Zero inventory (or “zero stock”) is a production and purchasing model in which a company produces or buys only what it needs and when it needs.
This differs from traditional inventory systems, in which a company stocks up on products in anticipation of future sales.
In this post, we’ll take a closer look at Zero Inventory systems, including how they work and their pros and cons. We’ll also offer some tips for businesses considering switching to Zero Inventory.
Definition
Zero inventory is a process set up in a business where the firm maintains a meager amount of inventory or no inventory to reduce the possession and storage costs.
That also facilitates the business to enjoy more liquidity which will help expand.
Zero Inventory Advantages
Reduced Costs
Traditional inventory management necessitates substantial storage space, security, and insurance costs, along with the risk of product obsolescence. By eliminating these overheads, businesses can reduce their costs significantly and allocate resources more efficiently.
Improved Cash Flow
With reduced capital tied up in inventory, companies have more liquidity at their disposal. This increased cash flow can be redirected into strategic investments, such as product development or expansion, fostering business growth.
Increased Efficiency
Having products delivered just in time reduces wasted time and energy.
Reduced Wastes
The waste reduction potential of zero inventory systems is remarkable. Excess inventory can lead to product spoilage or obsolescence, which results in financial losses and environmental impact. With a zero inventory approach, companies can reduce waste and their carbon footprint.
Improved Customer Service
It allows you to provide a faster and more efficient customer service experience.
More Time for Growth
It gives you more time to focus on growing your business.
Greater Flexibility
With it, you have the flexibility to change your product lines quickly and easily.
Disadvantages
Zero inventory has its own set of potential risks. For example, in an unexpected production plan, the firm might not get immediate stock which upsets the whole supply chain management.
The prices quoted by the suppliers in the short term are generally high, which might add extra costs to the company.
If there are long-term orders, the smooth process of the supply chain ensures that the overall cost of production is borne by the customer, which might not be the case in this scenario.
This system also benefits huge companies with a standard set of vendors they deal with. Still, small businesses might not profit from this as their vendors might change, and their production plan is not interpreted and is entirely unexpected.
How to Achieve Zero Inventory?
A proper supply chain management system is necessary to achieve zero inventory. The company should have an appropriate track of raw materials, stocks, and product demand.
Tips for implementing Zero Inventory in your business
Consider your needs
It is not suitable for every business. You need to consider your needs and what type of business you are in before deciding if Zero Inventory is the right choice.
Start small
Implementing it can be a significant change, so start small and see how it works for your business before making a complete switch.
Work with an expert
It can be complex, so it’s essential to work with an expert who can help you understand the pros and cons and decide if it’s right for your business.
Be prepared for changes
It will require changes in how you do business, so you must be prepared for those changes.
Train your staff
Make sure your staff is trained on how to use it so they can take advantage of all the benefits it has to offer.
Use technology
Technology can play a significant role in a Zero Inventory system, so make sure you use the latest and most excellent tools available.
Implementing a zero inventory production system
- Analyze the business process to identify and eliminate waste.
- Streamline the production process to ensure a smooth flow of materials and products.
- Implement a just-in-time (JIT) model to improve production efficiency.
- Create a detailed plan for material procurement and stock management.
- Train employees in Zero Inventory principles and practices.
- Monitor performance and adjust as necessary to ensure success.
Steps to implement zero stock purchasing
Zero stock means having no inventory on hand. Implementing zero-stock purchasing means taking steps to ensure that you never have to stock any inventory. Here are five steps to getting started with zero stock purchasing,
1. Determine what you need
The first step is to inventory everything you currently have in stock. Once you know what you have, you can determine what you need to keep on hand to meet customer demand.
2. Find a supplier who can provide what you need
Once you know what you need, it’s time to find a supplier who can provide those items. Again, finding a supplier who can meet your needs on short notice is crucial so you’re not left waiting for stock to arrive.
3. Create a purchasing plan
It would be best to create a purchasing plan that tells when and how much stock you will order from the supplier. This plan should ensure you always have the proper inventory without demanding too much or too little.
4. Place your orders
Once you have your purchasing plan in place, it’s time to start placing orders with your supplier. Again, communicate your needs clearly so that the supplier can provide the right products on time.
5. Monitor your inventory levels
The final step is to monitor your inventory levels and adjust your ordering as needed. This will help you avoid having too much or too little stock on hand and ensure that you always have the products your customers need.
Zero-stock purchasing can be a bit of a challenge, but with these five steps, you’ll be on your way to never having to stock inventory again.
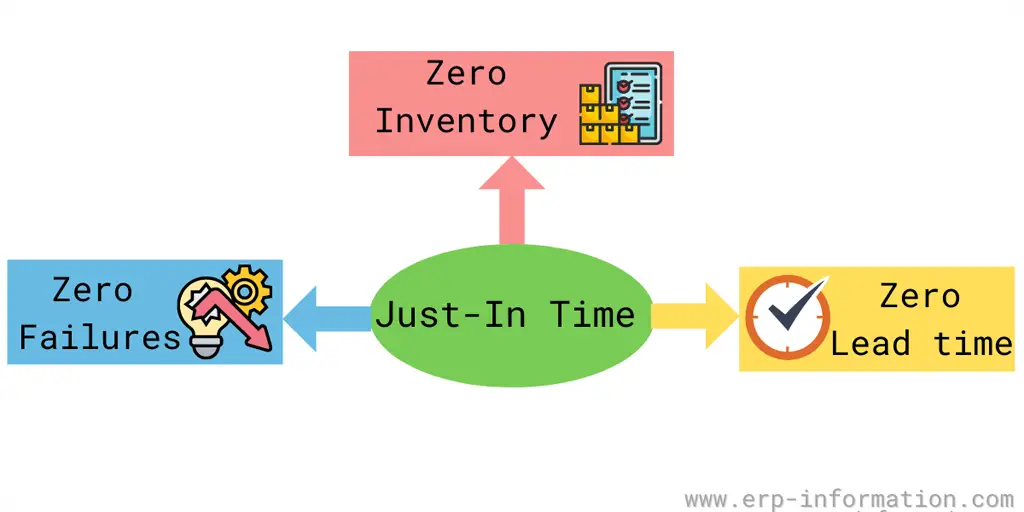
Just-In-Time(JIT) Inventory
Just-in-time inventory is a management strategy companies adopt to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Toyota is the first company who adopt this system. Hence it is also called as Toyota Production System(TPS).
