define the validation activities for each product. After the facility, utility, and equipment validation, the manufacturing process should be validated to check whether the products meet the final product specification.
All the parameters like manufacturing time, room temperature, product temperature, and equipment settings will be mentioned.
7. Process description
Please outline your process in this section. Document sampling tests for both in-process and final products. Validate the initial process by conducting three studies for each product formulation and filling/packaging configuration.
This approach ensures adherence to predetermined specifications for both in-process and final products, offering a reliable measure of variability across consecutive runs.
All documents related to manufacturing products are readied for assessment and used as part of the decision-making process for releasing products.
8. Validation scheduling and control
It refers to the completion of scheduled validation of equipment, services, and systems. After equipment installation and system construction, appropriate documentation and change control systems are established.
Documentation of standard operating procedures, calibration, qualification/validation protocols, batch records, training, and preventive maintenance help the validation process.
9. Facility validation
It consists of warehousing, facility cleaning validation, microbial contamination prevention and control, and environmental monitoring.
10. Utility validation
This includes a Heating Ventilation and air Conditioning System, WFI Generation and Distribution System, Clean Steam Generation and Distribution System, Nitrogen Gas System, Clean Compressed Air (CCA), Plant Steam, Chilled Water System (CHW), Heating Hot Water System (HHW)
11. Equipment validation
Constitutes Tanks, Vessels, and Skids, Temperature Controlled Chambers and Rooms (CTUs and CTRs), and Equipment Cleaning and Sterilization Validation
12. Additional things
Constitutes training, calibration, change control, maintenance of spare parts, logbooks, and checklists
When creating a VMP, it is important to consider the product design, intended use, user profiles, and regulatory requirements. The template should be altered to meet the specific needs of the project at hand and may require modifications over time as processes evolve or new regulations are introduced.
A well-crafted VMP template can be a valuable asset in ensuring compliance with applicable standards while saving time and helping to ensure the success of validation activities.
An easy-to-follow template can also streamline communication between team members, making it easier to track progress and identify potential issues before they become major obstacles.
VMP checklist
We are providing checkpoints for VMP. These checkpoints are designed to guide the evaluation of a Validation Master Plan, ensuring it is thorough, educational, and effective in outlining the validation process.
They serve as critical elements in achieving successful validation activities and maintaining the highest standards in product quality.
1. Resource Needs and Timelines
- Check Point: Does your Validation Master Plan comprehensively identify the potential resource requirements for specific validation activities? Is there a well-defined plan for establishing project timelines to ensure timely completion?
- Importance: This ensures that all necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials, are identified in advance. Clear project timelines contribute to efficient planning and execution of validation activities.
2. Leadership Understanding
- Check Point: Is your VMP designed to effectively educate the leadership team on the necessity and value of validation activities concerning product quality?
- Importance: A well-informed leadership team is crucial for obtaining necessary support and resources. This checkpoint ensures that the VMP serves as a tool for communicating the importance of validation in maintaining and enhancing product quality.
3. Prospective Schedules and Timelines
- Check Point: Does your VMP consist of prospective schedules and timelines for validation projects, providing a roadmap for when each validation activity is planned to occur?
- Importance: Prospective schedules and timelines enhance planning and coordination, helping teams and stakeholders understand the sequence and duration of validation activities. This contributes to efficient project management.
4. Comprehensive Validation Coverage
- Check Point: Does your VMP provide detailed coverage of all activities related to process validation, as well as qualifications for manufacturing equipment and utilities?
- Importance: A comprehensive VMP ensures that all critical aspects of validation are addressed, including the validation of processes, equipment, and utilities. This helps in maintaining compliance and product quality.
Benefits
Having a validation master plan in place is essential for successfully producing quality products that meet regulatory standards. In addition, it helps to ensure that all validation activities are conducted efficiently and timely and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
Risk management
It provides a systematic approach to assess and manage validation risks associated with the manufacturing process. It identifies potential risk areas and helps identify solutions to mitigate them.
Quality assurance
A VMP provides details on ensuring quality throughout the entire production process, from raw materials through finished products, by establishing standards that each stage of production must meet.
Compliance
The plan helps to ensure that the facility complies with federal, state, and local regulations. It identifies areas where there may be potential non-compliance and guides how to manage them.
Streamlined processes
It helps streamline processes, as all validation activities are documented in one centralized document. That allows for easier and more efficient tracking of validation efforts.
Cost savings
By documenting the steps and processes associated with validating a product or process, it is possible to identify areas where efficiencies can be made and costs reduced. Having a well-defined validation master plan reduces the amount of time spent on validating a product or process.
FAQs
What is a master validation strategy?
A Master Validation Strategy or Master Validation Plan is like a guiding document for businesses, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and manufacturing. It helps ensure that they make products of high quality and safety.
This plan lays out what needs to be checked, how to check it, who’s responsible, and what documents to create. Think of it as a roadmap that ensures everything is done correctly to meet quality standards and follow the rules. It’s essential for businesses that need to meet strict regulations to guarantee their products are safe and effective.
Who is primarily responsible for developing a Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
The development of a Validation Master Plan (VMP) is primarily handled by the quality assurance or validation teams within an organization. These professionals leverage their expertise in regulatory requirements and quality standards to create a thorough and compliant VMP.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Validation Master Plan guarantees precise and efficient execution of all validation activities.
Implementing a VMP template streamlines and standardizes organizational validation processes, minimizing errors and ensuring alignment with regulatory standards.
Moreover, a meticulously designed template provides assurance that validation activities are executed correctly, enabling prompt identification and resolution of any potential issues or concerns. Hope this post helped you understand the concept better.
Reference