In this system, a company purchases raw materials only when needed for production.
To achieve just-in-time inventory, the company needs to have constant production, sound quality machinery, well-experienced employees, and a genuine supplier.
The below image shows the just-in-time inventory process.
Just-In-Time Inventory Advantages
- Production runs are short. Hence it is easy to stop the production of one product and switch over to the production of another product to meet the customer’s need.
- It helps the company reduce the cost of raw materials because it orders the goods enough to produce the ordered product.
- It helps the company reduce inventory holding costs by avoiding over-ordering.
- It enables the company to avoid overproduction.
- It streamlines the production system and hence saves resources.
- It reduces product defects and increases productivity.
Disadvantages
- This system fails when the supplier cannot supply the raw materials in time. This leads to the late delivery of the product to the client.
Zero Inventory Example
Amazon, Walmart, and Alibaba are the best examples of practicing zero inventory. They are web-based business companies.
They take up orders from the customer through their website, link that order to the original manufacturer through the online inventory management system, and ship the product to the customer.
In this way, they avoid physical warehouses and reduce their warehouse cost.
Is the Zero Inventory Model Successful?
Yes, It is a very successful model. It is more inexpensive, constructive, and flexible than holding on-hand inventory. Today most business companies and enterprises use technologies to market their product or services.
So these companies operate using a zero inventory model. Generally, zero inventory suits industries like fashion, industries that produce more products.
FAQs
What is Zero Inventory?
While the goal is to minimize costs while maximizing profits, carrying inventory can quickly add up, especially for companies that sell physical goods.
Maintaining a warehouse full of products incurs high overhead costs, including rent, utilities, and insurance. In addition, holding the inventory can become outdated or damaged.
For these reasons, many businesses are turning to a zero-inventory model. Under this model, enterprises eliminate carrying any inventory, instead relying on just-in-time production and delivery, consignment selling, or drop shipping.
This allows businesses to save on costs and free up capital that can be invested elsewhere. As a result, the zero inventory model is becoming increasingly popular in today’s business world.
What are the four types of inventory?
The four types of inventory are
1. Raw materials
2. Work-in-process (WIP)
3. Finished items
4. Overhaul (MRO – maintenance, repair, operating supplies)
What is the concept of zero inventory management?
Zero inventory management refers to a supply chain strategy where companies aim to minimize or eliminate physical inventory. Instead, products are produced or acquired based on customer demand, reducing storage costs and the risk of overstocking or understocking.
What advantages do businesses gain from zero inventory management?
Zero inventory management offers benefits such as reduced carrying costs, minimized waste, and improved cash flow. It enables businesses to respond efficiently to changes in demand and market conditions. Additionally, it supports sustainability efforts by reducing excessive production and waste.
Which technologies are employed in zero inventory management?
Zero inventory management relies on advanced technologies like real-time data analytics, demand forecasting, and just-in-time production systems. Furthermore, it may involve the utilization of RFID, IoT sensors, and AI to monitor inventory levels and demand patterns.
What challenges are associated with implementing zero inventory management?
Implementing zero inventory management can present challenges such as accurate demand forecasting, logistics optimization, and potential disruptions in the supply chain. Businesses must also establish robust communication and data-sharing systems with suppliers and partners.
Is zero inventory management suitable for all industries?
Zero inventory management is most effective in industries characterized by rapidly changing demand and short product lifecycles, such as fashion, electronics, and certain aspects of food production. However, it may not be suitable for industries that have long lead times or highly customized products.
What are the examples of companies successfully utilizing zero inventory management?
Companies like Zara in the fashion industry and Toyota in the automotive sector have successfully implemented zero inventory or just-in-time inventory management strategies. They are recognized for their agility and efficiency in meeting customer demand.
Are there any risks associated with zero inventory management?
One of the main risks is supply chain disruptions, such as delays from suppliers or unforeseen changes in demand. It’s crucial to have contingency plans in place and maintain strong relationships with suppliers.
What should one keep in mind when practicing zero inventory management?
The main things to consider are, how fast you sell your stock, how quickly orders are fulfilled, whether deliveries are on time, and how well you predict customer demand. These measurements help companies judge how well their zero inventory plan is working.
How can advanced technologies like blockchain improve the effectiveness of zero inventory management?
Blockchain can make zero inventory management better by making supply chains more open and secure. It lessens the chance of cheating or mistakes. It also boosts trust between companies in the supply chain and makes the data used in zero inventory strategies more accurate.
Conclusion
Zero inventory is a business model with many benefits, but it’s not right for every business.
Consider your needs and speak with an expert before deciding if Zero Inventory is the right choice for you.
Hope this post was helpful! ?